Exploring Dactinomycin's Revolutionary R&D Successes and its Mechanism of Action on Drug Target
Dactinomycin's R&D Progress
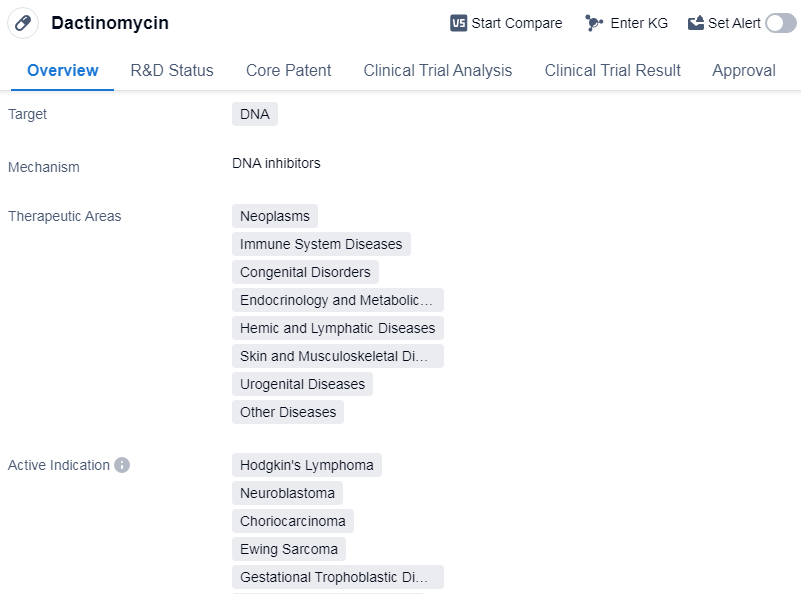
Dactinomycin is a small molecule drug that targets DNA and is used in the treatment of various diseases. It has been approved for use in multiple therapeutic areas, including neoplasms, immune system diseases, congenital disorders, endocrinology and metabolic disease, hemic and lymphatic diseases, and other diseases.
The drug has shown efficacy in treating several specific indications, including Hodgkin's lymphoma, neuroblastoma, choriocarcinoma, gestational trophoblastic disease, local neoplasm recurrence, rhabdomyosarcoma,etc.
Dactinomycin was first approved in the United States in December 1964, making it a well-established drug with a long history of use. It is worth noting that the drug has also received approval in China, indicating its global recognition and acceptance.
The originator organization of Dactinomycin is Recordati SpA, a pharmaceutical company that has played a significant role in the development and commercialization of the drug. As the highest phase of development for Dactinomycin is approved, it suggests that the drug has successfully completed clinical trials and demonstrated its safety and efficacy.
Dactinomycin's mechanism of action involves targeting DNA, which is crucial for the replication and functioning of cells. By interfering with DNA, the drug can inhibit the growth and proliferation of cancer cells, making it particularly effective in the treatment of various types of neoplasms.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for Dactinomycin: DNA inhibitors
DNA inhibitors are substances that interfere with the replication or transcription of DNA, thereby preventing the normal functioning of cells. From a biomedical perspective, DNA inhibitors are often used in cancer treatment as chemotherapy drugs. They work by targeting rapidly dividing cancer cells and inhibiting their ability to replicate their DNA, leading to cell death. DNA inhibitors can also be used as antimicrobial agents to target and inhibit the growth of bacteria or viruses by interfering with their DNA replication or transcription processes. Examples of DNA inhibitors include certain chemotherapeutic drugs like cisplatin and doxorubicin, as well as antibiotics like fluoroquinolones.
Drug Target R&D Trends for Dactinomycin
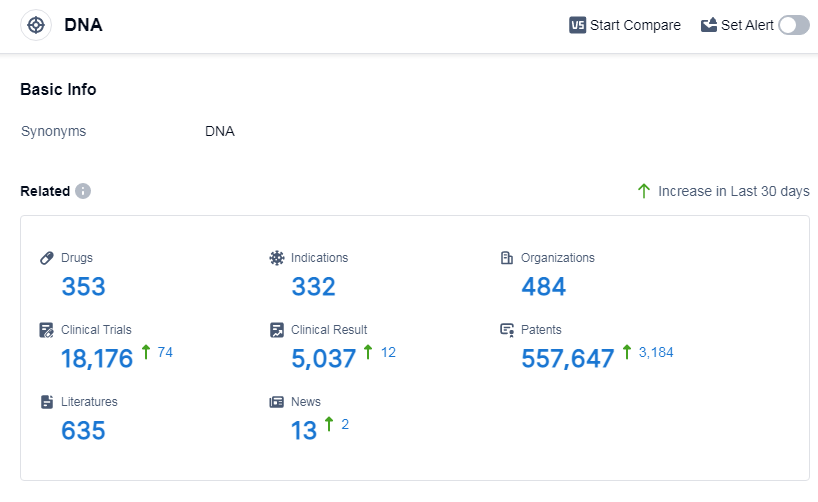
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 12 Sep 2023, there are a total of 353 DNA drugs worldwide, from 484 organizations, covering 332 indications, and conducting 18176 clinical trials.
The analysis of the target DNA in the pharmaceutical industry reveals that Pfizer Inc., Novartis AG, Baxter International, Inc., Takeda Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., and Johnson & Johnson are the companies growing fastest under this target. Lymphoma, ovarian cancer, and breast cancer are the indications with the highest number of approved drugs. Small molecule drugs, monoclonal antibodies, and antibody drug conjugates are the drug types progressing most rapidly. China, the United States, Japan, and the European Union are the countries/locations developing fastest under the target DNA. The competitive landscape is characterized by intense competition around biosimilars and a growing presence in China. The future development of the target DNA holds promising opportunities for further advancements in drug development and treatment options.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
In summary, Dactinomycin is a small molecule drug that targets DNA and has been approved for use in multiple therapeutic areas. It has shown efficacy in treating various indications, including Hodgkin's lymphoma, neuroblastoma, and choriocarcinoma. With its long history of use and global recognition, Dactinomycin is an important drug in the field of biomedicine.