Genentech's Vabysmo Improves Vision in Marginalized DME Patients in Landmark Study
Genentech, part of the Roche Group (SIX: RO, ROG; OTCQX: RHHBY), revealed encouraging one-year topline findings from the open-label, single-arm Phase IV ELEVATUM study, which assessed Vabysmo® (faricimab-svoa) in the management of diabetic macular edema (DME) among individuals from racial and ethnic backgrounds that are frequently underrepresented in clinical research.
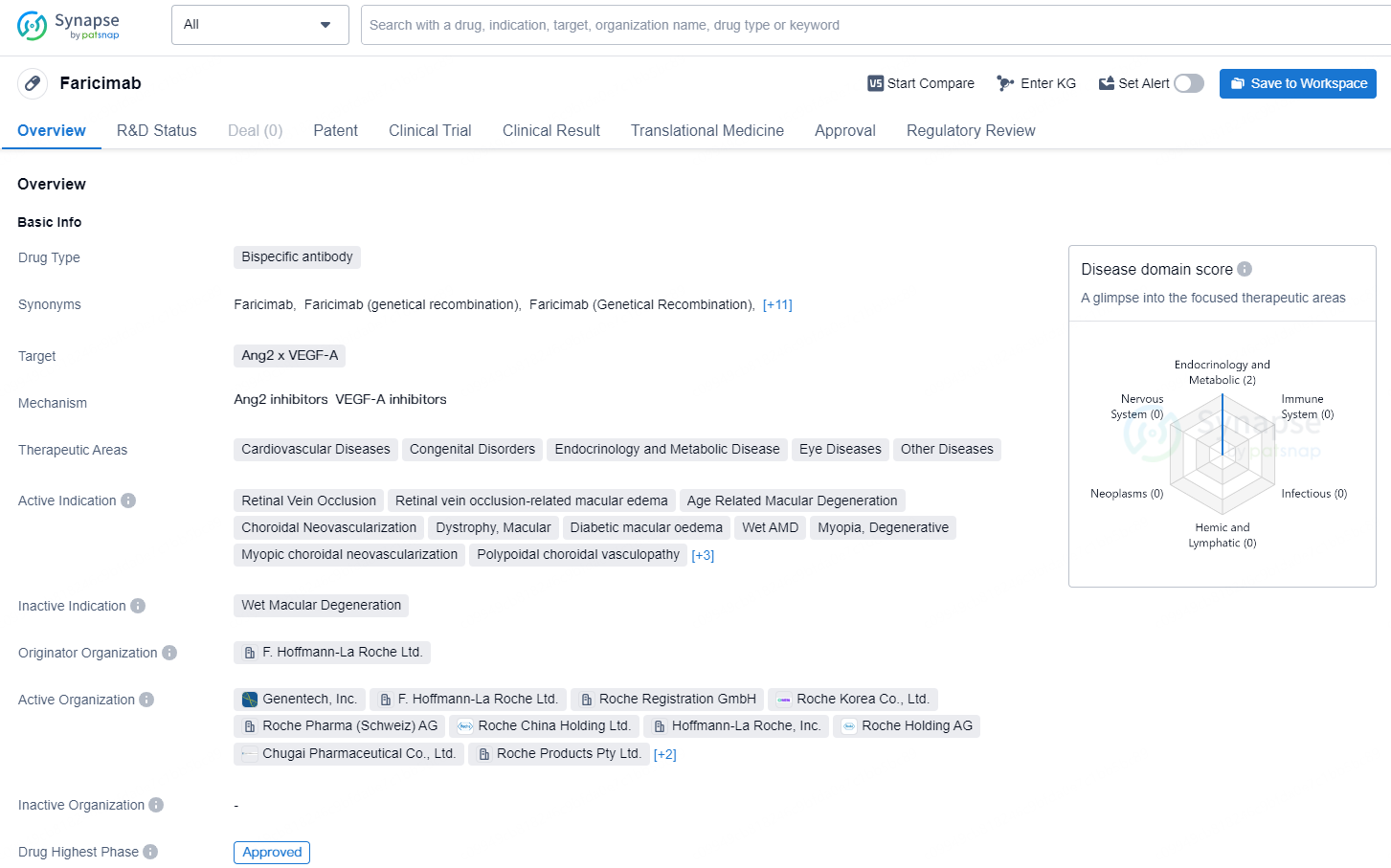
👇Discover comprehensive information about this drug, from its R&D status, core patents, clinical trials to approval status in global countries, by simply clicking on the image below. Dive deep into our drug database now.
Preliminary findings from a study involving 124 participants in the United States revealed that after one year of receiving Vabysmo treatment every eight weeks, participants experienced an average improvement of 12.3 letters in their reading ability—approximately two and a half lines on an eye chart. The outcomes were consistent across major racial and ethnic groups participating in the research. Notably, Hispanic and Latino participants began the study with the most severe form of the disease and showed an average improvement of 14.1 letters from their baseline measurement after one year, which corresponds to nearly three lines on an eye chart. The average increase for African American and Black participants was 11.3 letters from baseline after the same duration. Vabysmo demonstrated good tolerability, with no new safety concerns arising.
These findings were shared during a late-breaking oral presentation at the American Academy of Ophthalmology (AAO) Annual Meeting 2024 in Chicago on October 18. This study marks the first retinal trial focused on historically underrepresented groups.
“Vabysmo has proven to be a viable first-line treatment for diabetic macular edema, and for the first time, we have evidence showcasing its capacity to enhance vision in Black, African American, Hispanic, and Latino individuals who are disproportionately affected by this condition,” stated investigator Jeremiah Brown, M.D., of Retina Consultants of Texas, who presented the results at the AAO. “As a clinician serving these communities, I felt it vital to participate in this pioneering study and am hopeful that the findings will aid in improving the clinical care we offer our patients.”
The results aligned with those from the Phase III YOSEMITE and RHINE DME studies. A secondary endpoint indicated significant retinal drying with Vabysmo among these racial and ethnic groups, with an average reduction of 206.3 microns in central subfield thickness (CST) from baseline. The decrease in CST signifies retinal drying, a crucial clinical indicator, as swelling caused by excess fluid in the eye is related to blurred and distorted vision.
“Although certain ethnic and racial groups are affected by DME at higher rates, they remain significantly underrepresented in clinical trials,” commented Gregory A. Rippon, M.D., M.S., vice president of U.S. Medical Affairs. “We initiated the ELEVATUM study specifically to tackle this disparity and to gain insights into how underrepresented populations respond to Vabysmo treatment in order to enhance equitable care and influence the design of future clinical trials.”
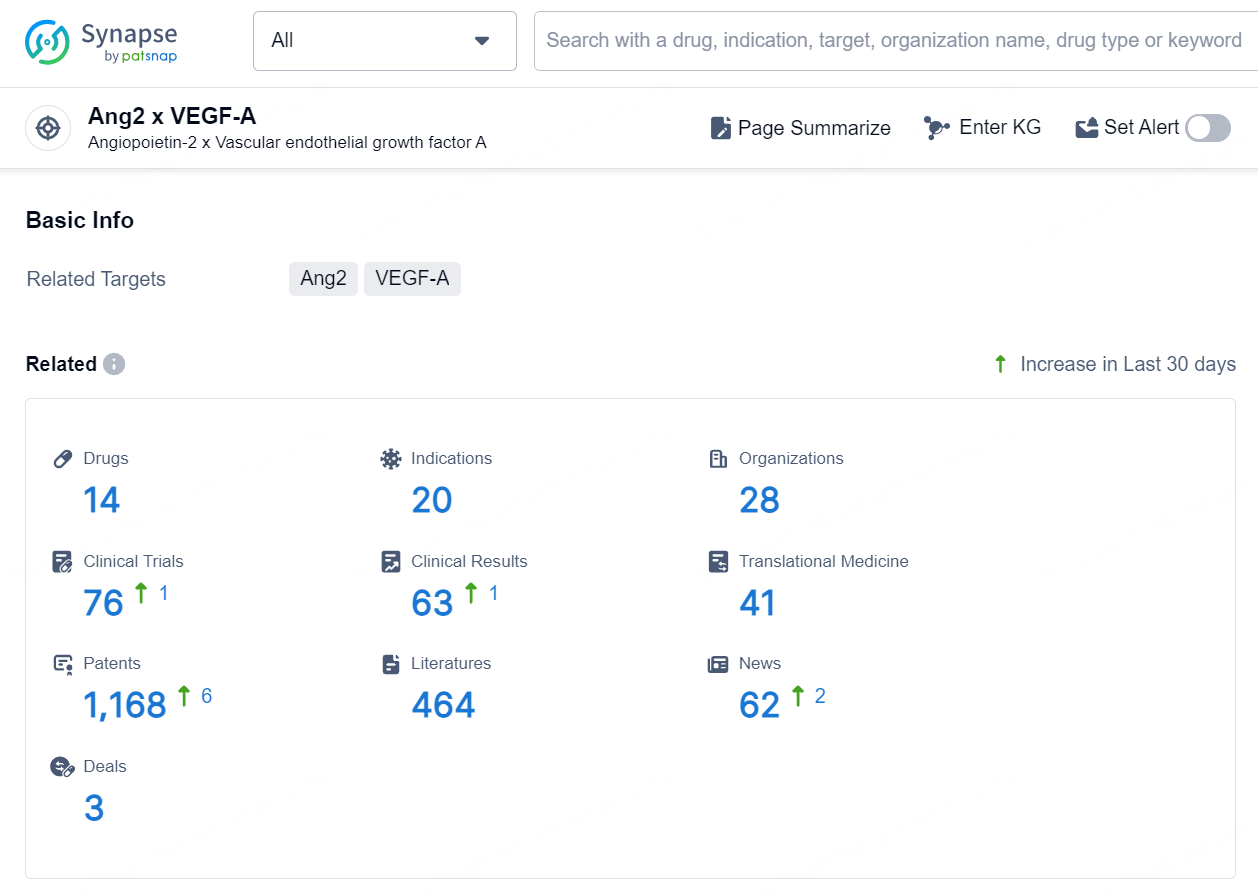
👇Explore the latest research progress on drug-related developments, indications, therapeutic organizations, clinical trials, results, and patents by clicking on the targeted picture link below. Unfold a world of comprehensive information on this target in just a click!
According to the data provided by the Synapse Chemical, As of October 23, 2024, there are 14 investigational drugs for the Ang2 and VEGF-A target, including 20 indications, 28 R&D institutions involved, with related clinical trials reaching 76, and as many as 1168 patents.
Faricimab is a bispecific antibody drug developed by F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd. It targets both Ang2 and VEGF-A and has been approved for use in the treatment of various medical conditions. The therapeutic areas of focus for Faricimab include cardiovascular diseases, congenital disorders, endocrinology and metabolic disease, eye diseases, and other diseases.