EU Approves Dupixent as Exclusive Treatment for Young Children with Eosinophilic Esophagitis
The European Medicines Agency has granted approval for Dupixent (dupilumab) to be used in treating eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) in pediatric patients starting from the age of one. This approval specifically targets children from one to 11 years old, provided they weigh a minimum of 15 kg, and who have not achieved adequate control with standard treatments, cannot tolerate them, or are unsuitable for traditional medicinal therapies. This marks an extension of the initial authorization within the European Union (EU) for treating adult and adolescent patients with EoE, establishing Dupixent as the sole medication approved for this younger demographic. Additionally, Dupixent holds similar authorizations for this age group in both the US and Canada.
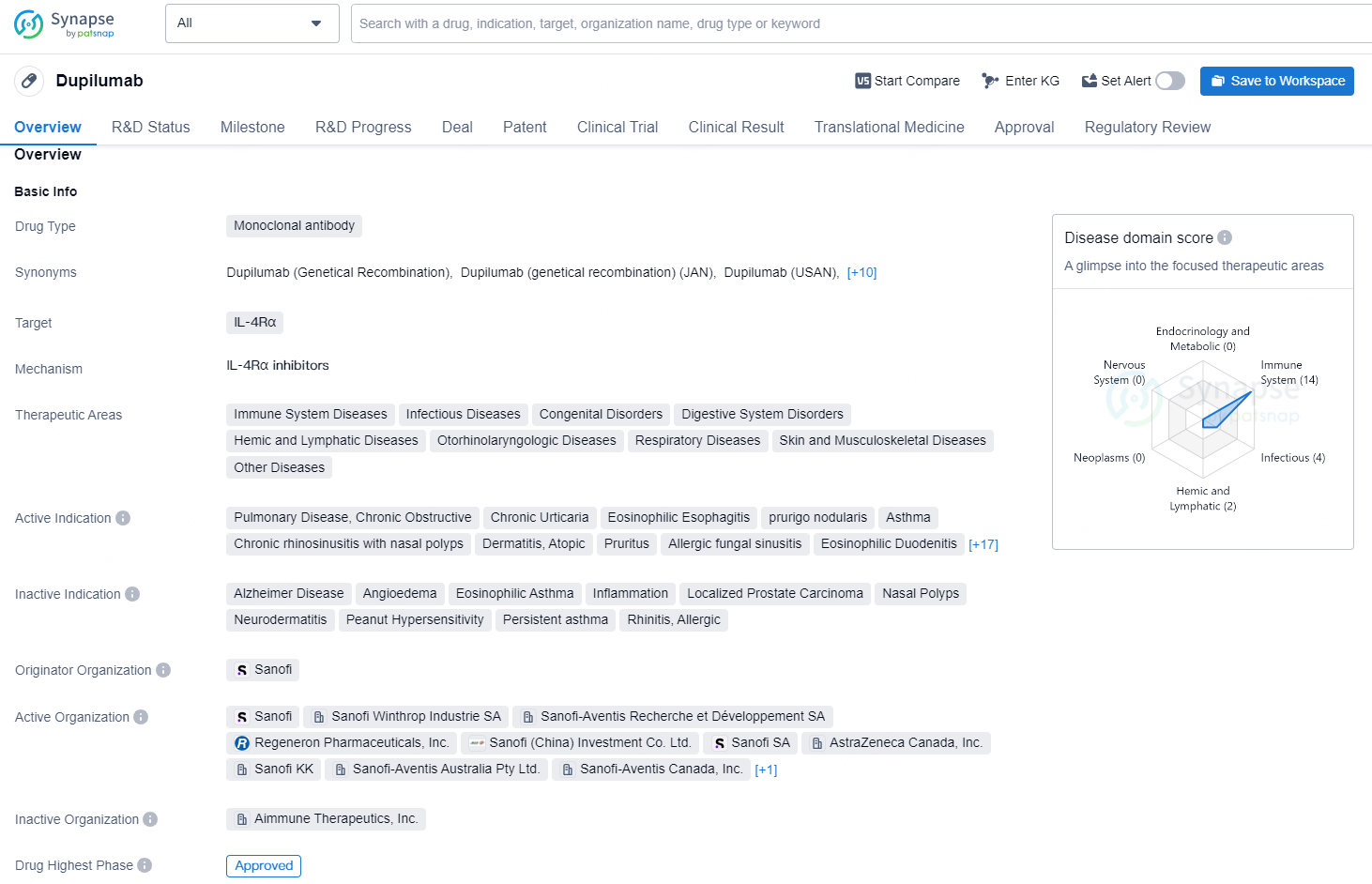
👇Discover comprehensive information about this drug, from its R&D status, core patents, clinical trials to approval status in global countries, by simply clicking on the image below. Dive deep into our drug database now.
Houman Ashrafian, MD, PhD
Executive Vice President, Head of Research and Development, Sanofi
"Approximately 50% of children in the European Union diagnosed with eosinophilic esophagitis do not achieve adequate control even with current standard treatments. Consequently, many of these pediatric patients face significant weight management challenges due to symptoms like swallowing difficulties and vomiting. This landmark approval offers a vital new therapy for young patients with no previously sanctioned treatment for their condition. By targeting a core aspect of eosinophilic esophagitis, Dupixent has the potential to enhance the quality of life for these children."
The authorization is grounded in the two-part EoE KIDS phase 3 trial involving children aged one to 11 years, which demonstrated that the response to Dupixent in young patients with EoE mirrors that observed in approved treatments for adults and adolescents. In Part A, children receiving a higher dosing of Dupixent (n=37), determined through a weight-adjusted regimen, showcased the following results after 16 weeks, compared to those on placebo (n=34):
- 68% achieved histological remission (≤6 eosinophils per high-power field) against a mere 3% in the control group, which was the primary endpoint. These findings were maintained for up to one year in Part B of the trial.
- A notable 86% drop in the peak eosinophil count within the esophageal epithelium from baseline, contrasted with a 21% rise in the placebo group.
- Decreased abnormal findings during endoscopic examinations and a reduction in the severity and extent of the disease, evaluated microscopically.
- A statistically meaningful improvement in the frequency and severity of EoE symptoms, alongside a numerical decrease in days presenting at least one sign of EoE, based on caregiver assessments.
Safety outcomes in the EoE KIDS study were largely in line with the established safety profile of Dupixent for adolescents and adults dealing with EoE. The most frequently reported adverse effects associated with Dupixent included injection site reactions, conjunctivitis, allergic conjunctivitis, joint pain, oral herpes, and elevated eosinophil levels. Additionally, injection site bruising was noted specifically in the EoE cohort. For the one to 11-year-old group, adverse events reported more frequently with Dupixent (≥10%) during Part A, compared to placebo, included COVID-19, nausea, pain at the injection site, and headaches. The long-term safety considerations observed in Part B were consistent with those in Part A.
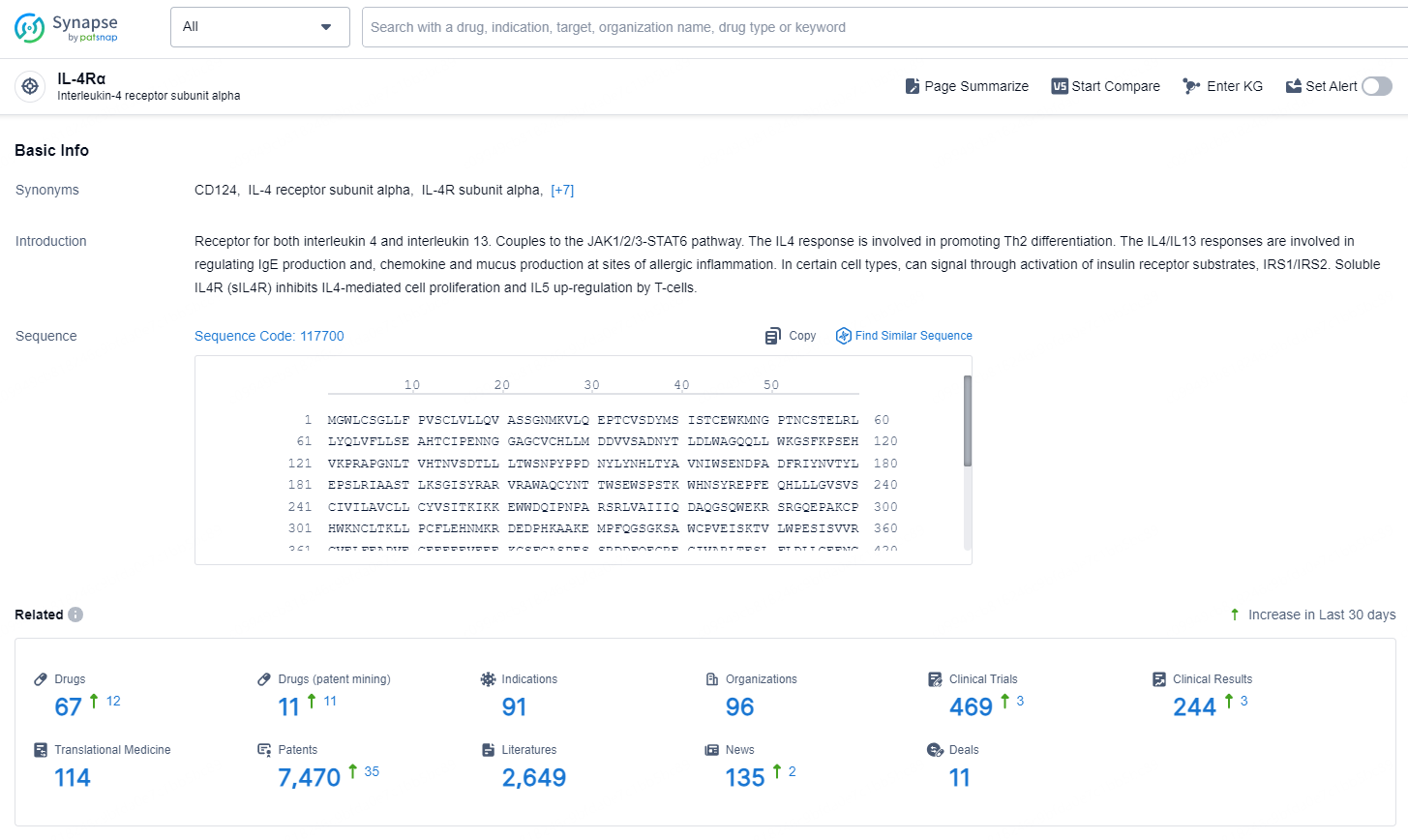
👇Explore the latest research progress on drug-related developments, indications, therapeutic organizations, clinical trials, results, and patents by clicking on the targeted picture link below. Unfold a world of comprehensive information on this target in just a click!
According to the data provided by the Synapse Database, As of November 7, 2024, there are 67 investigational drugs for the IL-4Rα target, including 91 indications, 96 R&D institutions involved, with related clinical trial reaching 469, and as many as 7470 patents.
Dupilumab is a monoclonal antibody drug that targets IL-4Rα and has been approved in various therapeutic areas such as immune system diseases, infectious diseases, congenital disorders, digestive system disorders, hemic and lymphatic diseases, otorhinolaryngologic diseases, respiratory diseases, skin and musculoskeletal diseases, and other diseases.