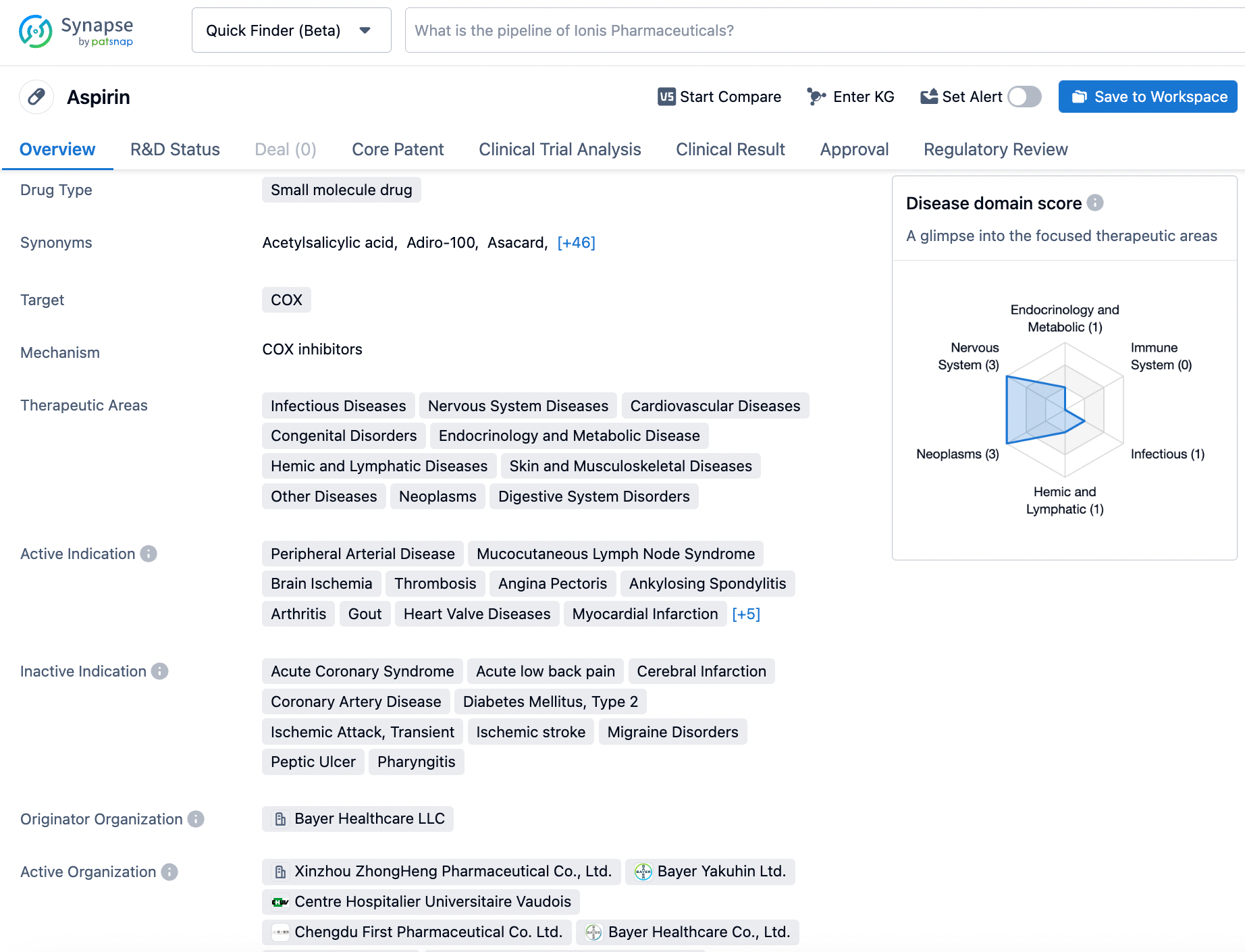
The Synapse User's Toolkit: Tips for Searching Aspirin
Aspirin, also known as acetylsalicylic acid (ASA), is a widely used nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that helps reduce pain, fever, and inflammation while also acting as an antithrombotic. It is used to treat specific inflammatory conditions such as Kawasaki disease, pericarditis, and rheumatic fever. Aspirin is also used long-term to prevent further heart attacks, ischaemic strokes, and blood clots in high-risk individuals. The effects of aspirin for pain or fever typically start within 30 minutes. Aspirin works similarly to other NSAIDs but also suppresses the normal functioning of platelets. Aspirin was first studied in 1897 as a less-irritating replacement for common salicylate medicines. By 1899, Bayer had named it "Aspirin" and sold it worldwide. Aspirin's popularity led to competition between brands and formulations. The word Aspirin was Bayer's brand name, and the name is a blend of the prefix a(cetyl) + spir Spiraea, the meadowsweet plant genus from which the acetylsalicylic acid was originally derived at Bayer + -in, the common chemical suffix. Click on the image below to begin the exploration journey of Aspirin through the Synapse database!
You can search for the latest pharmaceutical information such as drugs, targets, patents, transactions, clinical results, etc. through the Synapse database. Come and experience it!