Exploring Pralatrexate's Revolutionary R&D Successes and its Mechanism of Action
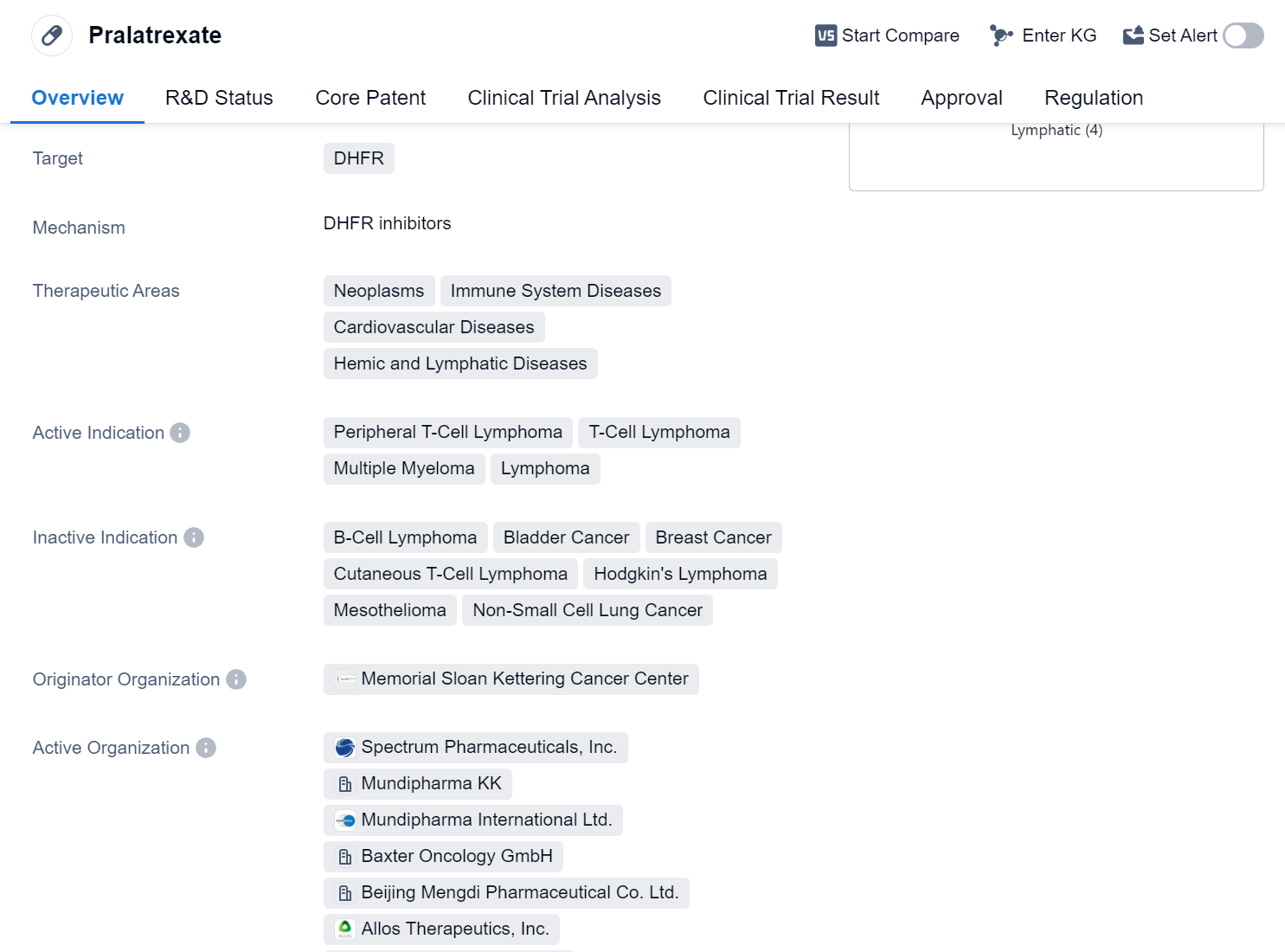
Pralatrexate is a small molecule drug that targets dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR). It is primarily used in the treatment of various neoplasms, immune system diseases, cardiovascular diseases, and hemic and lymphatic diseases. The drug has been approved for the treatment of peripheral T-cell lymphoma, T-cell lymphoma, multiple myeloma, and lymphoma.
Pralatrexate was developed by the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, a renowned cancer research and treatment institution. It has received approval for use in global market. The drug was first approved in the United States in September 2009.
In terms of regulatory status, Pralatrexate has undergone priority review and accelerated approval processes. It has also been designated as an orphan drug. These regulatory designations indicate that the drug addresses a significant unmet medical need and may provide substantial benefits to patients.
The approval of Pralatrexate marks an important milestone in the treatment of various cancers and immune system diseases. As a small molecule drug, it has the potential to target specific molecular pathways involved in the development and progression of these diseases. By targeting DHFR, Pralatrexate disrupts the synthesis of DNA and RNA, inhibiting the growth of cancer cells.
The approval of Pralatrexate in multiple indications highlights its versatility and potential to address different types of cancers and immune system diseases. This provides healthcare professionals with a valuable treatment option for patients who may not respond to other therapies.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for Pralatrexate: DHFR inhibitors
DHFR inhibitors are a type of medication that target and inhibit the activity of the enzyme dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR). DHFR is an essential enzyme involved in the synthesis of DNA, RNA, and proteins. By inhibiting DHFR, these inhibitors disrupt the production of these important molecules, particularly the synthesis of thymidine, which is necessary for DNA replication.
From a biomedical perspective, DHFR inhibitors are commonly used in the treatment of certain types of cancer, autoimmune diseases, and microbial infections. In cancer treatment, these inhibitors can be used to prevent the growth and division of cancer cells by interfering with their ability to replicate DNA. In autoimmune diseases, DHFR inhibitors can help suppress the immune system's activity, reducing inflammation and preventing damage to tissues. Additionally, DHFR inhibitors can be effective against microbial infections by inhibiting the growth and proliferation of the microorganisms.
It is important to note that DHFR inhibitors can have side effects, as they may also affect normal cells that rely on DHFR activity. Therefore, careful monitoring and dosage adjustments are necessary to minimize adverse effects while maximizing therapeutic benefits.
Drug Target R&D Trends for Pralatrexate
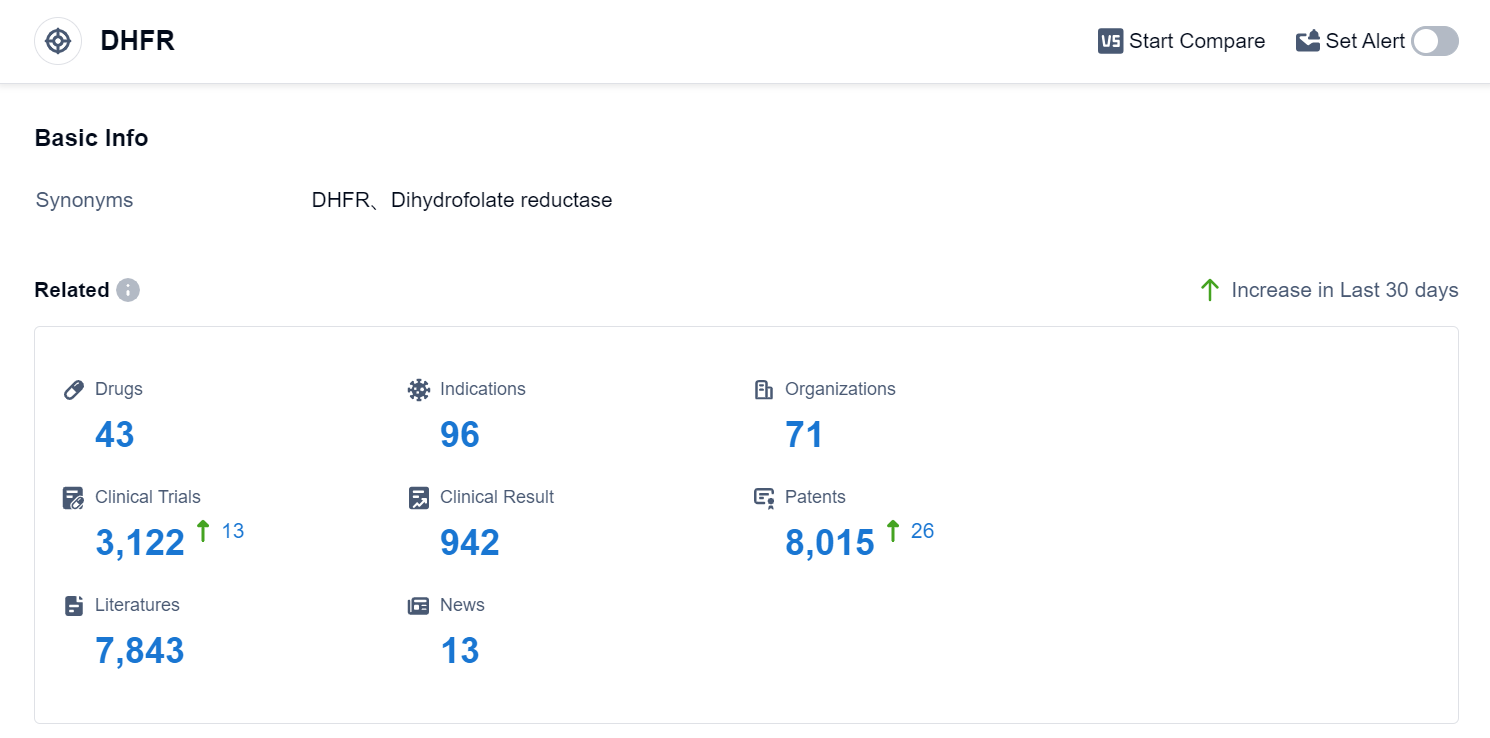
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 3 Sep 2023, there are a total of 43 DHFR drugs worldwide, from 71 organizations, covering 96 indications, and conducting 3122 clinical trials.
The analysis of the target DHFR in the pharmaceutical industry reveals a competitive landscape with multiple companies focusing on the development of drugs targeting DHFR. Pfizer Inc. is leading in terms of the highest stage of development, with several approved drugs. The indications for these drugs cover a wide range of diseases, indicating the potential for DHFR-targeted therapies in various therapeutic areas. Small molecule drugs are progressing rapidly, suggesting intense competition in the market. China is emerging as a key player in DHFR research and development, with a significant number of approved drugs. Overall, the target DHFR shows promise for future development and innovation in the pharmaceutical industry.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
In conclusion, Pralatrexate is a small molecule drug developed by the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center. It has been approved for the treatment of various neoplasms, immune system diseases, cardiovascular diseases, and hemic and lymphatic diseases. The drug targets DHFR and has shown efficacy in treating peripheral T-cell lymphoma, T-cell lymphoma, multiple myeloma, and lymphoma. Its regulatory status includes priority review, accelerated approval, and orphan drug designation. Pralatrexate represents an important advancement in the field of biomedicine and provides healthcare professionals with a valuable treatment option for patients in need.