FDA Approves UNLOXCYT™ (Cosibelimab-ipdl) by Checkpoint Therapeutics
Checkpoint Therapeutics, Inc. (Nasdaq: CKPT) announced that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration has granted approval for UNLOXCYT™ (cosibelimab-ipdl) to treat adults with metastatic cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (“cSCC”) or locally advanced cSCC who are not suitable for curative surgical procedures or radiation treatment. UNLOXCYT is the first and sole programmed death ligand-1 (“PD-L1”) inhibitor to obtain FDA marketing authorization for this use.
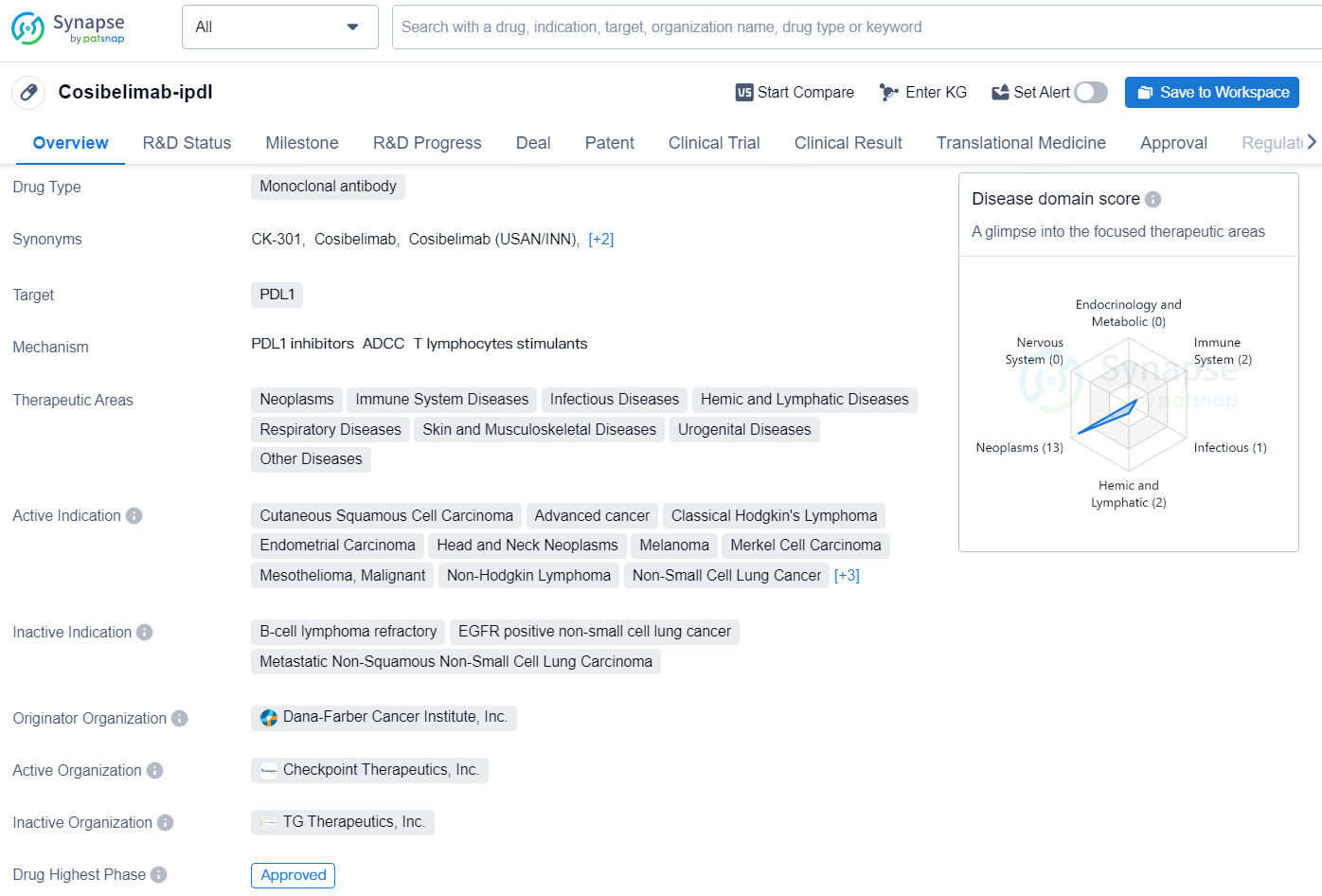
👇Discover comprehensive information about this drug, from its R&D status, core patents, clinical trials to approval status in global countries, by simply clicking on the image below. Dive deep into our drug database now.
The suggested commercial dosage for UNLOXCYT is 1,200 mg, delivered as an intravenous infusion over the span of 60 minutes every three weeks.
“The FDA's approval today of UNLOXCYT-our initial marketing authorization-is a crucial achievement for both Checkpoint and individuals suffering from advanced cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (cSCC),” stated James Oliviero, the President and CEO of Checkpoint. “This approval signifies Checkpoint’s evolution into a commercial entity, enabling us to compete in a U.S. market projected to exceed $1 billion each year. We believe that UNLOXCYT presents a distinct therapeutic alternative compared to existing treatments by targeting PD-L1 instead of programmed cell death receptor-1 (PD-1), thereby mitigating the inhibitory effects of PD-L1 on the anti-tumor immune response. Furthermore, UNLOXCYT has shown the capability to trigger antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC), which could further distinguish it from currently available therapies for cSCC patients.”
“Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma is the second most prevalent type of skin cancer, and patients with advanced forms, either recurrent or metastatic, face a grim outlook. There is an urgent need for more effective and tolerable treatment options, especially for individuals with concurrent hematologic malignancies, organ transplant recipients, or histories of autoimmune diseases,” indicated Emily Ruiz, M.D., M.P.H., Academic Director of the Mohs and Dermatologic Surgery Center at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Director of the High-Risk Skin Cancer Clinic at Dana-Farber Cancer Center, and Associate Professor of Dermatology at Harvard Medical School. “UNLOXCYT is the first PD-L1-blocking antibody approved by the FDA that has shown clinically significant objective response rates with lasting effects in advanced cSCC. With its dual modes of action and promising safety profile, this drug presents U.S. oncologists with an important new immunotherapy choice for treating cSCC.”
The FDA's approval of UNLOXCYT was based on significant objective response rates and duration data, as evaluated by an independent central review committee, from Study CK-301-101 (NCT03212404), a multicenter, multicohort, open-label investigation of UNLOXCYT in adults with advanced solid tumors, including cSCC.
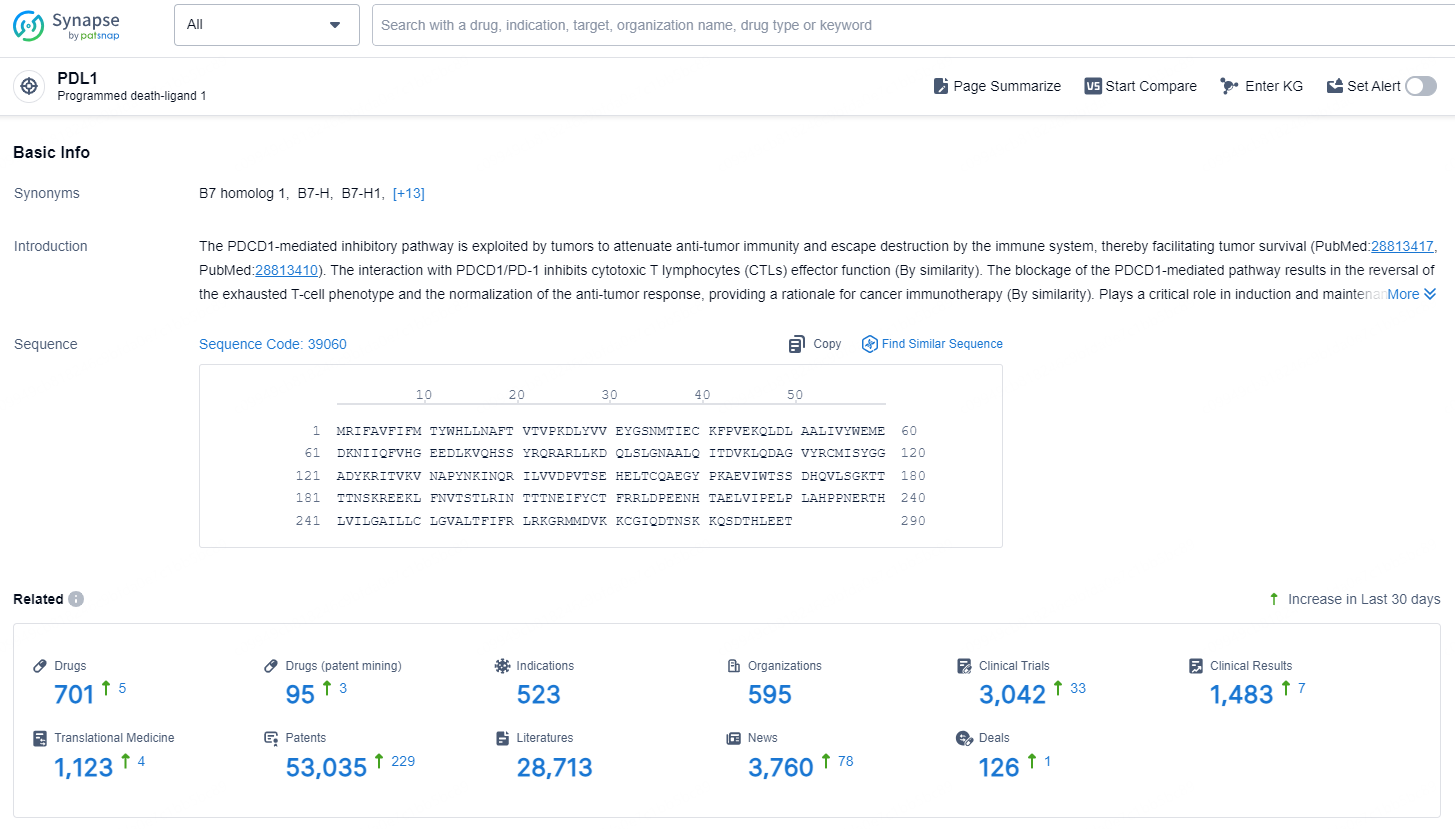
👇Explore the latest research progress on drug-related developments, indications, therapeutic organizations, clinical trials, results, and patents by clicking on the targeted picture link below. Unfold a world of comprehensive information on this target in just a click!
According to the data provided by the Synapse Database, As of December 20, 2024, there are 701 investigational drug for the PDL1 targets, including 523 indications, 595 R&D institutions involved, with related clinical trials reaching 3042, and as many as 53035 patents.
The drug Cosibelimab-ipdl is a monoclonal antibody that targets PDL1 and is used in the treatment of various therapeutic areas including neoplasms, immune system diseases, infectious diseases, hemic and lymphatic diseases, respiratory diseases, skin and musculoskeletal diseases, urogenital diseases, and other diseases.