Exploring alefacept's Revolutionary R&D Successes and its Mechanism of Action on Drug Target
Alefacept's R&D Progress
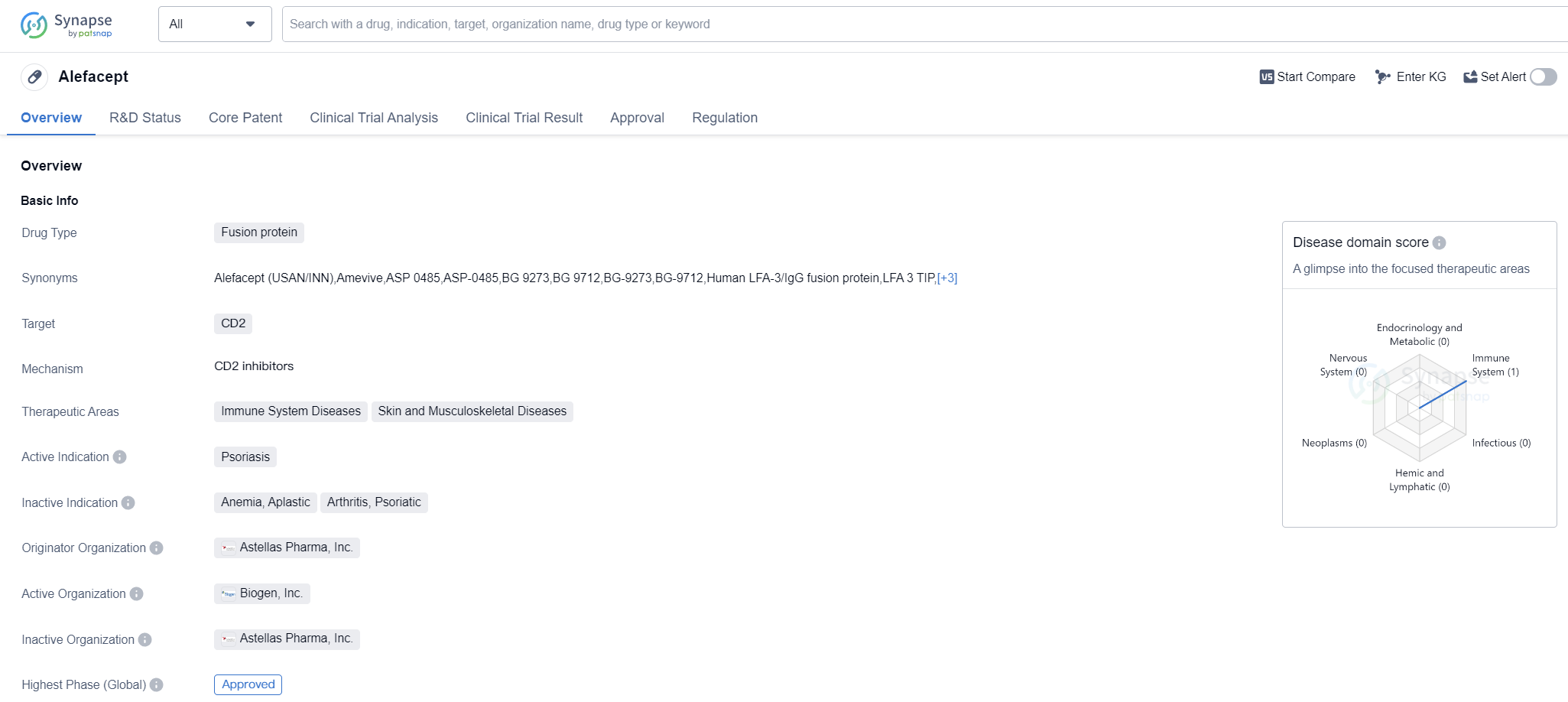
Alefacept is a fusion protein drug that targets CD2 and is primarily used for the treatment of psoriasisj. It falls under the therapeutic areas of immune system diseases and skin and musculoskeletal diseases. The drug was first approved in the United States in January 2003 and is regulated as an orphan drug.
Alefacept is developed by Astellas Pharma, Inc., a pharmaceutical organization that specializes in the research and development of innovative drugs. As a fusion protein, Alefacept is designed to target CD2, a protein found on the surface of certain immune cells. By binding to CD2, Alefacept modulates the immune response, specifically targeting the immune cells involved in the development of psoriasis.
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune disease characterized by the rapid buildup of skin cells, resulting in red, scaly patches on the skin. Alefacept works by inhibiting the activation and proliferation of T cells, a type of immune cell that plays a key role in the development of psoriasis. By reducing the number of activated T cells, Alefacept helps to alleviate the symptoms of psoriasis and improve the overall condition of the skin.
The approval of Alefacept as an orphan drug signifies its potential to address an unmet medical need for patients with psoriasis. Orphan drugs are typically developed for the treatment of rare diseases or conditions that affect a small number of individuals. The regulatory designation provides certain incentives and exclusivity rights to the manufacturer, encouraging the development of drugs for rare diseases.
Since its approval in 2003, Alefacept has been used in the United States and potentially other countries for the treatment of psoriasis. As the highest phase of development, Alefacept has successfully completed clinical trials and demonstrated its safety and efficacy in treating psoriasis. The drug's mechanism of action, targeting CD2, offers a unique approach to managing the immune system dysregulation associated with psoriasis.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for alefacept: CD2 inhibitors
CD2 inhibitors are a type of drug that target and inhibit the CD2 protein. CD2 is a cell surface glycoprotein found on T cells, a type of white blood cell involved in immune responses. CD2 plays a crucial role in T cell activation and signaling.
From a biomedical perspective, CD2 inhibitors are designed to block the interaction between CD2 and its ligands, which are molecules that bind to CD2 and activate T cells. By inhibiting this interaction, CD2 inhibitors can modulate immune responses and potentially treat certain autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis and multiple sclerosis.
CD2 inhibitors can be developed as small molecules or as biologic drugs, such as monoclonal antibodies. They can be administered orally, intravenously, or subcutaneously, depending on the specific drug formulation. The mechanism of action of CD2 inhibitors involves interfering with the CD2-mediated signaling pathways, leading to a dampened immune response.
Drug Target R&D Trends for alefacept
CD2, also known as Cluster of Differentiation 2, is a glycoprotein found on the surface of T cells, a type of white blood cell involved in the immune response. CD2 plays a crucial role in T cell activation and adhesion to other cells. It acts as a co-stimulatory molecule, enhancing the interaction between T cells and antigen-presenting cells, leading to a more robust immune response. CD2 also facilitates the formation of immunological synapses, allowing T cells to communicate and coordinate their activities with other immune cells. Overall, CD2 is essential for the proper functioning of the immune system and plays a vital role in immune surveillance and defense against pathogens.
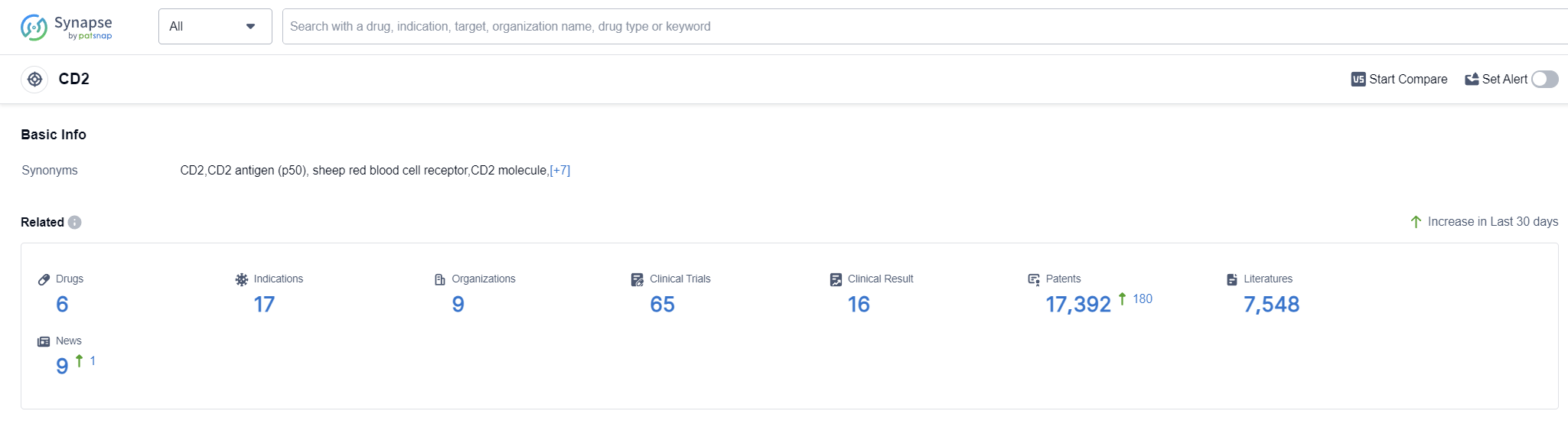
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 12 Sep 2023, there are a total of 6 CD2 drugs worldwide, from 9 organizations, covering 17 indications, and conducting 65 clinical trials.
The analysis of target CD2 reveals a dynamic competitive landscape and promising future development. Biogen, Inc., Itbmed AB, and Novartis AG are among the companies growing fastest in this field. The approved drugs under target CD2 indicate successful R&D efforts and potential therapeutic applications in indications such as Psoriasis, B-Cell Lymphoma, and Diabetes Mellitus Type 1. Fusion protein, Monoclonal antibody, Trispecific antibody, and CAR-T are the drug types progressing most rapidly, with Monoclonal antibodies indicating intense competition. Several countries and locations are actively developing under target CD2. These include Canada, Israel, Kuwait, Australia, Argentina, Switzerland, the European Union, Sweden, the United States, Japan, and the Netherlands. This global interest shows potential for collaboration and advancements in CD2 targeting. However, further research and analysis are necessary to gain a comprehensive understanding of the competitive landscape and future development of target CD2.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
In summary, Alefacept is a fusion protein drug developed by Astellas Pharma, Inc. for the treatment of psoriasis. It targets CD2 and modulates the immune response to alleviate the symptoms of psoriasis. The drug was first approved in the United States in 2003 and is regulated as an orphan drug, indicating its potential to address an unmet medical need.