Gossypol Unveiled: A Detailed Overview of its Revolutionary R&D Breakthroughs
Gossypol's R&D Progress
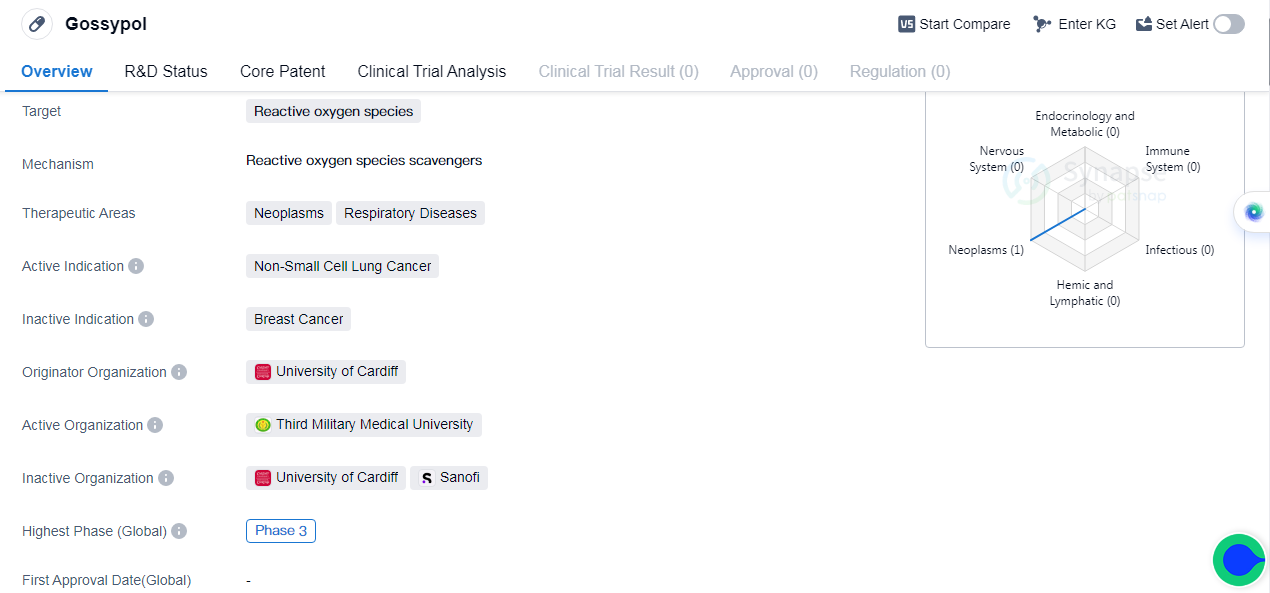
Gossypol is a small molecule drug that targets reactive oxygen species. It is primarily developed for the treatment of neoplasms and respiratory diseases, with a specific focus on non-small cell lung cancer. The drug is currently in phase 3 clinical trials globally.
Gossypol's originator organization is the University of Cardiff. The fact that it has reached phase 3 trials suggests that it has shown promising results in earlier stages of development, such as phase 1 and phase 2 trials.
As a small molecule drug, Gossypol is likely to have a relatively small molecular size, allowing it to easily penetrate cell membranes and interact with its target, reactive oxygen species. This mechanism of action suggests that Gossypol may have antioxidant properties, which could be beneficial in the treatment of neoplasms and respiratory diseases.
Non-small cell lung cancer is a type of lung cancer that accounts for the majority of lung cancer cases. It is a challenging disease, and there is a significant unmet need for effective therapies. The fact that Gossypol is developed specifically for this indication, which suggests that it may have demonstrated promising results in preclinical studies or earlier clinical trials.
The fact that Gossypol has reached phase 3 trials, which involve a large number of participants and are designed to provide definitive evidence of the drug's effectiveness and safety profile.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for Gossypol: Reactive oxygen species scaveng
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) scavenging refers to the process of removing or neutralizing harmful reactive oxygen species in the body. They are highly reactive molecules that contain oxygen and can cause damage to cells and tissues if their levels become too high. ROS include hydrogen peroxide, superoxide radicals, and hydroxyl radicals.
In the context of biomedicine, ROS scavenging is an important process in maintaining cellular homeostasis and preventing oxidative stress. Oxidative stress occurs when there is an imbalance between the production of ROS and the body's ability to detoxify or repair the resulting damage. Oxidative stress has been implicated in various diseases such as cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, cardiovascular diseases, and aging.
ROS scavenging can be achieved through various mechanisms. Antioxidant enzymes, such as superoxide dismutase, catalase, and glutathione peroxidase, play a crucial role in neutralizing ROS. Additionally, small molecules with antioxidant properties, such as vitamins C and E, carotenoids, and flavonoids, can also scavenge ROS. These antioxidants donate electrons or hydrogen atoms to ROS, thereby stabilizing them and preventing them from causing damage.
Overall, ROS scavenging is an essential process in maintaining cellular health and preventing oxidative damage.
Drug Target R&D Trends for Gossypol
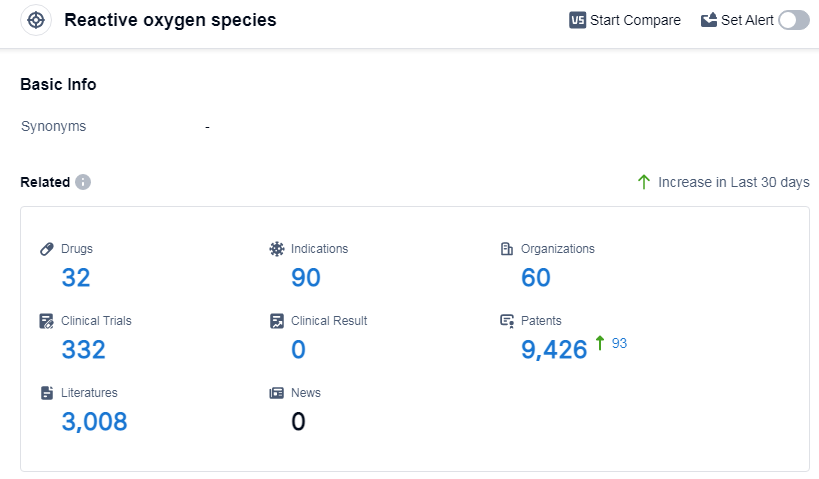
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 5 Sep 2023, there are a total of 32 Reactive oxygen species (ROS) drugs worldwide, from 60 organizations, covering 90 indications, and conducting 332 clinical trials.
The analysis of the current competitive landscape and future development of target (ROS) reveals that Solasia Pharma KK is the leading company in terms of R&D progress. The highest phase of development for drugs targeting ROS is in phase 3 stages, indicating significant progress in clinical development for various indications. Small molecule drugs are progressing most rapidly, suggesting intense competition in this area. China has shown progress in the development of drugs targeting ROS. Overall, ROS presents a promising area for pharmaceutical development.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
Overall, Gossypol is a small molecule drug developed by the University of Cardiff for the treatment of neoplasms and respiratory diseases, with a focus on non-small cell lung cancer. It is currently in phase 3 trials globally, indicating that it has shown promising results in earlier stages of development. If successful, Gossypol could potentially address the significant unmet need for effective therapies in these therapeutic areas.