Roche Clinical Trial Phase I of Oral Cyclic Peptide KRAS G12D Inhibitor
Recently, the TOP journal JACS has published a new article, which reviewed the development process of the KRAS clinical inhibitor Luna-18 from the hit optimization screened by Chugai, a subsidiary of Roche in Japan. Luna-18 is a cyclic peptide that targets intracellular proteins and still achieves a bioavailability of (21-47%) when taken orally without a special formulation. It is currently in Phase I of clinical trials, recruiting 195 patients and expected to complete the phase by March 31, 2025. The indications are locally advanced or metastatic solid tumors.
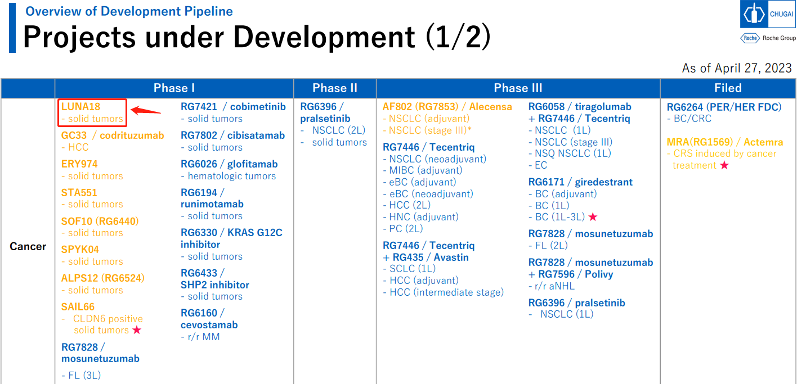
In April of this year, Roche updated part of its cancer clinical pipeline. The project marked with an arrow in the figure below is the LUNA18 project. It is clinically registered as a RAS inhibitor and conducted a Phase I clinical trial (NCT05012618) for solid tumors (combination treatment, single-drug treatment, metastatic disease, advanced disease, recurrent disease) (PO, capsule) in August 2021. The yellow parts are clinical projects underway globally, and the blue letters are projects authorized by Roche for development or sale in Japan, which includes the hotly debated KRAS G12C and SHP2 pipeline.
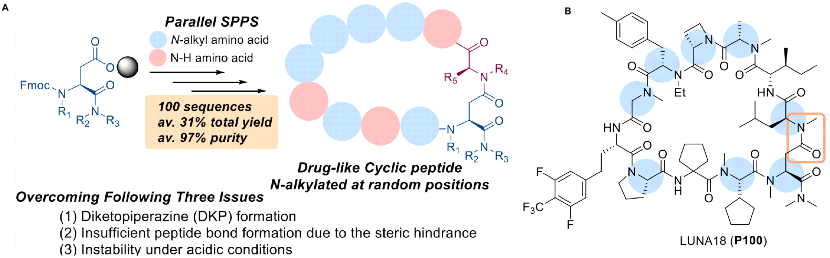
In fact, as early as August 2022, Chugai reported in the Journal of Medicinal Chemistry (JMC) a broadly applicable synthetic method for the synthesis of N-alkylated cyclic peptide-like drugs. The purpose of N-alkylation is to reduce the hydrogen bond donors, improve absorption, to meet the needs of oral drugs. This is a general parallel synthesis method to obtain highly and randomly N-alkylated cyclic peptide-like drugs, which fulfils the complex requirements to overcome three challenging issues: the formation of DKP (diketopiperazine), insufficient reactivity of amidation due to steric hindrance, and instability of cyclic peptides under acidic conditions. The JMC report proposed two different acid strength reaction conditions to maintain the stability of acid-unstable cyclic-peptide-like drugs; using this method, more than 4,000 cyclic peptides were synthesized, and the clinical cyclic peptide LUNA18 was finally discovered. The JMC at that time did not mention which hit was optimized based on, the focus was on the breakthrough of the synthesis method. The entire process reached a yield of 31% and a final product purity of 97%.
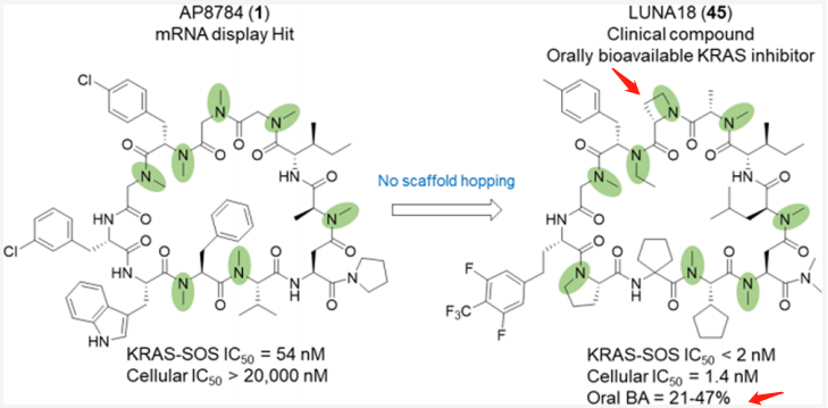
After screening, Chugai chemically optimized AP8747 from the mRNA display library without skeletal migration, focusing on increasing the plasma stability of the polypeptide, improving absorption, reducing clearance, and reducing hydrogen bond donors. Eventually, they discovered a clinical compound, LUNA18 (which reduces two hydrogen bond donors), which has oral bioavailability. This is an 11-mer cyclic peptide inhibitor targeting intracellular targets RAS.
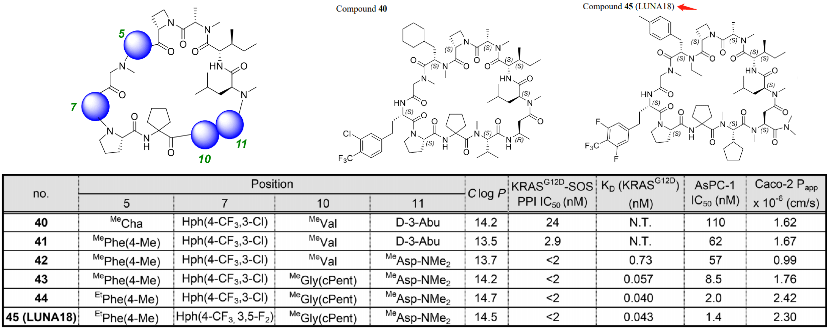
The key discoveries mainly include: 1. Two peptide side chains have been identified, each of which increases RAS affinity by more than 10 times; 2. Physical and chemical properties, including Clog P, can be adjusted by modifying side chains to increase membrane permeability; 3. Restricting the conformation of cyclic peptides can effectively adjust the physical and chemical properties of polypeptides, enhancing biological activity. 4. In the Caco-2 permeability test, permeability was observed to increase to 0.4×10−6 cm/s or more, and cell activity rose from over 20000nM of AP8784 to 1.4nM of LUNA18, an improvement of more than 14,000 times; 5. It was microscopically confirmed that while keeping the main chain conformation of the cyclic peptide unchanged, the structure of RAS protein can undergo significant changes by inducing matching the peptide side chains.
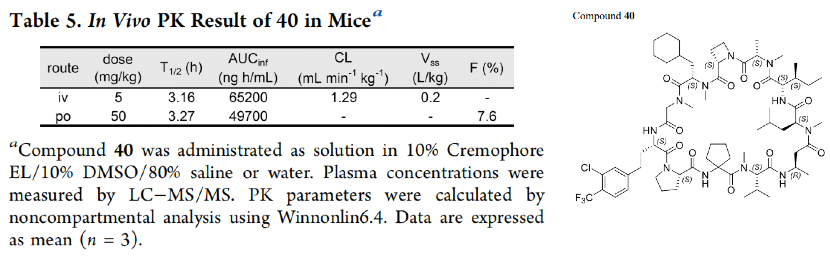
However, it is somewhat regrettable that the article did not provide the animal PK data for LUNA18, more data will be disclosed in subsequent articles (A platform to create oral drugs beyond rule of 5 for intracellular tough targets. J. Am. Chem. Soc., Submitted). This JACS only provided the mouse PK data for compound 40, with an exposure of 65200 ng h/ml under the administration of 5 mpk IV, a half-life of more than 3 hours, and a Vss of only 0.2 L/kg; however, after a tenfold increase in oral dosage, the mouse exposure still could not reach the IV effect, with a bioavailability of only 7.6%, which obviously did not meet the requirements for oral drugs. Although the oral bioavailability of Sermorelin is only 0.8%, this poses a huge challenge for the formulation. Compound 40 still needs further optimization for absorption and clearance.
Compounds 40 and LUNA18 only differ on four amino acids. The SAR has the following three characteristics: 1. The side chain at position 5 prefers aromatic to aliphatic; 2. PCP can be adjusted at position 11; 3. Adjusting the amino acids at positions 7 and 10 can enhance biological activity. Guided by this strategy, the cyclohexyl group at position 5 of compound 40 has been changed to p-tolyl; the chlorotrifluoromethylphenyl at position 7 was changed to difluorotrifluoromethylphenyl; the isopropyl at position 10 was changed to cyclopentyl; and, at position 11, the methyl was changed to N,N-dimethylcarbamoyl. The cell IC50 of compound 45 is 1.4 nM (AsPC-1), and the Caco-2 Papp is 2.3×10−6 cm/s. Compared with compound 40, the data in all aspects have improved overall.
In addition to AsPC-1, compound 45 displayed significant cellular activity (IC50=0.17-2.9nM) against cell lines with KRAS gene mutations, such as LS180 (colorectal cancer, KRAS G12D), GSU (gastric cancer, KRAS G12D), NCI-H441 (non-small cell lung cancer, KRAS G12V), NCI-H2122 (non-small cell lung cancer, KRAS G12C), and MiaPaCa-2 (pancreatic cancer, KRAS G12C).
In vivo efficacy of luna-18 was evaluated in NCI-H441 or MiaPaCa-2 xenograft-bearing mice. Compound luna18 was orally administered once daily for 14 days, and mouse body weight and tumor volume were measured. At a dose of 10 mg/kg, tumor regression was observed with no significant loss in body weight.
PK studies of luna18 were conducted in mice, rats, monkeys, and dogs. Following oral administration, the bioavailability of compound luna18 in these four animals ranged from 21-47%. These results suggested that this cyclic peptide, luna18, has therapeutic potential as an oral drug for the treatment of various cancers with KRAS gene mutations. Currently, 45 (LUNA18) is undergoing Phase 1 clinical trials in Japan/USA.
It's worth noting that the cyclic peptide molecule in this study has very potent inhibitory activity against cells with a KRAS G12D mutation. No data are currently available on in vivo efficacy. However, if potent in vivo efficacy is also achieved, it could undoubtedly strengthen the competition for oral KRAS G12D inhibitors, attracting many companies to follow this type of cyclic peptide inhibitor.
The KRAS G12D mutation affects approximately 180,000 patients in the United States and Europe, showing an incidence rate about 2.5 times higher compared to the KRAS G12C mutation. Currently, there are no targeted tumor treatments for these patients. In preclinical models of KRAS G12D mutated pancreatic cancer as well as lung and colorectal cancer, significant tumor responses were observed with MRTX1133. This drug has good pharmacological properties, including low off-target activity and low risk of drug interactions, with an expected half-life in humans of more than 50 hours.
Globally, MRTX1133 is the only oral G12D inhibitor which was approved by the FDA in January 2023 and is currently under investigation in Phase I/Ib clinical trials. MRTX1133 has been discovered for two years and frequently reported in literature. However, due to extremely low bioavailability when administered orally, it had not been able to apply for an Investigational New Drug (IND) application. Ultimately, it was made possible for oral administration through formulation strategies, but the Area Under the Concentration-time Curve (AUC) only improved about 10-fold, the bioavailability remains very low, leaving much room for optimization.
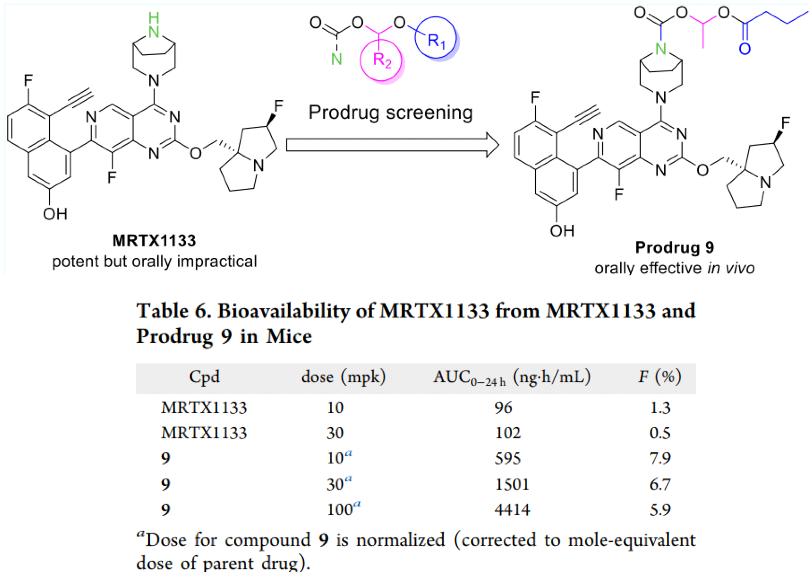
Moreover, RisenPharma reported a prodrug strategy to improve the oral bioavailability of MRTX1133 by formulating it into the form of an amino methanoate ester derivative. Compared with the parent compound, the prodrug 9 showed improved pharmacokinetic characteristics in mice (the F value increased from 0.5-1.3% to 6.7-7.9%), and it was effective in the oral KRASG12D mutant heterograft mouse tumor model.
Although the prodrug strategy can improve the physicochemical properties and PK properties of the compound, and increase the reliability and effectiveness of drug development, the research process of prodrugs involves many unknown risks different from "standard" drug research processes, such as synthesis, efficacy, pharmacokinetics, and toxicology. Therefore, it is essential to carefully select the appropriate strategy.
In Conclusion, the development of inhibitors of KRAS G12D faces significant technical hurdles, not only breaking through the obstacles of G12D difficult to be medicated but also solving the challenges of poor oral PK. Faced with this urgent unmet clinical need, for the major pharmaceutical companies, the development of oral KRAS G12D inhibitors is both a significant challenge and a rare opportunity.
Reference
1.Mikimasa Tanada et.al; Development of Orally Bioavailable Peptides Targeting an ntracellular Protein: From a Hit to a Clinical KRAS Inhibitor. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.3c03886.
2.Kenichi Nomura et al;Broadly Applicable and Comprehensive Synthetic Method for N-Alkyl-Rich Drug-like Cyclic Peptides.J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 13401−13412.
3.Xiang Ji et al; Discovery of Prodrug of MRTX1133 as an Oral Therapy for Cancers with KRASG12D Mutation,ACS Omega 2023, 8, 7211−7221.
4.www.mirati.com




