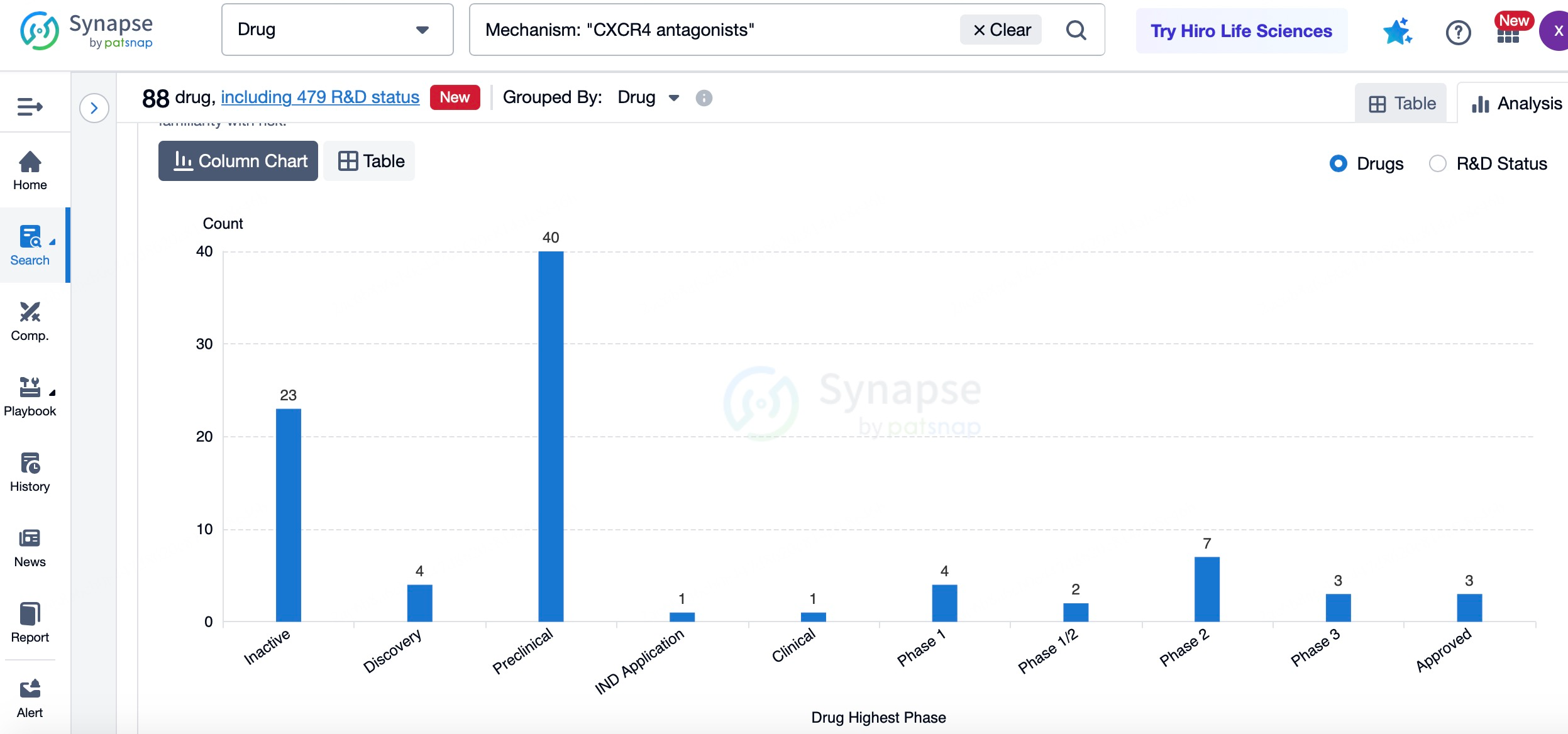
The Emerging Role and Market Potential of CXCR4 Antagonists in Modern Medicine
Currently, only three CXCR4 (C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 4) antagonists have been approved globally: Plerixafor, Motixafortide, and Mavorixafor, indicating significant market potential. With a deeper understanding of the role of CXCR4 in tumor progression, the demand for CXCR4 antagonists continues to grow. In 2024, the global CXCR4 antagonist market is valued at several billion RMB, with steady growth projected in the coming years.
Key players in the global market include Sanofi, BioLineRx, X4 Pharmaceuticals, Eli Lilly, and Roche. The increasing global aging population and the rising incidence of chronic diseases such as cancer create a vast market opportunity for anti-tumor drugs like CXCR4 antagonists. Advances in drug development further inject vitality into the CXCR4 antagonist market.
Mechanism of Action of CXCR4 Antagonists
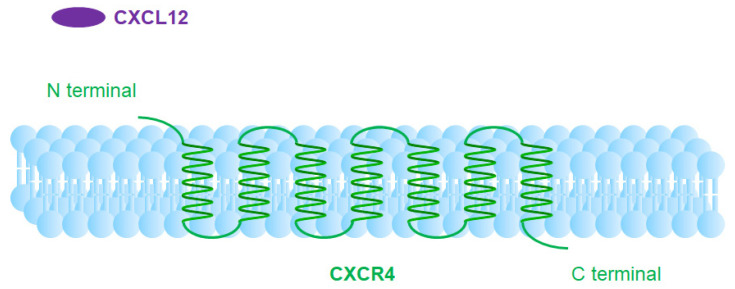
CXCR4 is a seven-transmembrane G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) widely expressed across various cell types, particularly immune cells, hematopoietic stem cells, endothelial cells, and numerous tumor cells. Its primary ligand is the chemokine CXCL12 (also known as SDF-1, stromal cell-derived factor 1). Binding of CXCL12 to CXCR4 induces conformational changes in CXCR4, activating the G-protein complex. The G-protein complex dissociates into Gα and Gβγ subunits, with Gβγ activating the PI3K and RAS-MAPK pathways.
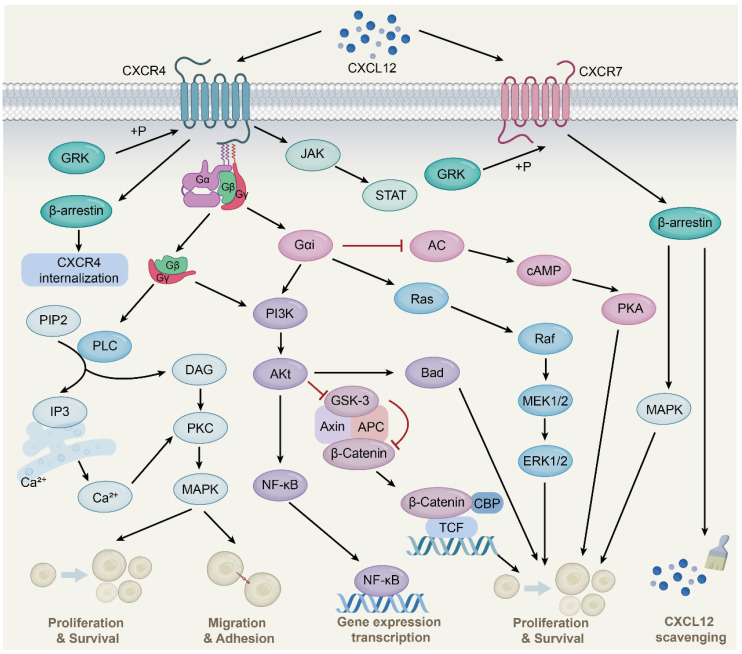
Subsequently, the Gβγ subunit activates guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs), such as SOS. These GEFs facilitate the exchange of GDP for GTP on RAS proteins, activating them. Activated RAS proteins, in turn, stimulate the MAPK (mitogen-activated protein kinase) and MEK1/2 (mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1/2) pathways. Activated MEK1/2 phosphorylates and activates ERK1/2 (extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1/2). ERK1/2 activation promotes cell proliferation and survival. Additionally, ERK1/2 can activate transcription factors such as c-Fos and c-Jun, further regulating gene expression. Once activated, ERK1/2 enters the nucleus and phosphorylates various transcription factors, including c-Fos and c-Jun, which bind to specific DNA sequences to regulate gene expression, ultimately affecting cell proliferation, differentiation, and survival.
When CXCR4 interacts with CXCL12, it activates signaling pathways including RAS-MAPK, PI3K-AKT-mTOR, JAK-STAT, and PLC. These pathways play crucial roles in cell migration, proliferation, and survival. Under normal physiological conditions, CXCR4 is critical for regulating cell migration and localization during development, homeostasis, and inflammation, aiding immune system activation and facilitating cell movement. High CXCR4 expression is associated with poor prognosis and chemotherapy resistance in various cancer subtypes, partly due to enhanced interactions between cancer cells and the stroma. The CXCR4/CXCL12 signaling axis plays a central role in tumor progression through autocrine and paracrine mechanisms. Similar to other GPCRs, CXCR4 undergoes homo- or heterodimerization in its functional signaling regions on the cell surface. Receptor aggregation in dimers or oligomers significantly enhances the sensitivity and intensity of chemokine responses.
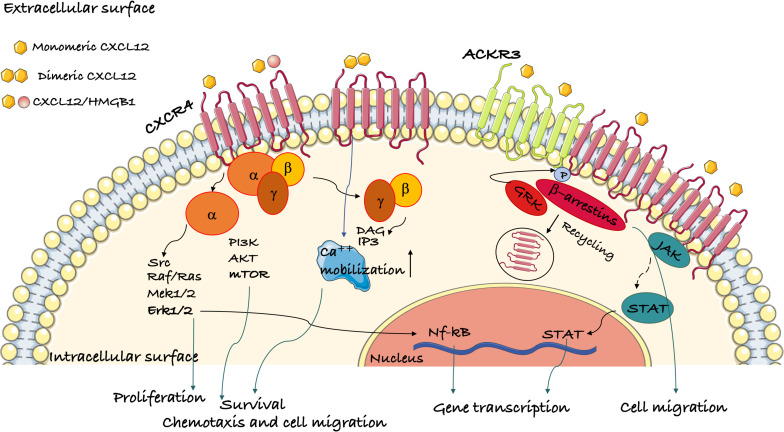
CXCR4 antagonists block the binding of CXCL12 to CXCR4, inhibiting tumor cell migration and invasion, reducing HIV infection and transmission, regulating immune cell migration, and promoting hematopoietic stem cell mobilization, showcasing significant applications across multiple fields. In oncology, CXCR4 antagonists like Motixafortide, combined with Keytruda and chemotherapy, have significantly improved objective response rates (ORR) and progression-free survival (PFS) in patients with advanced pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and demonstrated antitumor effects in breast and lung cancers. For HIV treatment, CXCR4 antagonists like Plerixafor and AMD3100 reduce viral infection and spread by blocking HIV-CXCR4 interactions while enhancing the host immune response. In autoimmune diseases, CXCR4 antagonists mitigate inflammatory responses by reducing immune cell migration, alleviating symptoms in conditions like systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA). In hematopoietic stem cell mobilization, CXCR4 antagonists such as Plerixafor and Motixafortide facilitate the release of hematopoietic stem cells from bone marrow into peripheral blood for autologous transplantation in diseases like non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) and multiple myeloma (MM).
Market Drivers for CXCR4 Antagonist Development
With advancements in precision medicine, targeted therapeutics are increasingly prioritized. As a critical target in various diseases, CXCR4 antagonist development aligns with the precision medicine trend. CXCR4 antagonists hold significant value in treating hematological disorders such as multiple myeloma. Furthermore, these antagonists are being explored for new indications like breast cancer, WHIM syndrome, and Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia, all of which represent substantial patient populations and offer vast market potential. The combination of CXCR4 antagonists with other therapies, such as chemotherapeutics and immune checkpoint inhibitors, markedly enhances therapeutic efficacy and addresses clinical needs. Additionally, governmental and regional policy and financial support for innovative drug development have attracted extensive attention to and support for CXCR4 antagonists as promising innovative drugs.
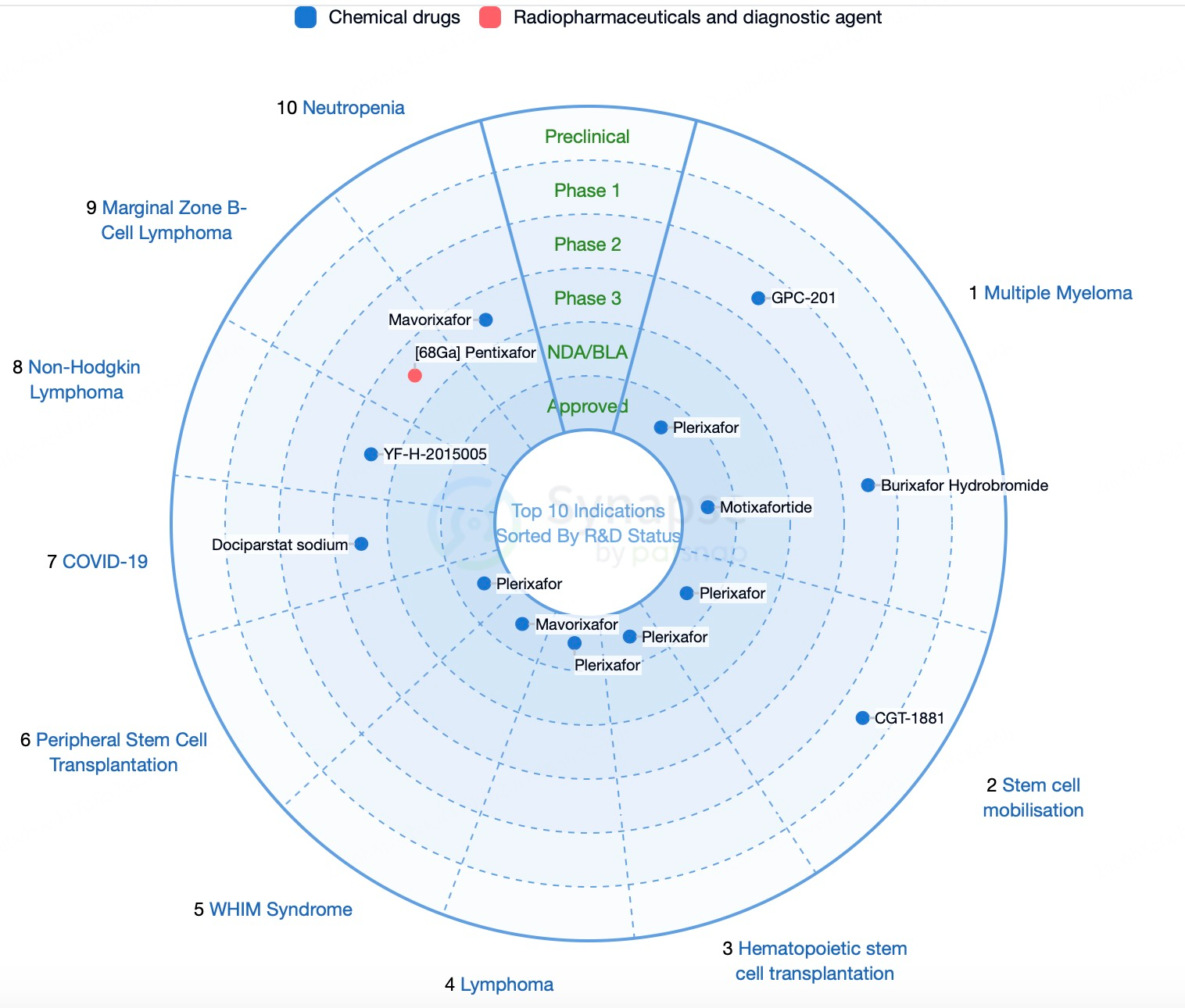
Technological advancements and innovation have significantly driven the development of CXCR4 antagonists. Novel small-molecule antagonists such as Plerixafor and Mavorixafor, as well as peptide-based antagonists like Motixafortide, have demonstrated high affinity and favorable pharmacological efficacy. The application of antibody-based therapies and nanotechnology has further enhanced drug specificity and effectiveness. Multiple clinical trials have highlighted the substantial efficacy and safety of CXCR4 antagonists across various diseases. Some of these drugs have received FDA designations as Breakthrough Therapies or Fast Track therapies, expediting their development and approval.
Regional Development Analysis of CXCR4 Antagonists
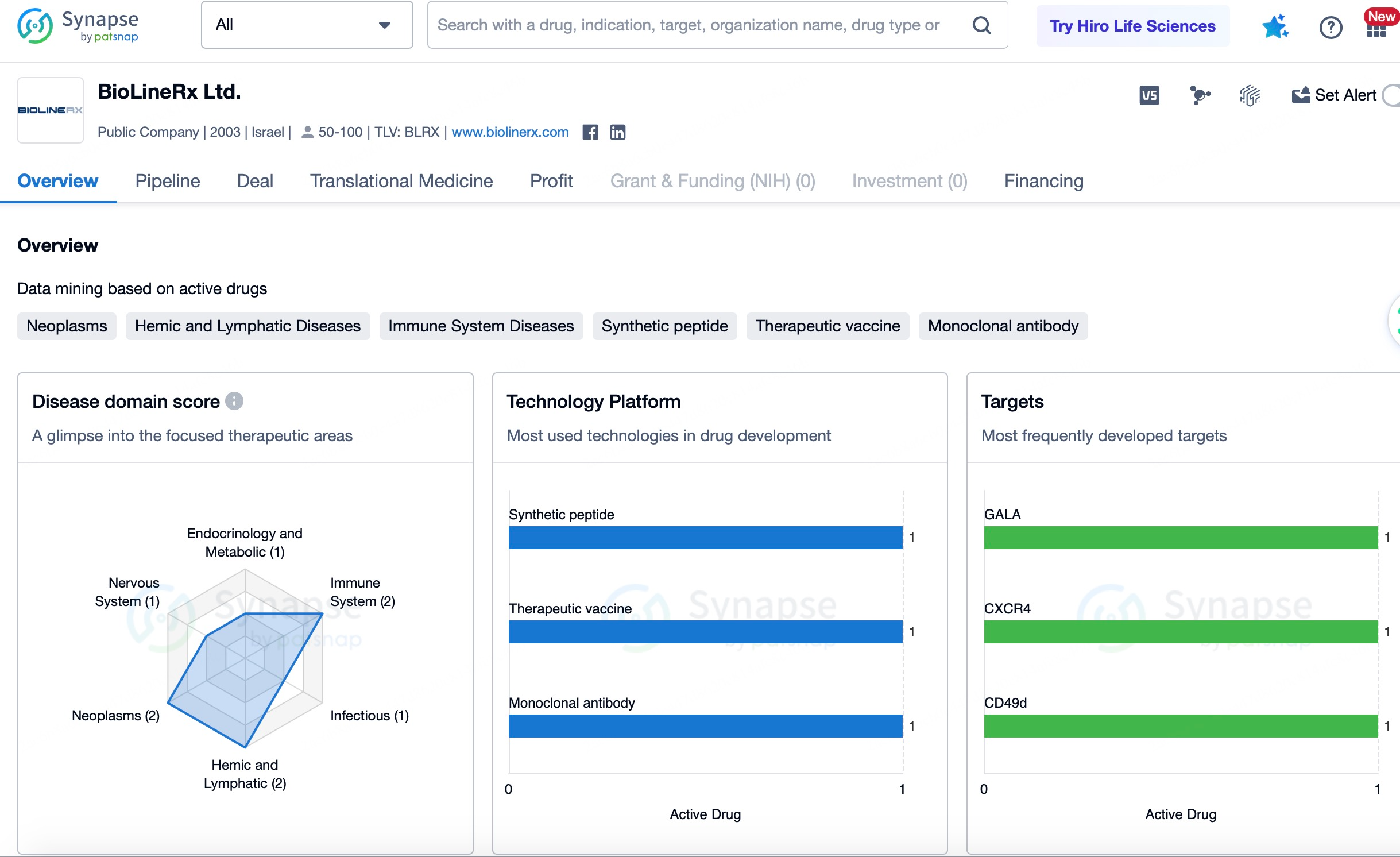
North America leads in the development and market adoption of CXCR4 antagonists due to its advanced medical technology and robust regulatory framework. Significant investments from both the U.S. government and private sector have spurred research by major pharmaceutical companies and biotech startups. With a substantial patient population suffering from cancers, HIV infections, immune disorders, and requiring hematopoietic stem cell transplants, demand for CXCR4 antagonists remains strong. Key drugs, including Plerixafor and Mavorixafor, have achieved notable progress in this region.
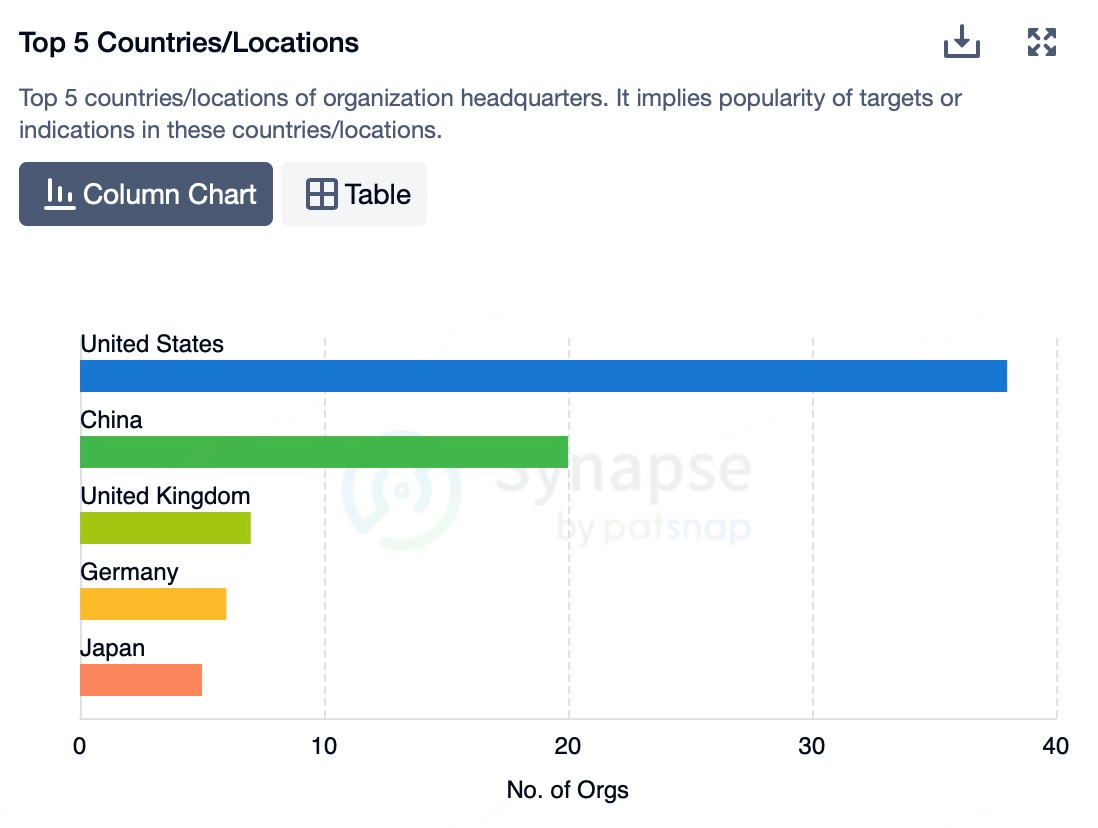
In Europe, biopharmaceutical R&D is highly active, with many institutions and companies advancing work on CXCR4 antagonists. While the European Medicines Agency (EMA) maintains stringent drug approval processes, it is continuously optimizing these procedures to accelerate the market entry of innovative medicines. Europe's comprehensive healthcare systems and high patient receptivity to novel therapies drive demand for CXCR4 antagonists in oncology, HIV, immune disorders, and stem cell transplantation. Prominent drugs such as Motixafortide and Balixafortide are undergoing extensive clinical trials in the region.
In Asia, particularly in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea, the biopharmaceutical market is expanding rapidly, with increasing demand for innovative drugs. Rich clinical trial resources and a large patient base create favorable conditions for CXCR4 antagonist research. The region exhibits significant potential due to its high prevalence of cancers, HIV infections, immune disorders, and stem cell transplant requirements. Representative drugs, such as Balixafortide, introduced by Fosun Pharma, are undergoing clinical trials for breast cancer. Numerous Asian pharmaceutical companies and research institutions are actively developing various CXCR4 antagonists.
Market Competition Landscape for CXCR4 Antagonists
Plerixafor was the first FDA-approved CXCR4 antagonist, primarily used in autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Sanofi holds a first-mover advantage in the CXCR4 antagonist market, with a significant market share. The successful application of Plerixafor in stem cell transplantation has provided Sanofi with valuable data and experience, enabling further exploration of additional indications. For instance, Sanofi is investigating the potential of Plerixafor in oncology, particularly in enhancing immune cell infiltration within the tumor microenvironment and improving the efficacy of immunotherapies. Moreover, Sanofi is exploring Plerixafor's application in HIV treatment, aiming to reduce viral infection and transmission by blocking the interaction between HIV and CXCR4.
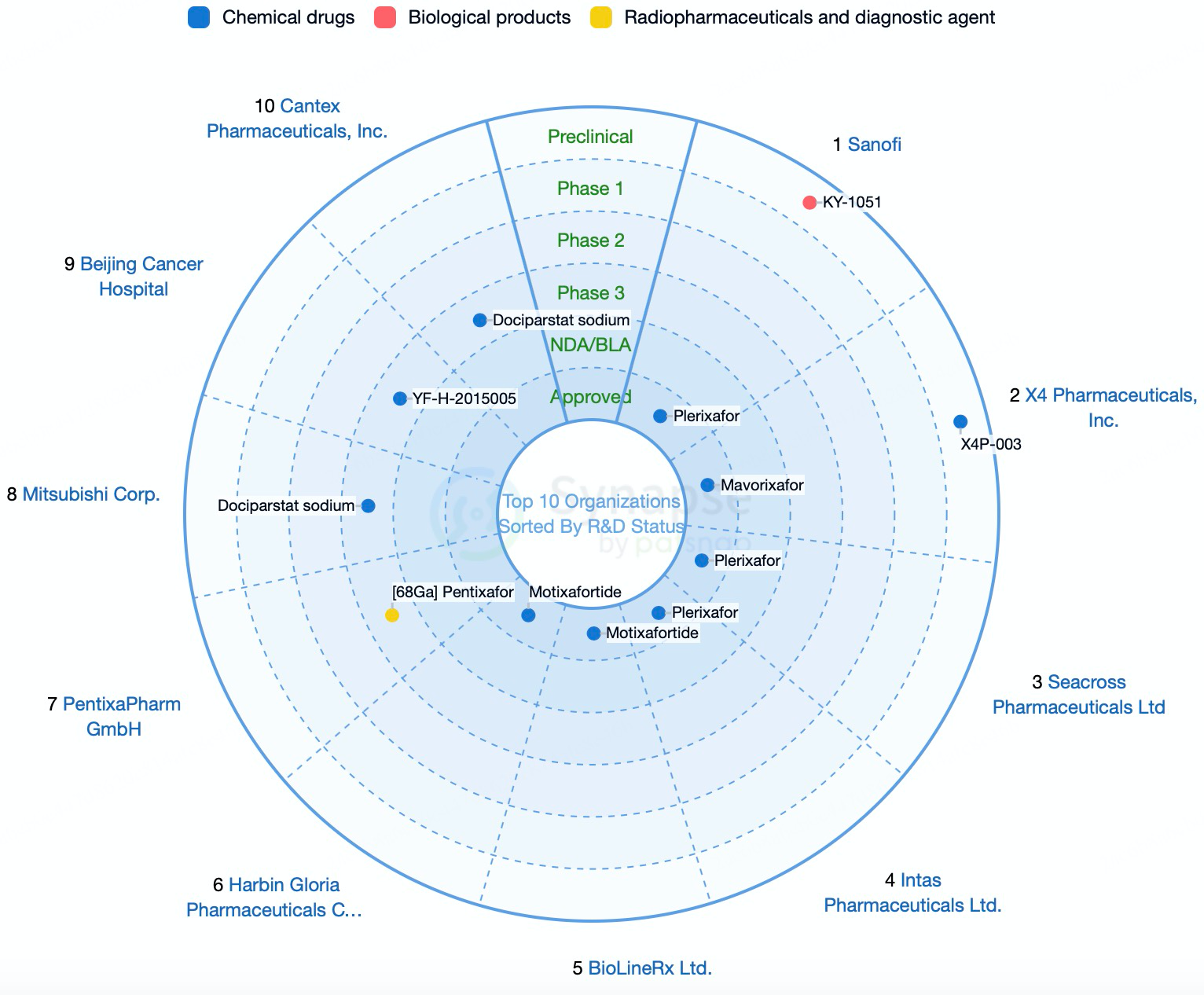
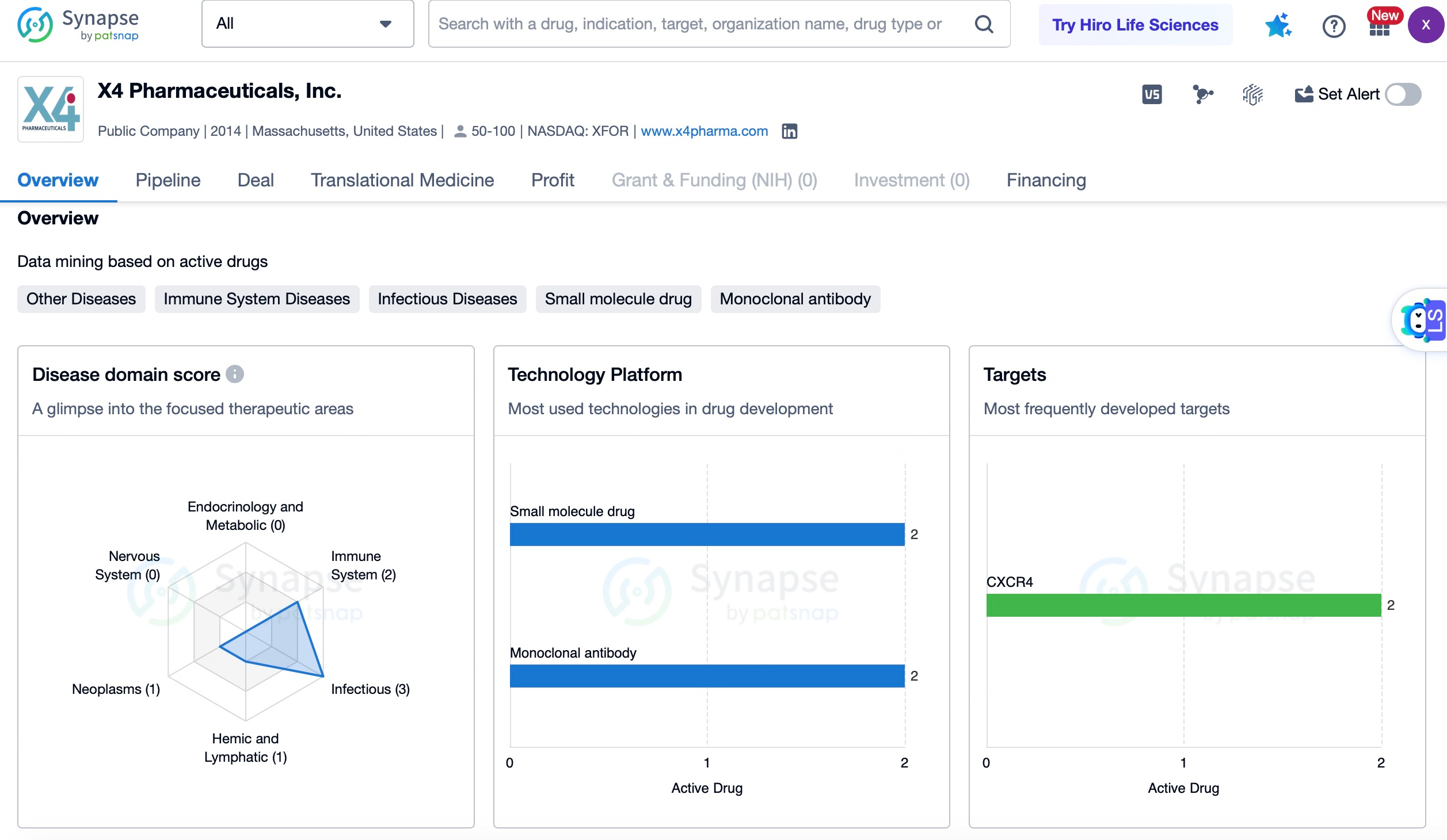
The CXCR4 antagonist Mavorixafor, the flagship product of X4 Pharmaceuticals, has received FDA priority review designation for the treatment of WHIM syndrome. WHIM syndrome is a rare primary immunodeficiency characterized by recurrent infections, hypogammaglobulinemia, and bone marrow abnormalities. The approval of Mavorixafor represents the first targeted therapy for WHIM syndrome, addressing an unmet medical need. In Phase 3 clinical trials for WHIM syndrome, Mavorixafor demonstrated positive outcomes, including favorable safety and efficacy profiles. These clinical results not only supported its regulatory submission but also bolstered X4 Pharmaceuticals’ market presence and investor confidence. Additionally, X4 Pharmaceuticals is actively exploring the use of Mavorixafor in other conditions, such as HIV infection and certain forms of chronic neutropenia.
BioLineRx's Motixafortide has shown remarkable efficacy in the treatment of pancreatic cancer and other malignancies. In collaboration with major pharmaceutical companies such as Merck and Roche, BioLineRx is advancing the development and commercialization of Motixafortide. Clinical trial data indicate that the combination of Motixafortide with Keytruda and chemotherapy significantly improves objective response rates (ORR) and progression-free survival (PFS) in patients. Motixafortide has also demonstrated promising results in autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (ASCT). When combined with granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF), Motixafortide substantially enhances the efficiency and quality of CD34+ stem cell collection. In the GENESIS global Phase 3 trial, the combination achieved significantly higher success rates compared to the placebo group, with 88.8% of patients achieving an optimal CD34+ cell dose in a single apheresis session and 92.5% in up to two sessions.
Beyond pancreatic cancer and ASCT, BioLineRx is investigating Motixafortide in other oncology applications, including breast cancer, gastric cancer, and prostate cancer. Preliminary findings suggest that Motixafortide enhances antitumor immune responses by blocking CXCR4 receptors, reducing immunosuppressive cells in the tumor microenvironment, and increasing the infiltration of effector T cells and other antitumor immune cells. BioLineRx is also exploring combination therapies involving Motixafortide and other immunotherapies, such as PD-1 inhibitors and chemotherapeutic agents, which have demonstrated synergistic effects in early studies.
BioLineRx has established strategic partnerships with major pharmaceutical companies such as Merck and Roche to jointly develop and promote Motixafortide. These collaborations have accelerated the clinical research and market entry of Motixafortide, enhancing its global market presence. For example, BioLineRx partnered with Merck to conduct clinical trials of Motixafortide in combination with Keytruda for the treatment of pancreatic cancer. Additionally, BioLineRx collaborated with China-based Genfleet Therapeutics to develop Motixafortide for the Chinese market. Genfleet is independently responsible for designing and developing first-line combination therapies targeting advanced pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma in mainland China. This partnership expedites Motixafortide's entry into the Chinese market, addressing the treatment needs of local patients.
Fosun Pharma, through its collaboration with Polyphor, introduced Balixafortide for the treatment of breast cancer and other potential cancers. Balixafortide has demonstrated notable efficacy in breast cancer treatment. Clinical trial data from Fosun Pharma showed that Balixafortide, combined with eribulin mesylate injection, exhibited good efficacy and safety in HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer patients. In a global Phase 3 clinical trial, this combination achieved an objective response rate (ORR) of 40%, a median progression-free survival (mPFS) of 8.5 months, and a disease control rate (DCR) of 75%. Fosun Pharma is also exploring the application of Balixafortide in other cancers, such as pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). According to an announcement by Spexis AG, Balixafortide demonstrated good safety and efficacy in PDAC patients, inhibiting tumor growth and metastasis. Additionally, Fosun Pharma is investigating combination therapies involving Balixafortide and other chemotherapeutic agents. For instance, the combination of Balixafortide with eribulin not only enhanced therapeutic efficacy but also reduced side effects, improving patients' quality of life. This combined therapy strategy offers new approaches to cancer treatment.
Conclusion
CXCR4 antagonists demonstrate immense potential across various medical fields, particularly in oncology, HIV infection, immune disorders, and hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Advances in technology and supportive policies have provided robust backing for the development of CXCR4 antagonists, which hold promising market prospects. As more clinical trials are conducted and new drugs are approved, CXCR4 antagonists are poised to become vital tools for treating diverse diseases, offering hope and new options for patients.
How to obtain the latest research advancements in the field of biopharmaceuticals?
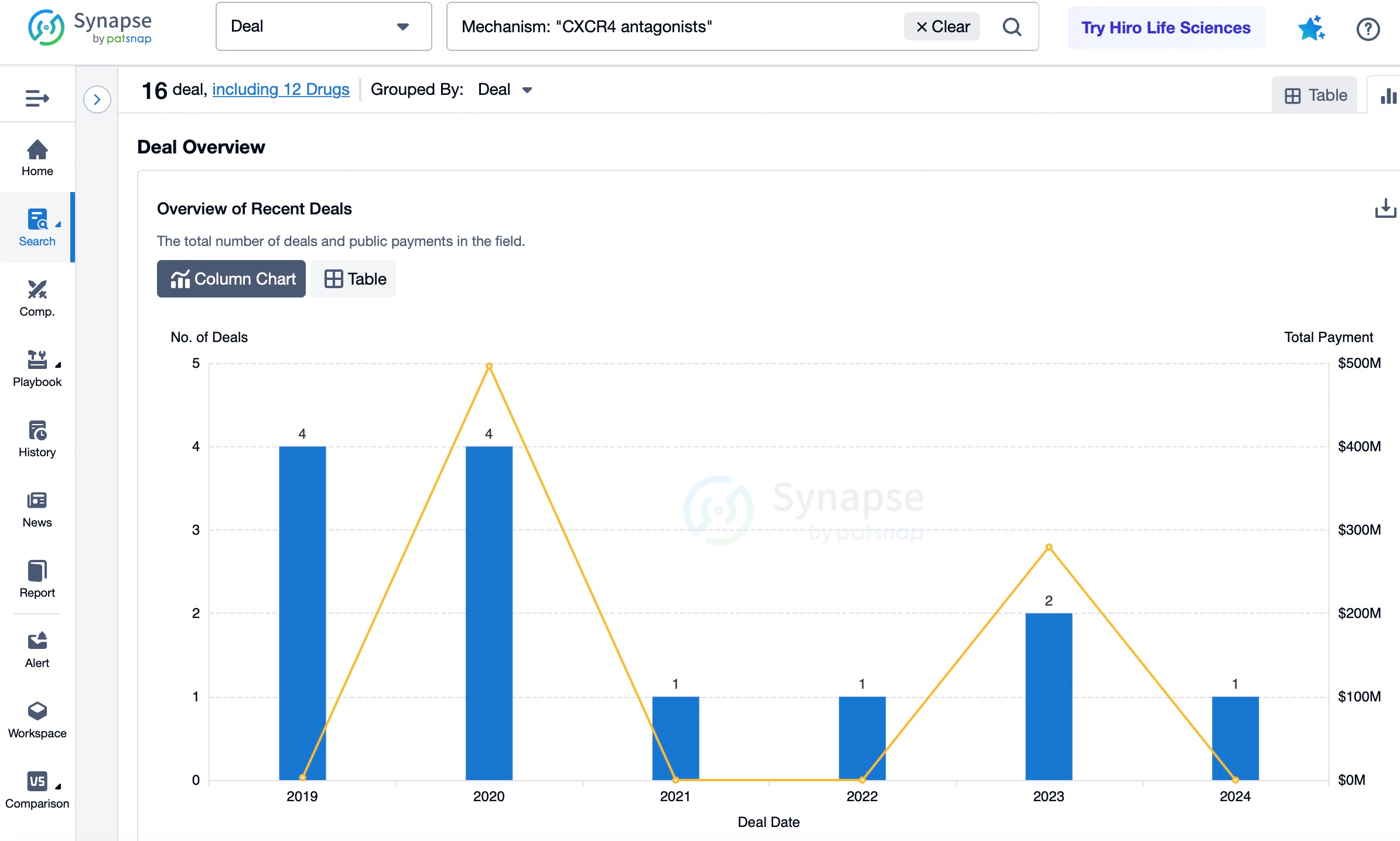
In the Synapse database, you can keep abreast of the latest research and development advances in drugs, targets, indications, organizations, etc., anywhere and anytime, on a daily or weekly basis. Click on the image below to embark on a brand new journey of drug discovery!
Refrence
- 1.Yu, J., X. Zhou, and L. Shen, CXCR4-Targeted Radiopharmaceuticals for the Imaging and Therapy of Malignant Tumors. Molecules, 2023. 28(12).
- 2.Yang, Y., et al., CXCL12-CXCR4/CXCR7 Axis in Cancer: from Mechanisms to Clinical Applications. Int J Biol Sci, 2023. 19(11): p. 3341-3359.
- 3.Bianchi, M.E. and R. Mezzapelle, The Chemokine Receptor CXCR4 in Cell Proliferation and Tissue Regeneration. Front Immunol, 2020. 11: p. 2109.