Exploring ingenol mebutate's Revolutionary R&D Successes and its Mechanism of Action on Drug Target
Ingenol mebutate's R&D Progress
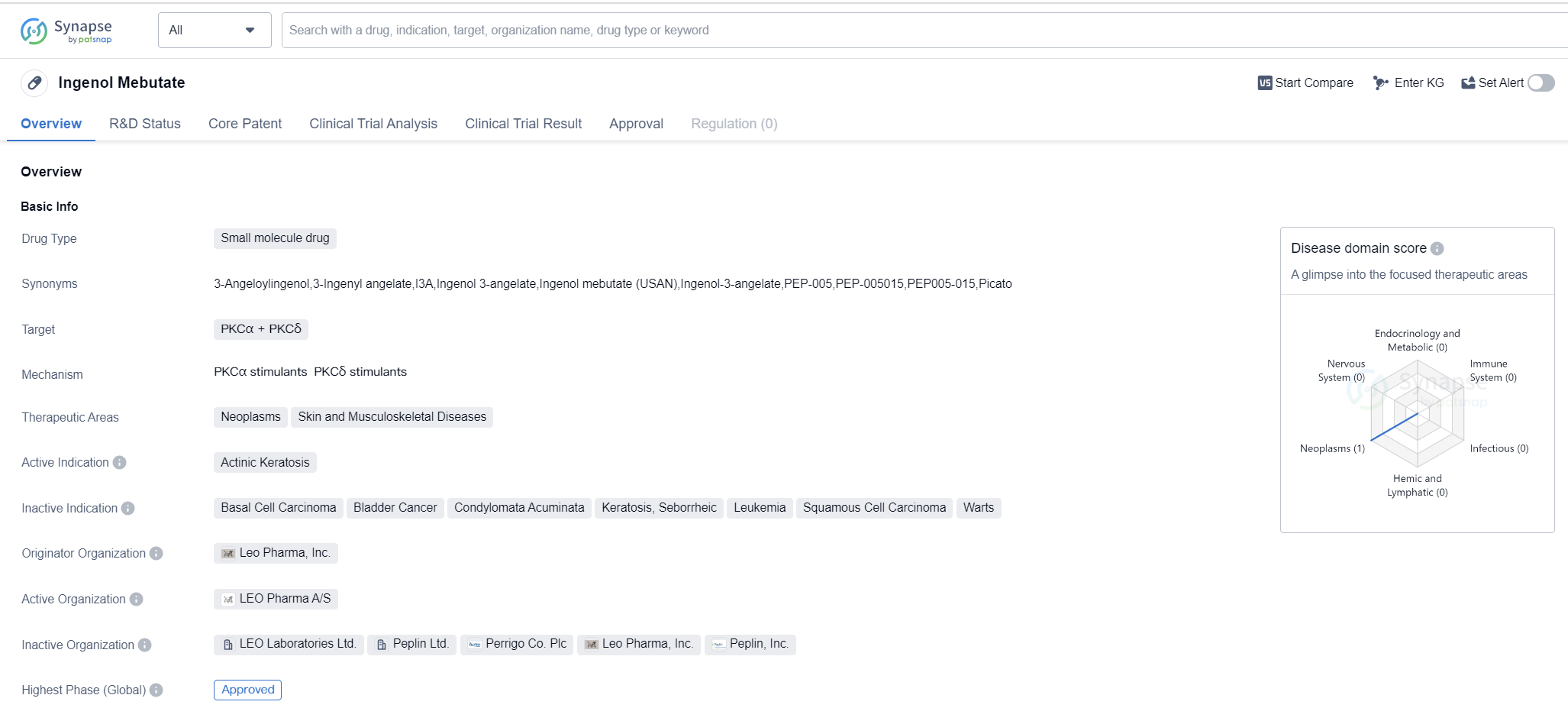
Ingenol Mebutate is a small molecule drug that targets PKCα and PKCδ. It is primarily used in the treatment of actinic keratosis, a precancerous skin condition. The drug was first approved in the United States in January 2012. The highest R&D phase of this drug is approved.
The originator organization of Ingenol Mebutate is Leo Pharma, Inc., a pharmaceutical company specializing in dermatology and critical care. Leo Pharma, Inc. played a crucial role in the development and commercialization of this drug.
Actinic keratosis is a common skin condition caused by long-term sun exposure. It is characterized by rough, scaly patches on the skin, which can potentially develop into skin cancer if left untreated. Ingenol Mebutate works by selectively targeting and activating protein kinase C (PKC) enzymes, specifically PKCα and PKCδ. These enzymes play a role in cell signaling and regulation, and their dysregulation is associated with the development of various diseases, including cancer.
The approval of Ingenol Mebutate represents a significant milestone in the treatment of actinic keratosis. It provides healthcare professionals with an effective and targeted therapeutic option for managing this condition. By specifically targeting PKCα and PKCδ, Ingenol Mebutate aims to induce cell death in the abnormal cells present in actinic keratosis lesions, leading to their elimination.
The approval of Ingenol Mebutate in the United States in 2012 demonstrates its safety and efficacy profile. It has undergone rigorous clinical trials and regulatory assessments to ensure its quality and effectiveness. The drug's approval in the highest phase of development indicates that it has met all the necessary requirements and has been deemed suitable for use in patients.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for ingenol mebutate: PKCα stimulants PKCδ stimulants
PKCα and PKCδ are abbreviations for protein kinase C alpha and protein kinase C delta, respectively. Protein kinase C (PKC) is an enzyme that plays a crucial role in cellular signaling pathways. It is involved in regulating various cellular processes, including cell growth, differentiation, and survival.
PKCα stimulants refer to substances or agents that can activate or stimulate the activity of PKCα. These stimulants can enhance the function of PKCα, leading to increased phosphorylation of target proteins and subsequent cellular responses.
Similarly, PKCδ stimulants are substances or agents that specifically activate or stimulate the activity of PKCδ. These stimulants can trigger the activation of PKCδ, resulting in the phosphorylation of specific target proteins and the initiation of cellular signaling cascades.
From a biomedical perspective, the activation of PKCα and PKCδ can have significant implications in various disease processes. Dysregulation of PKC signaling has been implicated in the pathogenesis of several diseases, including cancer, cardiovascular disorders, and neurological conditions. Therefore, understanding the mechanisms of PKC activation and the development of specific stimulants can have therapeutic potential in managing these diseases.
Drug Target R&D Trends for ingenol mebutate
PKCα and PKCδ are two isoforms of protein kinase C (PKC) enzymes that play crucial roles in various physiological processes in the human body. PKCα is involved in cell proliferation, differentiation, and survival, and is particularly important in the cardiovascular system. It regulates smooth muscle contraction, platelet activation, and cardiac function. On the other hand, PKCδ is primarily associated with apoptosis, or programmed cell death. It is involved in regulating cell growth, immune responses, and neuronal function. Both PKCα and PKCδ are key players in signal transduction pathways and have implications in numerous diseases, making them potential targets for therapeutic interventions in the pharmaceutical industry.
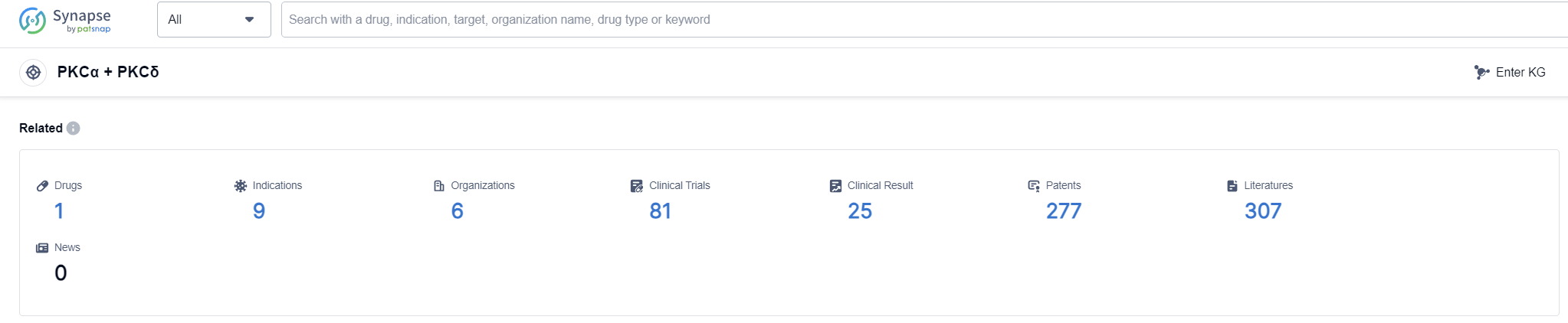
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 12 Sep 2023, there are a total of 1 PKCα + PKCδ drugs worldwide, from 6 organizations, covering 9 indications, and conducting 81 clinical trials.
The analysis of the target PKCα + PKCδ reveals that LEO Pharma A/S is the leading company in terms of development phase, with one drug approved and one drug in an inactive phase. The approved drug is indicated for Actinic Keratosis, a common skin condition caused by sun exposure. Small molecule drugs are progressing rapidly in the development of treatments for PKCα + PKCδ. The countries/locations showing the fastest development include Australia, Canada, New Zealand, Switzerland, and Brazil. The competitive landscape for PKCα + PKCδ appears to be promising, with a focus on dermatology and skin-related conditions. Further research and development efforts are needed to explore additional indications and expand the reach of treatments targeting PKCα + PKCδ.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
In conclusion, Ingenol Mebutate is a small molecule drug developed by Leo Pharma, Inc. for the treatment of actinic keratosis. It targets PKCα and PKCδ enzymes and has been approved for use in the United States since 2012. This drug represents a significant advancement in the field of biomedicine, providing healthcare professionals with an effective and targeted therapeutic option for managing actinic keratosis.