Pharmaceutical Insights: Sintilimab's R&D Progress and its Mechanism of Action on Drug Target
Sintilimab's R&D Progress
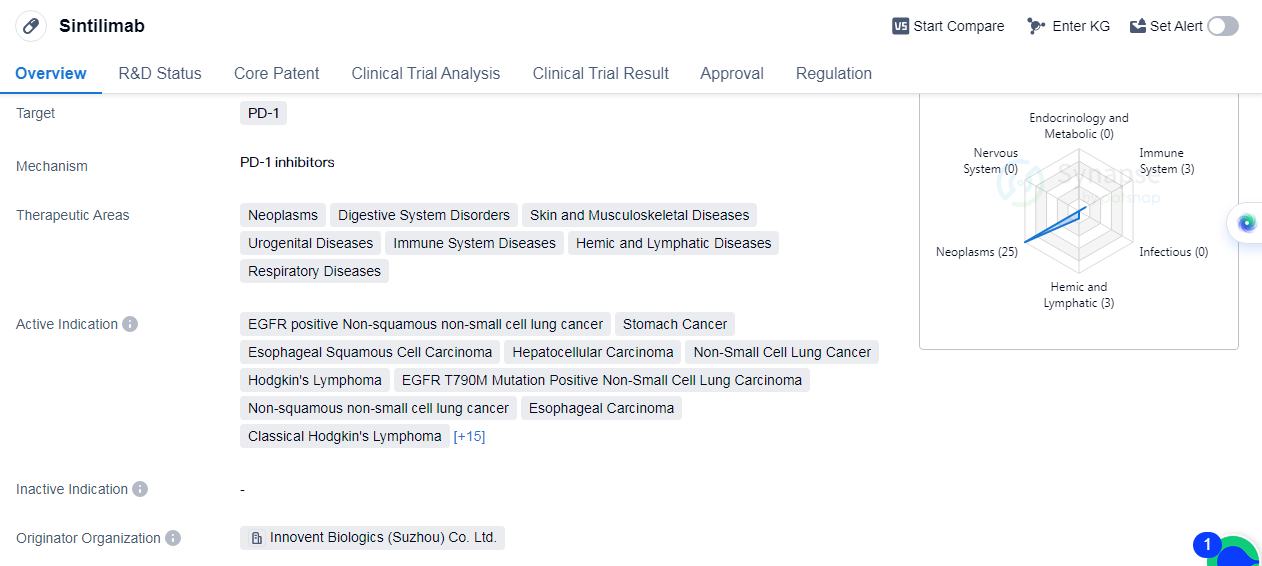
Sintilimab is a monoclonal antibody drug that targets PD-1, a protein involved in regulating the immune system. The drug has been developed by Innovent Biologics (Suzhou) Co. Ltd. and
received its first approval in China in December 2018. It has since been approved globally.
Sintilimab has shown potential in treating various therapeutic areas, including neoplasms, digestive system disorders, skin and musculoskeletal diseases, urogenital diseases, immune system diseases, hemic and lymphatic diseases, and respiratory diseases.
In terms of active indications, Sintilimab has demonstrated efficacy in treating several types of cancers, such as EGFR positive non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer, stomach cancer, esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, hepatocellular carcinoma, non-small cell lung cancer, and etc.
Sintilimab has undergone various regulatory processes, including priority review, breakthrough therapy designation, special review project, and orphan drug status. These designations highlight the potential of Sintilimab in addressing unmet medical needs and expediting its development and approval process.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for Sintilimab: PD-1 inhibitors
PD-1 inhibitors are a type of medication used in biomedicine to treat certain types of cancer. PD-1 stands for programmed cell death protein 1, which is a protein found on the surface of immune cells called T cells. PD-1 plays a role in regulating the immune response by inhibiting T cell activity.
In cancer, tumor cells can hijack the PD-1 pathway to evade the immune system and continue growing. PD-1 inhibitors work by blocking the interaction between PD-1 and its ligands, preventing the inhibition of T cell activity. This allows the immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells more effectively.
By blocking PD-1, these inhibitors help to unleash the immune system's ability to target and destroy cancer cells. They have shown significant success in treating various types of cancer, including melanoma, lung cancer, and bladder cancer. PD-1 inhibitors are often used as immunotherapy agents and can be administered through intravenous infusion.
It is important to note that PD-1 inhibitors can have side effects, as they can also affect the immune system's normal regulation. Common side effects include fatigue, rash, diarrhea, and inflammation of organs such as the lungs, liver, or colon. However, these side effects are typically manageable and reversible.
Overall, PD-1 inhibitors have revolutionized cancer treatment by harnessing the power of the immune system to fight against cancer cells. They have significantly improved outcomes for many cancer patients and continue to be an active area of research and development in biomedicine.
Drug Target R&D Trends for Sintilimab
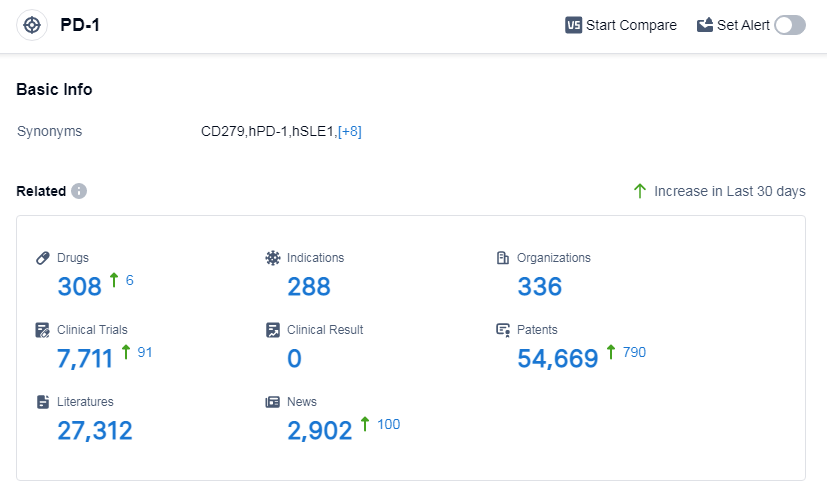
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 7 Sep 2023, there are a total of 308 PD-1 drugs worldwide, from 336 organizations, covering 288 indications, and conducting 7711 clinical trials.
The analysis of the target PD-1 reveals a highly competitive landscape in the pharmaceutical industry. Companies like Akeso, Inc., Bristol Myers Squibb Co., and Merck & Co., Inc. are leading the development of PD-1 inhibitors. The most common indications for approved drugs include Hodgkin's lymphoma, non-small cell lung cancer, melanoma, and esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Monoclonal antibodies and biosimilars are the most rapidly progressing drug types, indicating intense competition. China is emerging as a major player in PD-1 inhibitor development, with a significant number of drugs in various stages of development. Overall, the target PD-1 shows promising potential for future advancements in the treatment of various cancers.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
Overall, Sintilimab is a promising monoclonal antibody drug that targets PD-1 and has shown efficacy in treating a wide range of cancers and other diseases. The global approval and the regulatory designations it has received, demonstrate its potential as a valuable therapeutic option in the field of biomedicine.