Exploring Lorlatinib's Revolutionary R&D Successes
Lorlatinib's R&D Progress
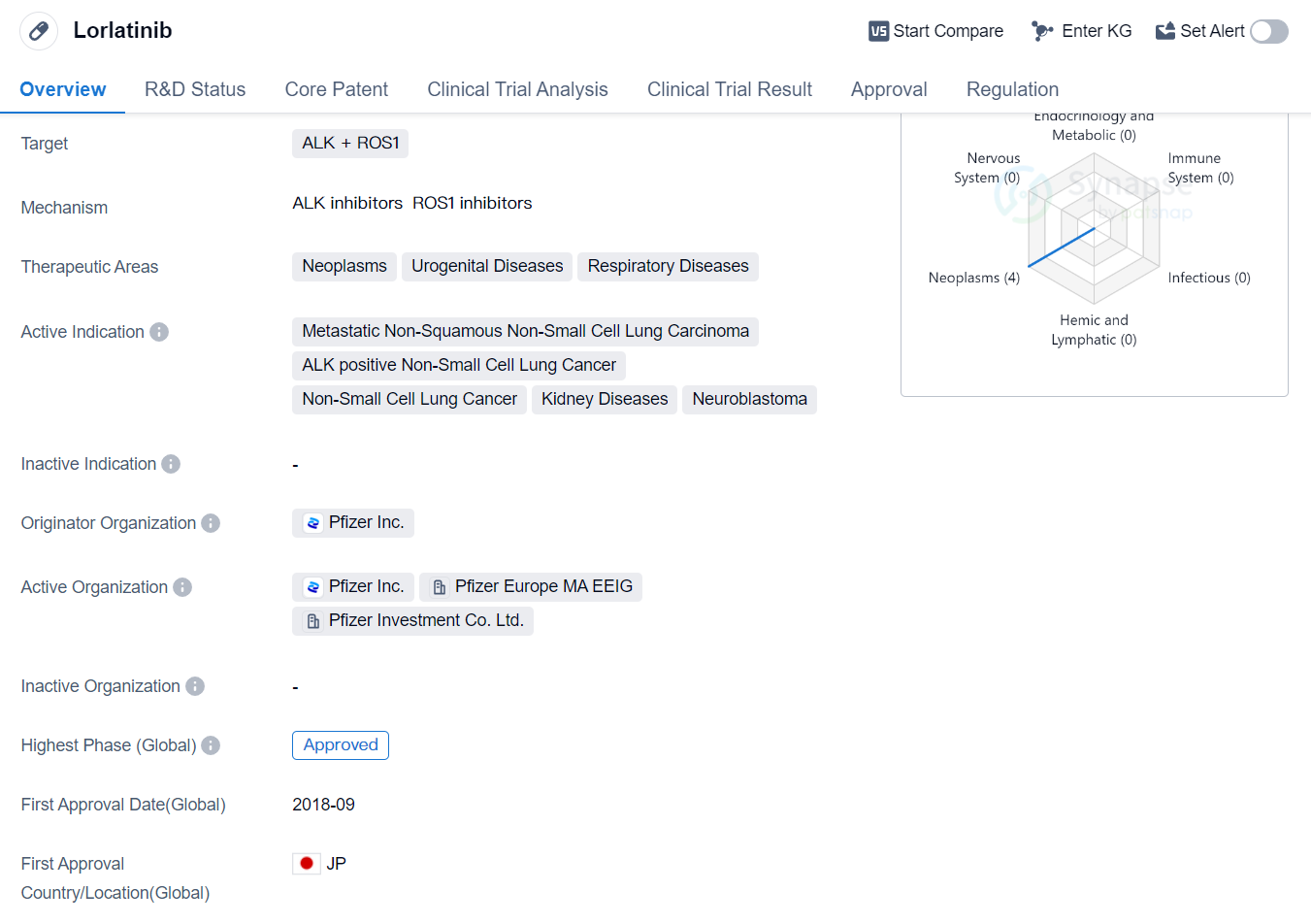
Lorlatinib is a small molecule drug developed by Pfizer Inc. It is primarily used in the treatment of various neoplasms, urogenital diseases, and respiratory diseases. The drug targets ALK (anaplastic lymphoma kinase) and ROS1 (c-ros oncogene 1) proteins.
The active indications for Lorlatinib include metastatic non-squamous non-small cell lung carcinoma, ALK positive non-small cell lung cancer, non-small cell lung cancer, kidney diseases, and neuroblastoma. These conditions are often characterized by abnormal cell growth and proliferation, and Lorlatinib aims to inhibit the activity of ALK and ROS1 proteins, which are known to play a role in these diseases.
Lorlatinib received its first approval in Japan in September 2018, making it available for use in the treatment of the approved indications. The drug has also received approvals in other countries, although specific details regarding these approvals are not provided in the given information.
In terms of regulatory status, Lorlatinib has undergone priority review, accelerated approval, breakthrough therapy designation, and orphan drug designation. These regulatory designations indicate that the drug has shown promising results in clinical trials and may provide significant benefits to patients with unmet medical needs.
As a small molecule drug, Lorlatinib is likely to have a well-defined chemical structure and can be easily synthesized in a laboratory setting. This characteristic makes it suitable for large-scale production and potential commercialization.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for Lorlatinib: ALK inhibitor and ROS1 inhibitor
ALK inhibitors and ROS1 inhibitors are both types of drugs used in biomedicine to treat certain types of cancer.
ALK inhibitors are drugs that specifically target and inhibit the activity of anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK), a protein that is often abnormal or mutated in certain types of cancer, such as non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). By inhibiting the activity of ALK, these drugs can help slow down or stop the growth of cancer cells that depend on ALK signaling for their survival and proliferation.
ROS1 inhibitors, on the other hand, target and inhibit the activity of ROS1, a receptor tyrosine kinase that is also frequently found to be abnormal or mutated in various cancers, including NSCLC. Similar to ALK inhibitors, ROS1 inhibitors work by blocking the signaling pathways mediated by ROS1, thereby hindering the growth and spread of cancer cells that rely on ROS1 signaling.
Both ALK inhibitors and ROS1 inhibitors are considered targeted therapies, as they specifically target and inhibit the activity of proteins that play a crucial role in the development and progression of certain cancers. These drugs have shown promising results in clinical trials and have been approved for the treatment of specific cancer subtypes where ALK or ROS1 abnormalities are present.
Drug Target R&D Trends for Lorlatinib
The analysis of the target ALK + ROS1 reveals a competitive landscape with multiple companies actively involved in the development of drugs. Roche Holding AG, Novartis AG, Pfizer Inc., Takeda Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Betta Pharmaceuticals Co., Ltd., and Zai Lab Ltd. are some of the companies growing fastest under this target. The highest stage of development is the Approved stage, with multiple companies having drugs approved for relevant indications. Small molecule drugs are progressing rapidly, indicating intense competition in the market. China is one of the fastest-developing countries under this target, with a significant number of drugs in the Approved and Preclinical stages. The future development of target ALK + ROS1 is promising, with ongoing research and development efforts by various companies and countries.
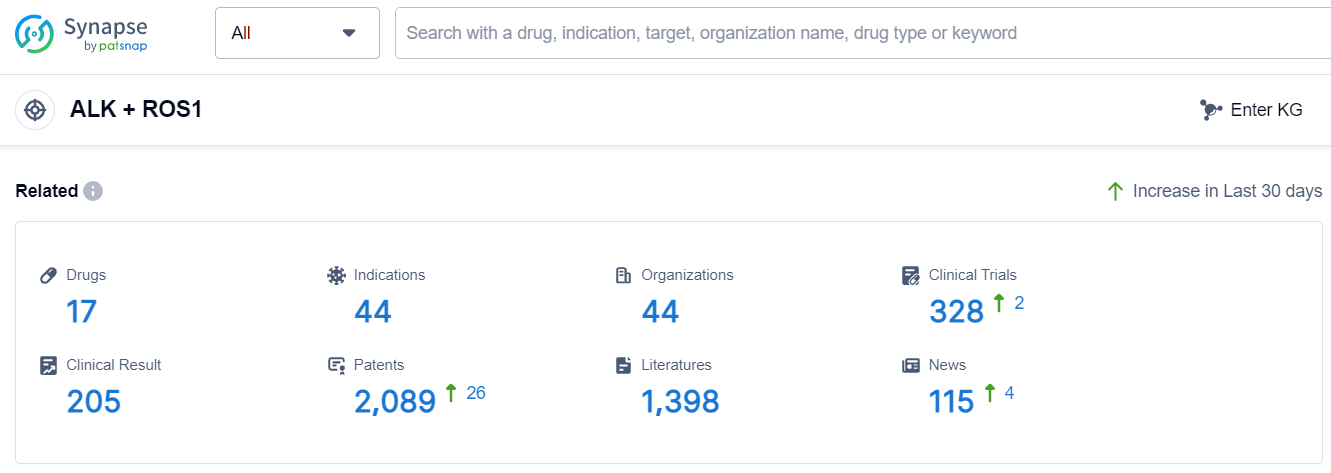
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 8 Sep 2023, there are a total of 17 ALK + ROS1 drugs worldwide, from 44 organizations, covering 44 indications, and conducting 328 clinical trials.
Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
Overall, Lorlatinib is a promising drug in the field of biomedicine, specifically in the treatment of various cancers and urogenital diseases. Its approval in multiple countries and regulatory designations highlight its potential as an effective therapeutic option. However, further research and clinical trials may be necessary to explore its full potential and evaluate its long-term safety and efficacy.