A Comprehensive Review of Phenazepam's R&D Innovations and Drug Target Mechanism
Phenazepam's R&D Progress
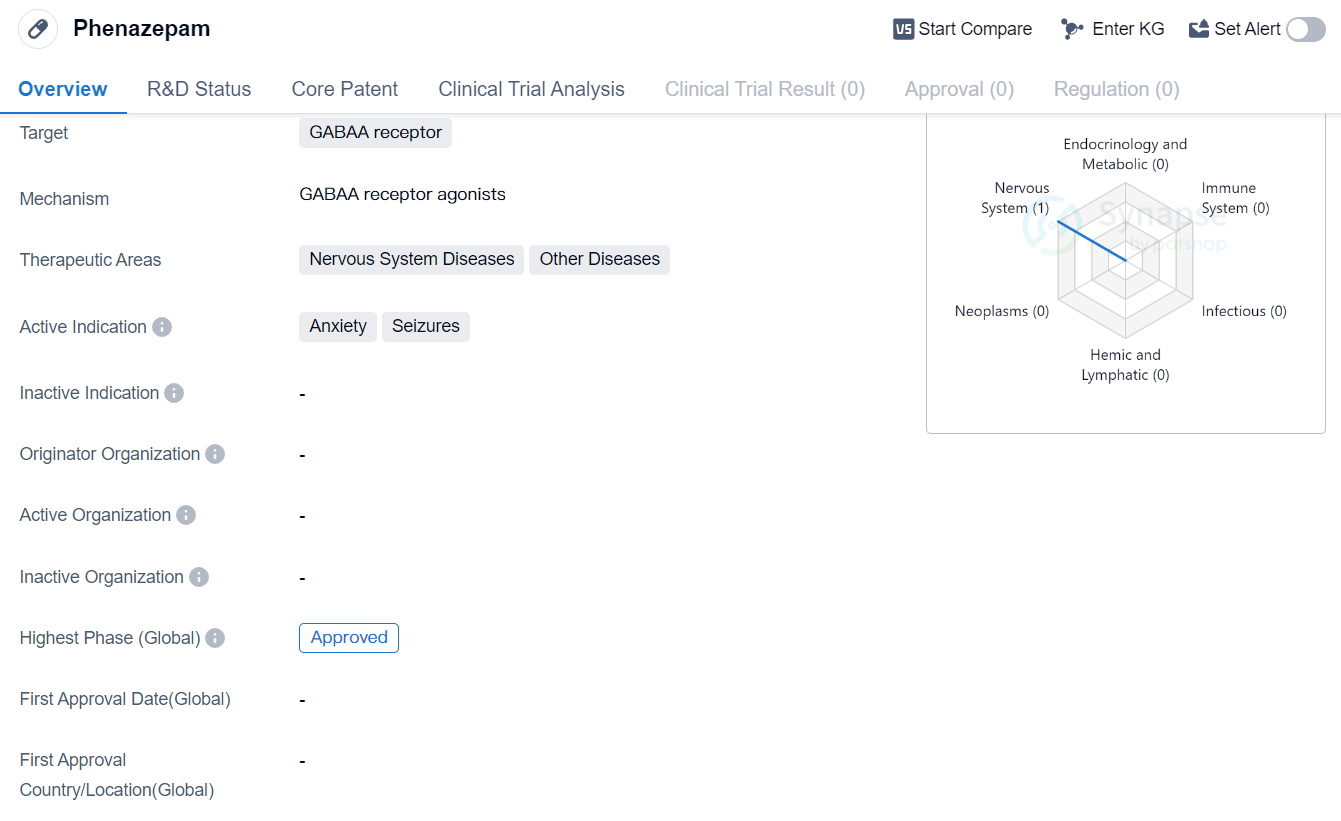
Phenazepam is a small molecule drug that targets the GABAA receptor. It is primarily used in the treatment of nervous system diseases and other diseases. The drug is specifically indicated for the management of anxiety and seizures.
Phenazepam belongs to the class of drugs known as benzodiazepines, which act on the GABAA receptor in the central nervous system. This receptor plays a crucial role in regulating neuronal excitability, and by targeting it, Phenazepam helps to reduce anxiety and prevent seizures.
The drug has been approved for use in various countries. As an approved drug, Phenazepam has met the necessary regulatory requirements and has been deemed suitable for use in the treatment of anxiety and seizures.
Anxiety disorders are among the most common mental health conditions, affecting millions of people worldwide. They are characterized by excessive worry, fear, and apprehension, which can significantly impact a person's daily life. Phenazepam, with its ability to modulate the GABAA receptor, helps to alleviate these symptoms and promote a sense of calmness and relaxation.
Seizures, on the other hand, are abnormal electrical activities in the brain that can lead to convulsions, loss of consciousness, and other neurological symptoms. By targeting the GABAA receptor, Phenazepam helps to inhibit excessive neuronal firing and prevent the occurrence of seizures.
The approval of Phenazepam in the highest phase globally signifies its potential as a therapeutic option for anxiety and seizures. It is important to note that while Phenazepam has shown efficacy in these indications, it should be used under the supervision of a healthcare professional due to its potential for abuse and dependence.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for Phenazepam: GABAA receptor agonist
GABAA receptor agonists are a type of drugs that bind to and activate the GABAA receptors in the brain. GABAA receptors are a type of neurotransmitter receptor that respond to the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). When GABAA receptors are activated, they inhibit the activity of neurons, leading to a decrease in neuronal excitability and a calming effect on the brain.
GABAA receptor agonists enhance the effects of GABA by binding to the receptor and mimicking the action of GABA. This results in an increase in the inhibitory signals in the brain, leading to sedative, anxiolytic (anti-anxiety), and anticonvulsant effects. These drugs are commonly used in the treatment of anxiety disorders, insomnia, epilepsy, and muscle spasms.
By activating GABAA receptors, GABAA receptor agonists help to restore the balance of neurotransmitters in the brain and alleviate symptoms associated with excessive neuronal activity. However, it's important to note that these drugs can have sedative effects and may cause drowsiness, impaired coordination, and other side effects. They should be used under medical supervision and prescribed at appropriate doses to minimize the risk of adverse effects.
Drug Target R&D Trends for Phenazepam
The analysis of the target GABAA receptor reveals a competitive landscape with multiple companies actively involved in research and development. Pfizer Inc., Sumitomo Chemical Co., Ltd., Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., Jiangsu Nhwa Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., and Mitsubishi Chemical Group Corp. are some of the companies with the highest stage of development on this target.
The approved drugs for indications such as Sleep Initiation and Maintenance Disorders, Anesthesia, Anxiety, Epilepsy, and Seizures provide treatment options for patients suffering from these conditions. Small molecule drugs are the primary focus of research and development for this target.
China has shown significant progress in the development of drugs targeting the GABAA receptor, indicating its potential as a key player in the future.
Overall, the target GABAA receptor presents opportunities for further research and development, with the potential for new treatments and advancements in the pharmaceutical industry.
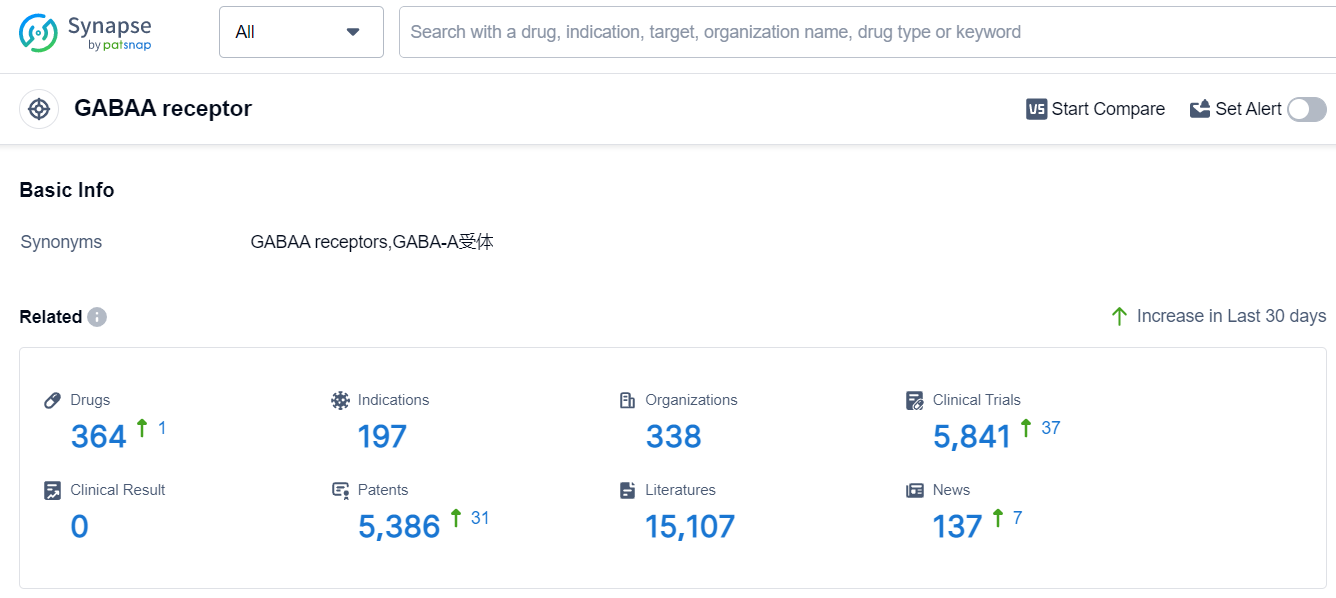
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 11 Sep 2023, there are a total of 364 GABAA receptor drugs worldwide, from 338 organizations, covering 197 indications, and conducting 5841 clinical trials.
Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
In summary, Phenazepam is a small molecule drug that targets the GABAA receptor and is approved for the treatment of anxiety and seizures. Its approval in the highest phase globally highlights its potential as a therapeutic option in the field of biomedicine. However, caution should be exercised in its use due to its potential for abuse and dependence.