Effortless Searching: How to Find Metronidazole on Synapse
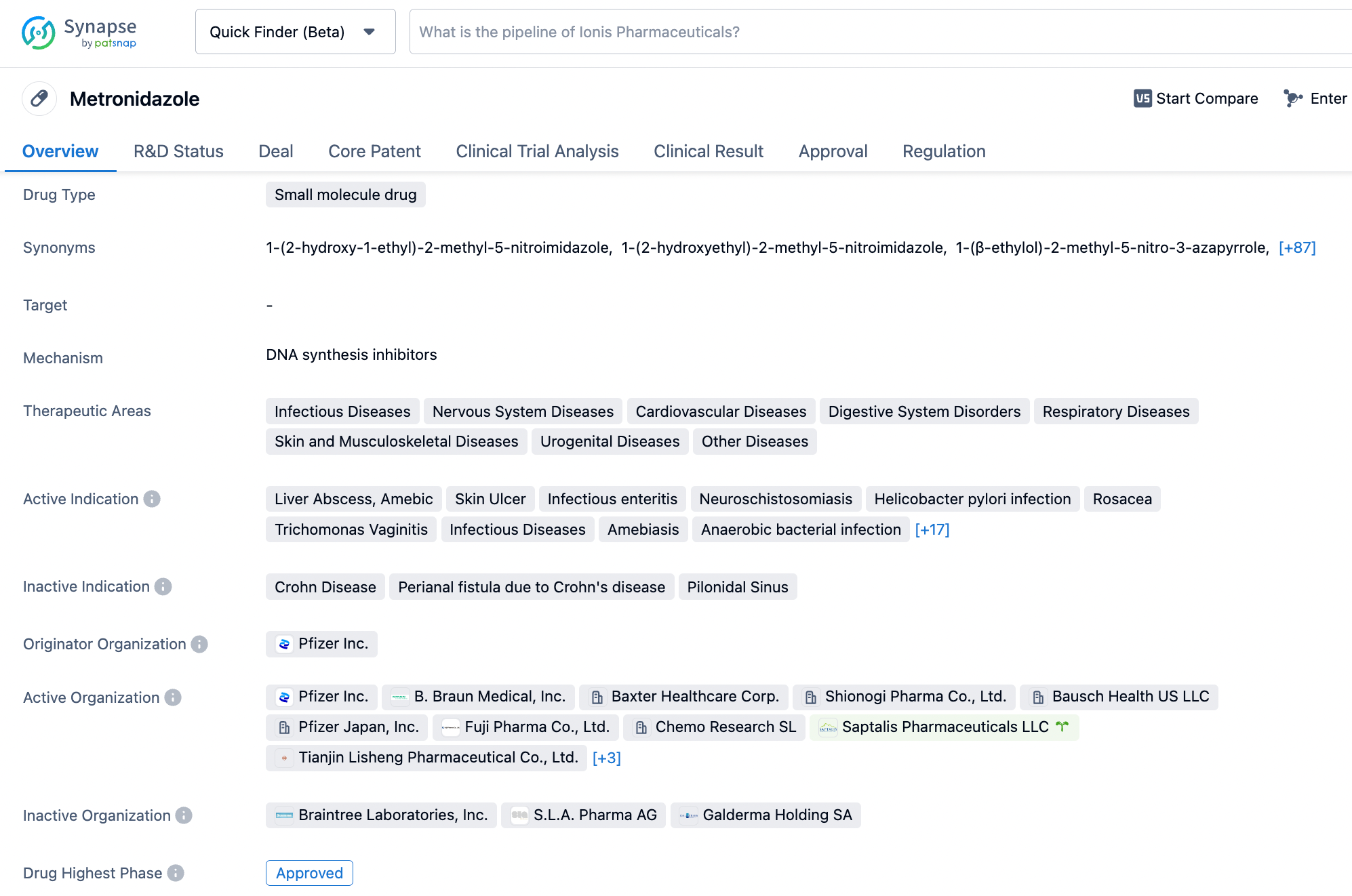
Metronidazole, a small molecule drug approved in 1960 by Pfizer Inc., inhibits DNA synthesis and is highly effective against anaerobic bacteria and protozoa. Its versatility is demonstrated by its indication for a wide range of conditions, including skin ulcers, enteritis, Helicobacter pylori infection, rosacea, trichomonas vaginitis, and amebiasis. By disrupting DNA synthesis, metronidazole inhibits growth and multiplication of these microorganisms. It also shows potential as a substitute therapy for some antibiotic-resistant bacterial infections. However, like all drugs, metronidazole has potential adverse effects such as nausea, regurgitation, and metallic taste in the mouth. Patients should carefully follow prescribed dosages and treatment durations to avoid antibiotic resistance and the risk of side effects. Click on the image below to begin the exploration journey of Metronidazole through the Synapse database!
You can search for the latest pharmaceutical information such as drugs, targets, patents, transactions, clinical results, etc. through the Synapse database. Come and experience it!