Inozyme Pharma reports promising initial results from ongoing INZ-701 phase 1/2 studies in adults with ENPP1 and ABCC6 (PXE) deficiencies
Inozyme Pharma, Inc., a biopharmaceutical firm specializing in the research and development of new therapies for abnormal mineralization and intimal proliferation, today revealed encouraging preliminary findings on safety, drug metabolism, pharmacokinetics, and exploratory effectiveness from their continuing Phase 1/2 clinical studies on INZ-701 for adults with ENPP1 Deficiency and ABCC6 Deficiency.
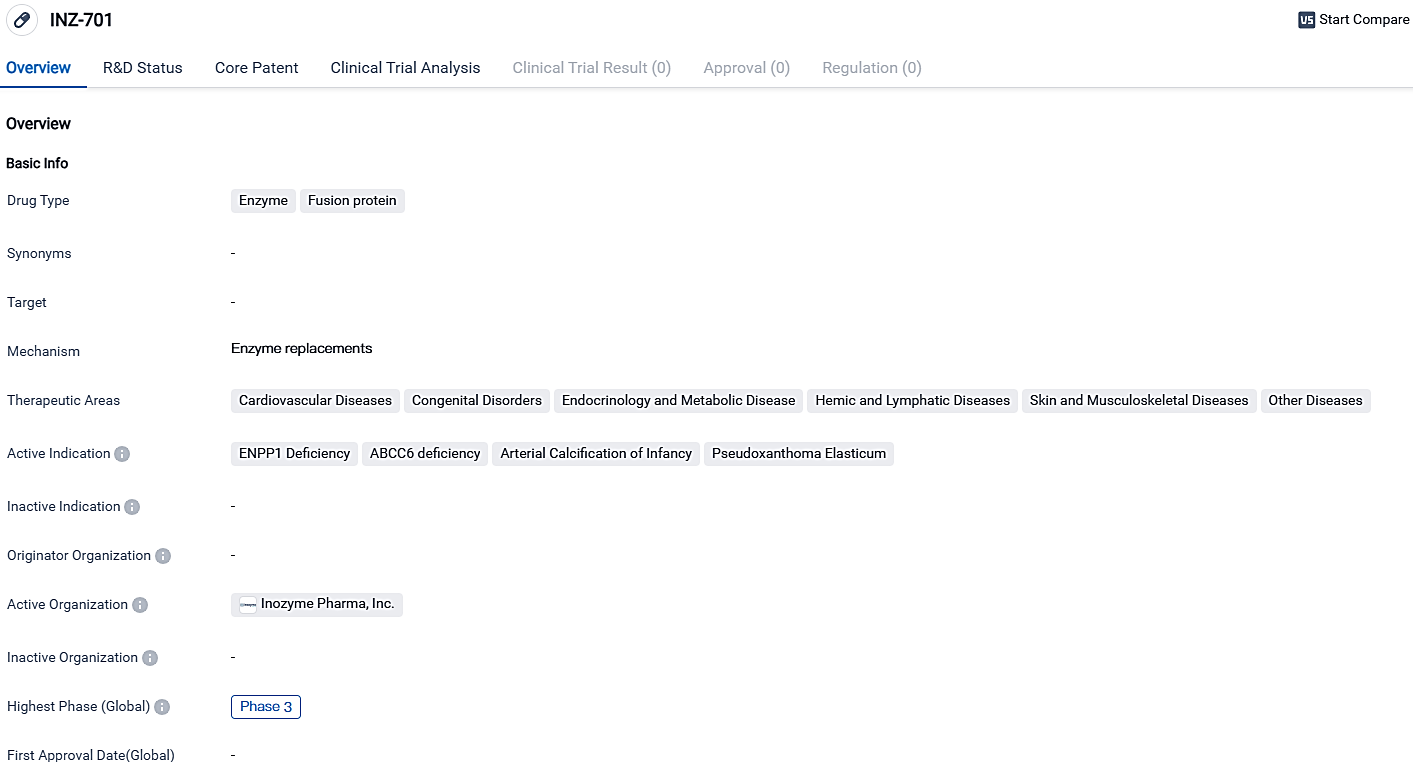
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
"We are gratified that these experimental trials have succeeded in their essential objectives of showcasing that INZ-701 is generally safe, well-received and significantly elevates PPi levels in ENPP1 patients,” expressed Kurt Gunter, M.D., the senior vice president and chief medical officer at Inozyme Pharma.
He further added, “The progressing indications of an improvement in key clinical measures of bone metabolism in adults suffering from ENPP1 Deficiency suggest the feasibility of INZ-701 for the treatment of rickets in our upcoming crucial trial for pediatric patients suffering from this condition.”
"Observations from these preliminary human trials of INZ-701 are genuinely promising for patients and medical practitioners dealing with ENPP1 Deficiency and ABCC6 Deficiency.
I am especially thrilled at the early indications that INZ-701 could alleviate symptoms in adult ENPP1 Deficiency patients, which might translate into clinical advantages for infant and adolescent patients desperately in need of a treatment option,” commented Michael Levine, M.D., Emeritus Professor, Pediatrics and Medicine, and Emeritus Chief.
ENPP1 Deficiency is an advancing condition that presents as a range of diseases. Cases starting in utero or infancy are generally identified as generalized arterial calcification of infancy (GACI), notorious for widespread vascular calcification and intimal proliferation (the excessive growth of smooth muscle cells within blood vessels) and that may cause myocardial infarction, stroke, or severe cardiac or multi-organ failure.
Roughly half of the infantile patients suffering from ENPP1 Deficiency do not survive beyond six months post-birth. Children affected by ENPP1 Deficiency commonly develop rickets, a condition identified as autosomal-recessive hypophosphatemic rickets type 2 (ARHR2), while teenagers and adults may acquire osteomalacia (bone softening). Both ARHR2 and osteomalacia result in pain and mobility problems. Patients may also display signs and symptoms of hearing impairment, arterial and joint calcification, and cardiovascular issues.
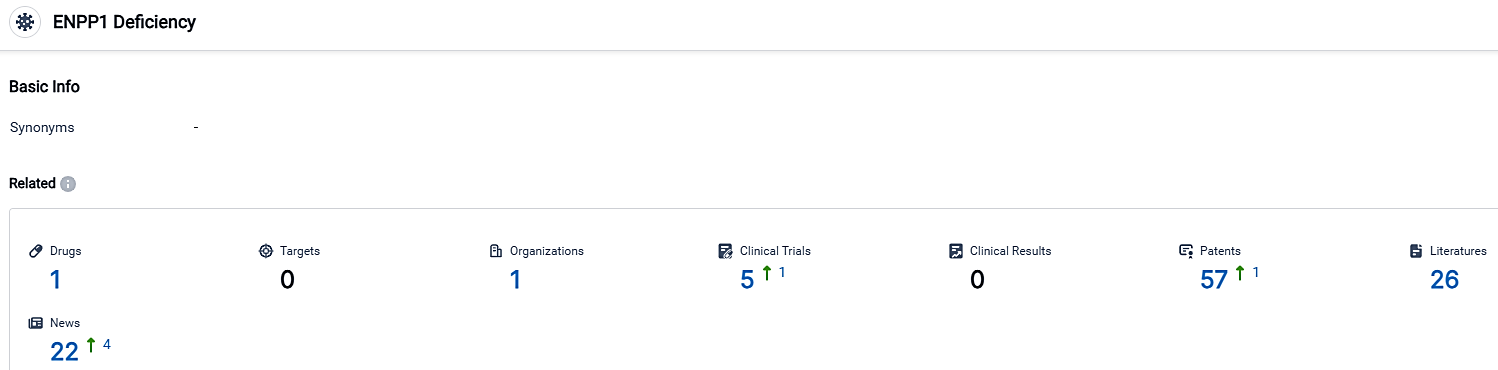
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or login directly if you have freemium accounts, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, targets, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this indication.
According to the data provided by the Synapse Database, As of October 1, 2023, there are 1 investigational drugs for the ENPP1 Deficiency, 1 R&D institutions involved, with related clinical trials reaching 5,and as many as 57 patents.
The bio-engineered Fc fusion protein, INZ-701, serves as an ENPP1 enzyme replacement therapeutic agent, currently in progress for addressing uncommon diseases affecting the blood vessels, soft tissues, and skeletal system. Through early stages of testing, this experimental treatment has displayed a propensity to inhibit undesirable mineralization and intimal proliferation.