How to find the structure and classification of Eculizumab?
Eculizumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody that targets the complement protein C5. Developed by Alexion Pharmaceuticals, Eculizumab is classified as a therapeutic protein and is primarily indicated for the treatment of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH), atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (aHUS), neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders (NMOSD), and generalized myasthenia gravis (gMG). It is used to prevent the terminal complement cascade, reducing the risk of hemolysis and organ damage.
Summary of Research Progress:
The research progress of Eculizumab has been extensive and impactful. Its mechanism of action involves binding to the C5 component of the complement system, preventing its cleavage into C5a and C5b. This inhibition blocks the formation of the membrane attack complex (MAC), which is responsible for cell lysis and tissue damage. By preventing the activation of the terminal complement pathway, Eculizumab reduces the destruction of red blood cells in PNH, prevents thrombotic microangiopathy in aHUS, and reduces inflammation in NMOSD and gMG.
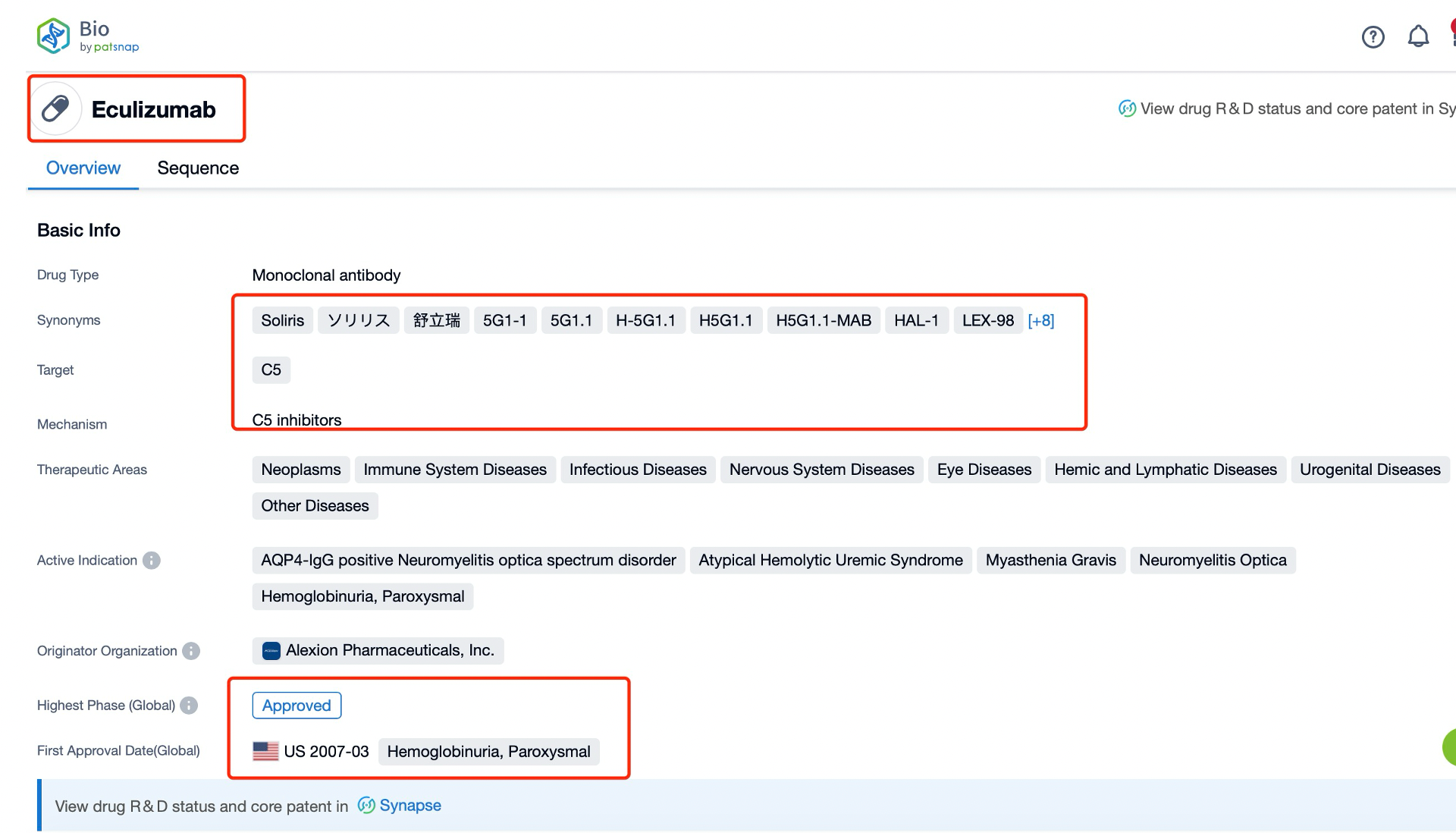
Globally, Eculizumab has been approved in numerous countries, including the United States, Europe, and Japan. It received FDA approval in 2007 for the treatment of PNH and has since been approved for aHUS in 2011, NMOSD in 2019, and gMG in 2017. Eculizumab has also been approved in many other regions, making it a widely used therapeutic agent in rare and serious diseases.
The competitive landscape for Eculizumab is relatively limited due to the rarity of the conditions it treats. However, there are emerging therapies that aim to address similar pathways. In PNH, competitors include ravulizumab (Ultomiris), another C5 inhibitor developed by Alexion Pharmaceuticals. In aHUS, there are no direct competitors, but off-label use of eculizumab is common. For NMOSD, competitors include inebilizumab (Upliza) and satralizumab (Enspryng). In gMG, competitors include efgartigimod (Vyvgart) and rozanolixizumab (Zilucoplan). Despite this competition, Eculizumab has maintained a strong market presence due to its well-established efficacy and safety profile. Clinical trials have consistently demonstrated its effectiveness in reducing disease burden and improving quality of life for patients.
Type of Immunoglobulin of Eculizumab
Eculizumab is a humanized IgG2κ immunoglobulin. Humanized antibodies are engineered to contain minimal murine sequences, reducing the risk of immunogenicity while maintaining high affinity and specificity for the target antigen. The κ light chain is one of the two types of light chains found in immunoglobulins, the other being λ. The κ light chain is more common and provides stability and specificity to the antibody structure.
Light and Heavy Chains and Structural Characteristics of Eculizumab
The heavy chain of Eculizumab is a humanized IgG2 molecule, which consists of four domains: variable (VH), constant 1 (CH1), constant 2 (CH2), and constant 3 (CH3). The VH domain is responsible for antigen binding, while the CH1 domain forms part of the Fc region, which is crucial for the antibody's effector functions. The CH2 and CH3 domains are involved in the interaction with Fc receptors and complement proteins, respectively. Unlike IgG1, IgG2 does not activate complement through the classical pathway, which is advantageous in preventing unwanted immune responses.
The light chain of Eculizumab is a κ chain, which also consists of two domains: variable (VL) and constant (CL). The VL domain pairs with the VH domain to form the antigen-binding site, ensuring high specificity and affinity for the target antigen. The CL domain, like the CH1 domain, contributes to the stability and function of the antibody.
Structurally, Eculizumab is a well-characterized and highly specific monoclonal antibody. The variable regions of both the heavy and light chains are designed to recognize and bind to the C5 component of the complement system with high affinity. This binding prevents the cleavage of C5 into C5a and C5b, effectively blocking the formation of the membrane attack complex (MAC) and the subsequent cell lysis and tissue damage. The constant regions of the heavy and light chains provide additional functional properties to Eculizumab. The Fc region, composed of the CH2 and CH3 domains, is capable of engaging Fc receptors on immune cells, leading to various effector functions such as antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC). However, the lack of complement activation by IgG2 reduces the risk of unwanted immune responses, making Eculizumab particularly suitable for its therapeutic applications.
Summary and Prospect
In summary, Eculizumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody that targets the complement protein C5, making it a valuable therapeutic option for the treatment of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria, atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome, neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders, and generalized myasthenia gravis. Its mechanism of action involves binding to C5 and preventing its cleavage, thereby blocking the formation of the membrane attack complex and reducing cell lysis and tissue damage. Eculizumab has been approved globally for multiple indications and has maintained a strong market presence due to its well-established efficacy and safety profile. As a humanized IgG2κ immunoglobulin, Eculizumab exhibits well-defined structural characteristics that contribute to its high specificity and efficacy. The heavy and light chains, with their respective variable and constant domains, ensure precise antigen binding and robust effector functions, making Eculizumab a valuable and effective treatment for a range of rare and serious diseases. Future research and development efforts will likely focus on optimizing its delivery methods, exploring new indications, and enhancing its therapeutic benefits for patients.
How to find the structure and classification of antibody drugs?
In Patsnap Bio, you can find the sequence and latest research and development advances of all antibody drugs.
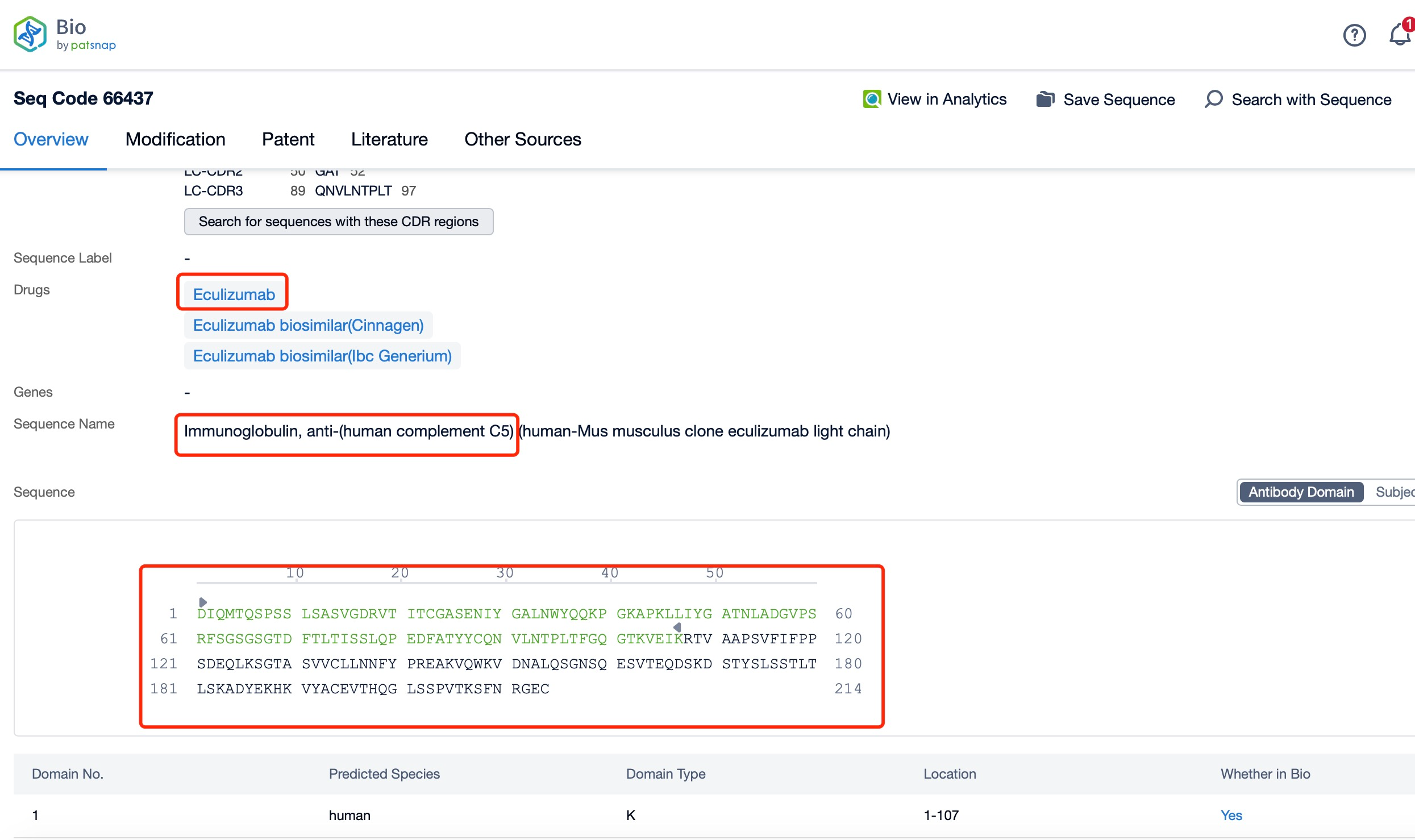
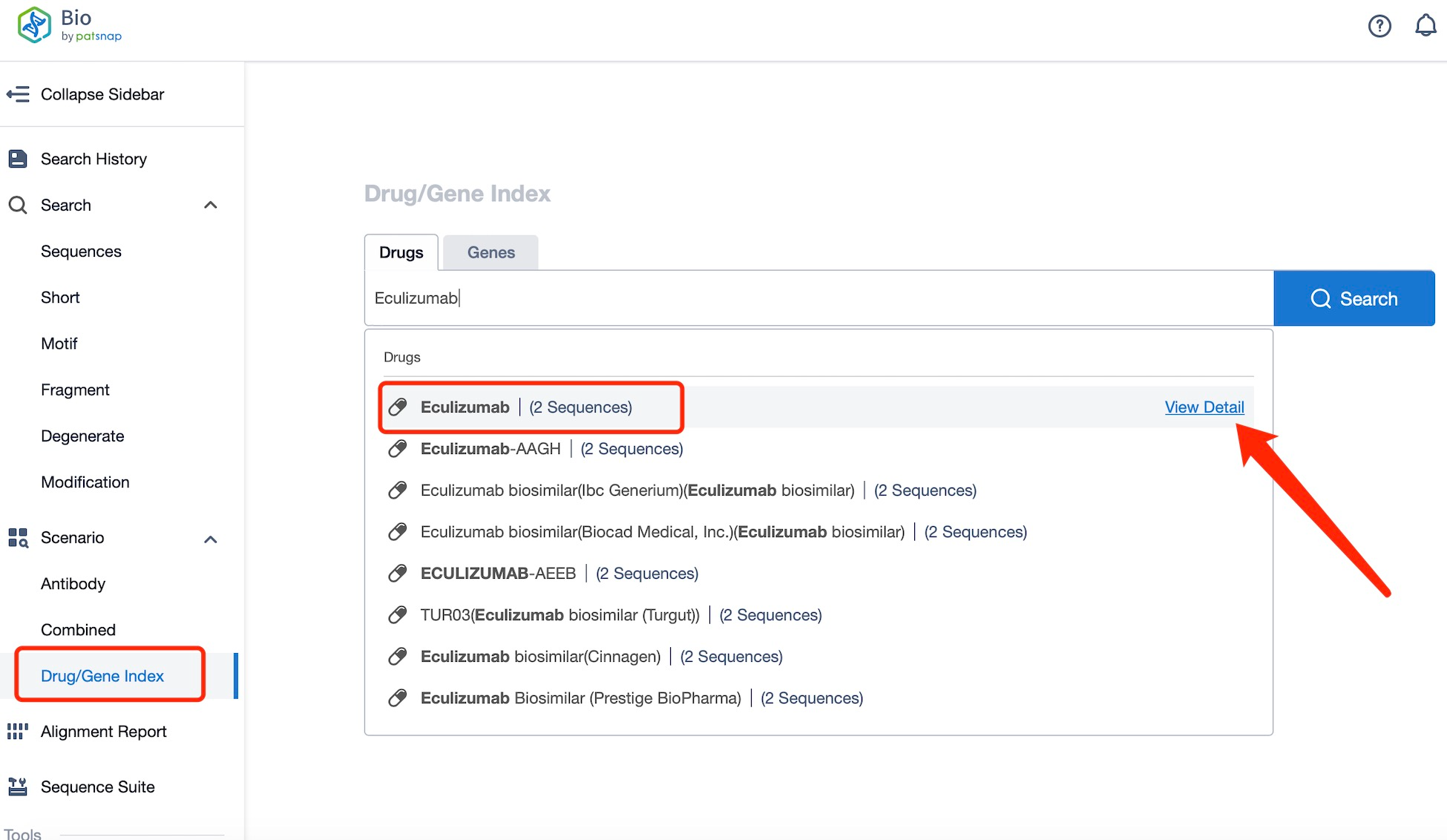
Taking Eculizumab as an example, first click on the Drug/Gene Index on the Patsnap Bio homepage. Here you can search for sequence information by drug and gene names. Enter ' Eculizumab ' in the search box and click to view the details. On the details page, you can find the basic information and research progress of Eculizumab.

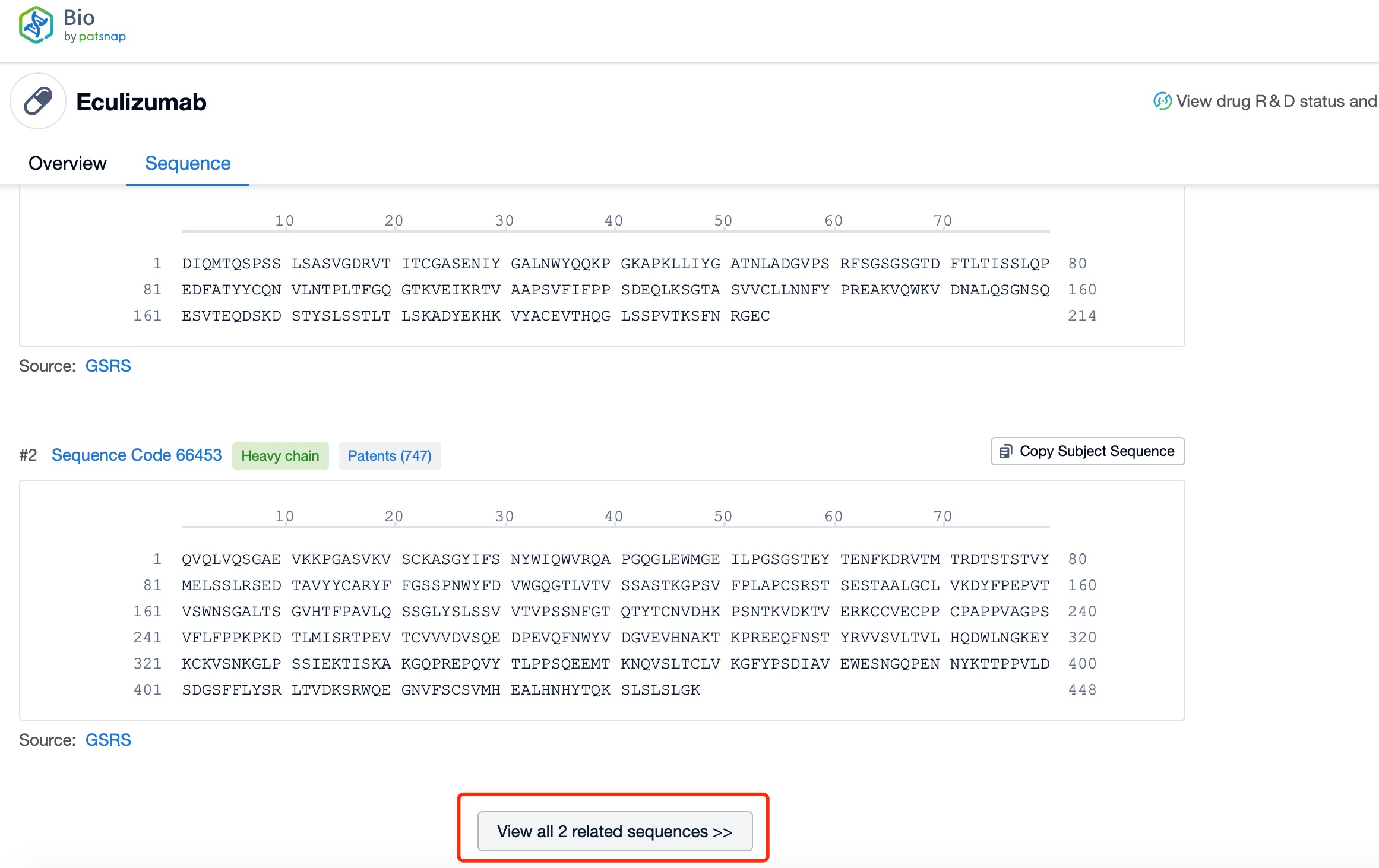
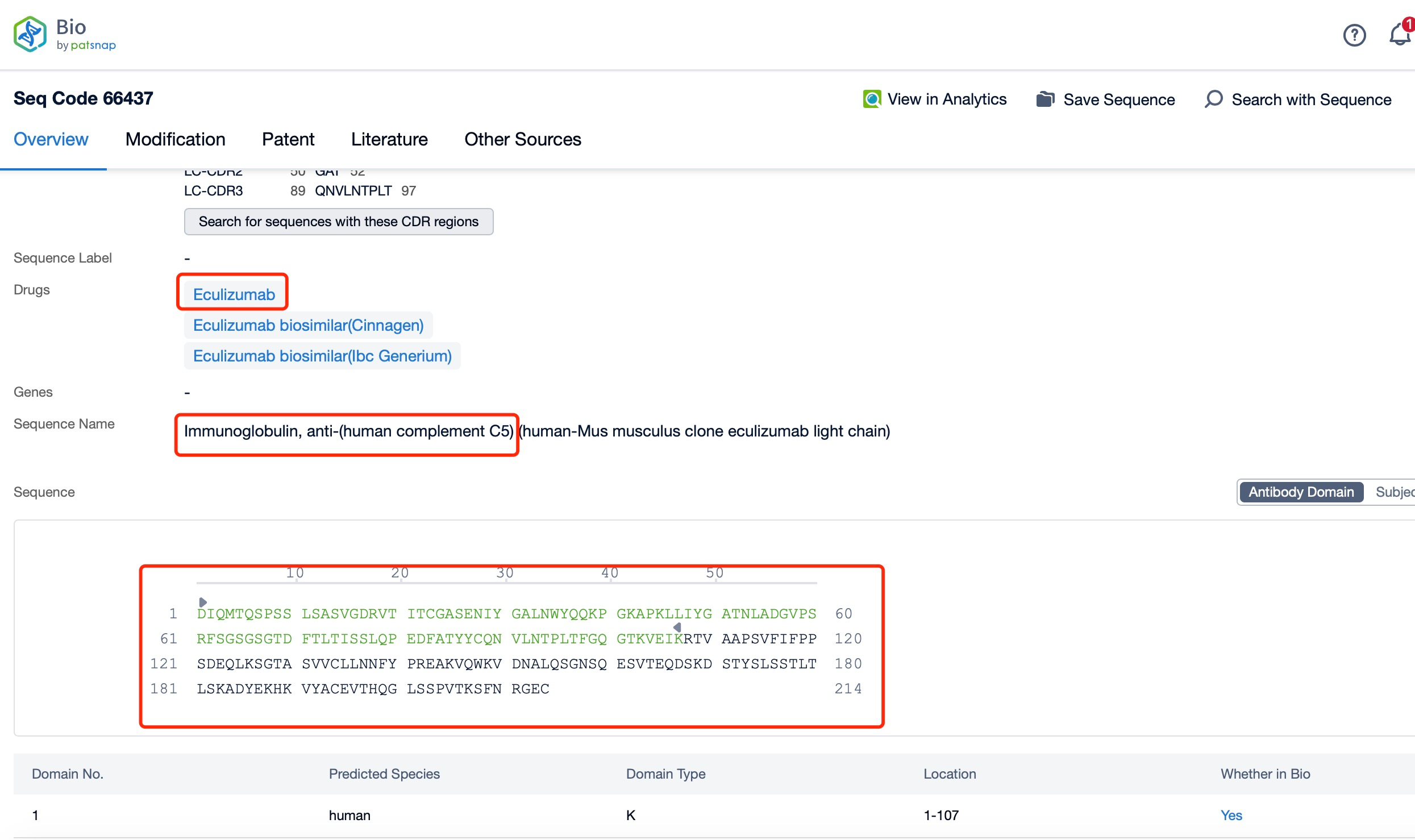
Click "View all related sequences" below the sequence information to search for and retrieve all biological sequences similar to this information.
Clicking on the sequence name will provide you with all the basic information of that sequence. Here, you can easily query the sequence and action of the light and light chains of antibodies.
Patsnap Bio helps you turn weeks into minutes with cutting-edge AI-enabled tools built to master the complexities of sequence retrieval and automate IP analysis with precision and ease.