What Does Semaglutide Do?
Semaglutide, a cutting-edge medication, has been making significant strides in the treatment of type 2 diabetes, weight loss, and reducing cardiovascular risk. Marketed under the brand names Ozempic, Wegovy, and Rybelsus, this drug targets the glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptors in the body, mimicking the action of a natural hormone that regulates blood sugar levels. Developed by the renowned pharmaceutical company Novo Nordisk, semaglutide is an incretin mimetic, a class of drugs that has revolutionized diabetes management. Ozempic and Wegovy are administered as subcutaneous injections once a week, while Rybelsus is an oral tablet taken once daily. Each formulation serves a slightly different purpose, with Ozempic focusing on blood sugar control, Wegovy on weight loss, and Rybelsus on both blood sugar control and cardiovascular risk reduction.
Semaglutide Mechanism of Action
Semaglutide's primary mechanism of action involves stimulating the pancreas to release more insulin when blood sugar levels are high. It also reduces the amount of glucagon, a hormone that increases blood sugar, and slows down gastric emptying, which can enhance satiety and reduce appetite. By targeting the GLP-1 receptors, semaglutide helps to regulate appetite and food intake, contributing to weight loss in patients with obesity. This multifaceted approach makes semaglutide a versatile treatment option for a range of metabolic conditions.
How to Use Semaglutide
The administration of semaglutide varies by brand. Ozempic and Wegovy injections are self-administered subcutaneously once a week, typically in the abdomen, thigh, or upper arm, and can be taken at any time of day, regardless of meals. Rybelsus tablets are taken once daily, at least 30 minutes before the first food, beverage, or other oral medications, with no more than 4 ounces of plain water. It is crucial to follow the prescribed dosage and schedule provided by a healthcare professional. If a dose is missed, the instructions vary by brand, so it's essential to consult the specific guidelines for each type of semaglutide.
Semaglutide Side Effects
While semaglutide has proven effective, it also comes with a range of potential side effects. Common side effects may include low blood sugar (in people with type 2 diabetes), upset stomach, heartburn, burping, gas, bloating, nausea, vomiting, stomach pain, loss of appetite, diarrhea, constipation, headache, dizziness, and tiredness. More serious side effects can occur, such as signs of an allergic reaction, vision changes, mood changes, rapid heartbeats, and symptoms of pancreatitis or thyroid tumor. Patients are advised to seek medical help immediately if they experience any serious side effects.
Interactions with Other Drugs
Semaglutide can interact with other medications, particularly those that affect blood sugar levels or are absorbed through the gastrointestinal tract. Insulin and other diabetes medications may increase the risk of low blood sugar when used with semaglutide. Additionally, because semaglutide slows digestion, it may affect the absorption of oral medications. It is vital to inform healthcare providers of all current medications, including prescription drugs, over-the-counter products, vitamins, and herbal supplements, to ensure safe and effective treatment.
In conclusion, semaglutide is a powerful therapeutic option for patients with type 2 diabetes, obesity, and those at risk of cardiovascular events. By understanding its mechanism of action, usage guidelines, potential side effects, and possible drug interactions, patients can make informed decisions about their treatment. As with any medication, the decision to use semaglutide should be made in consultation with a healthcare professional who can provide personalized advice based on individual health conditions and needs.
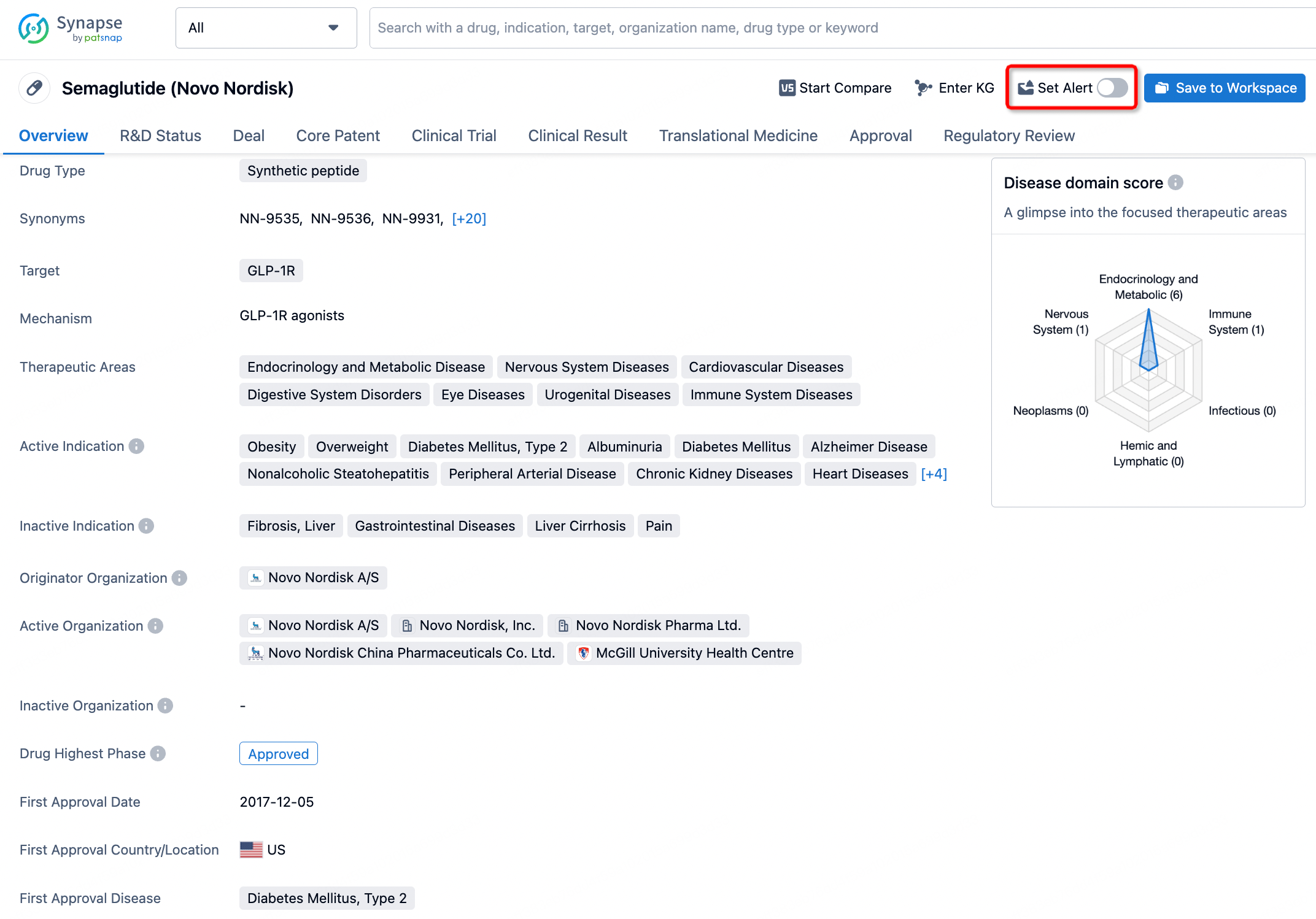
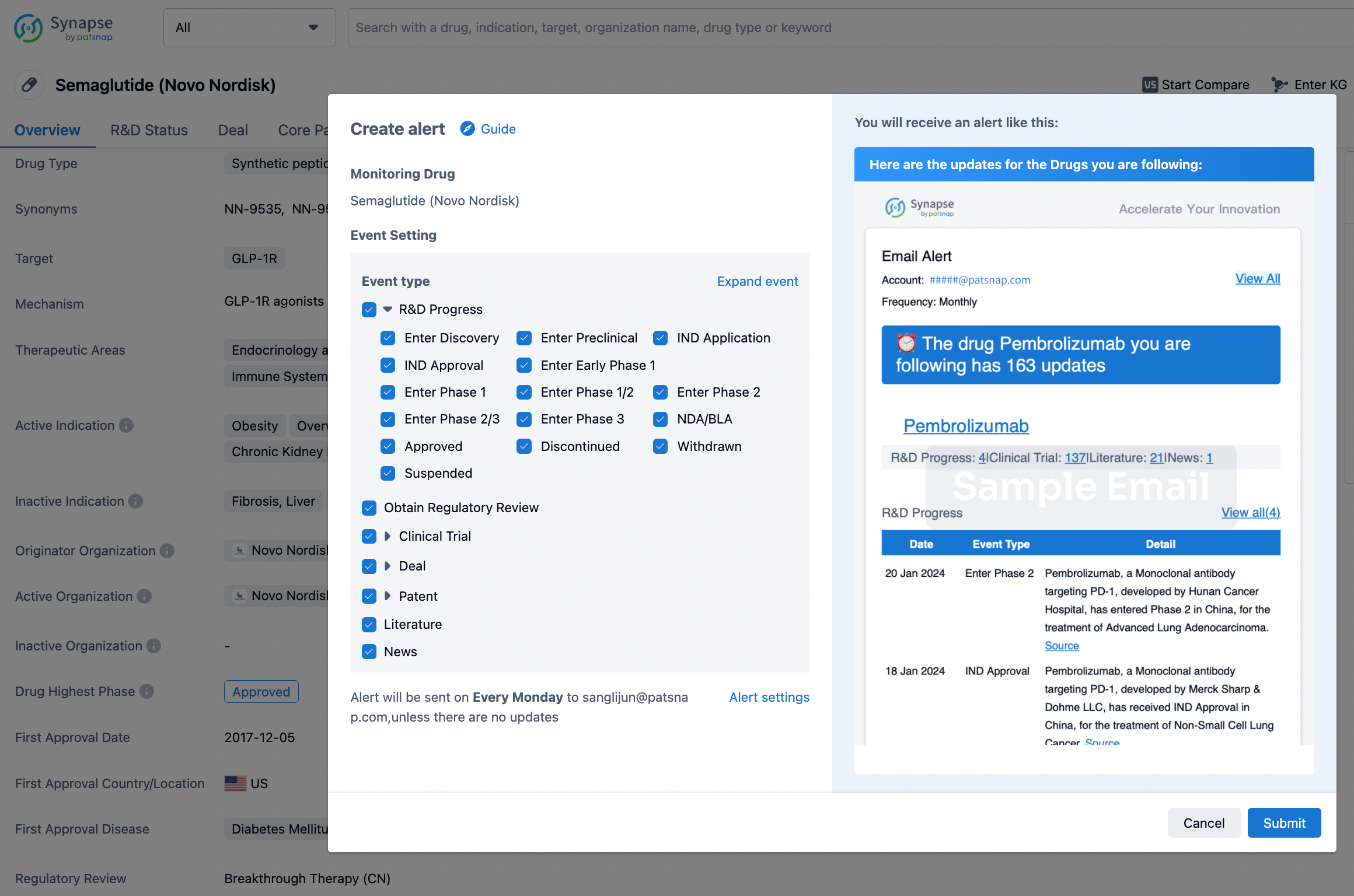
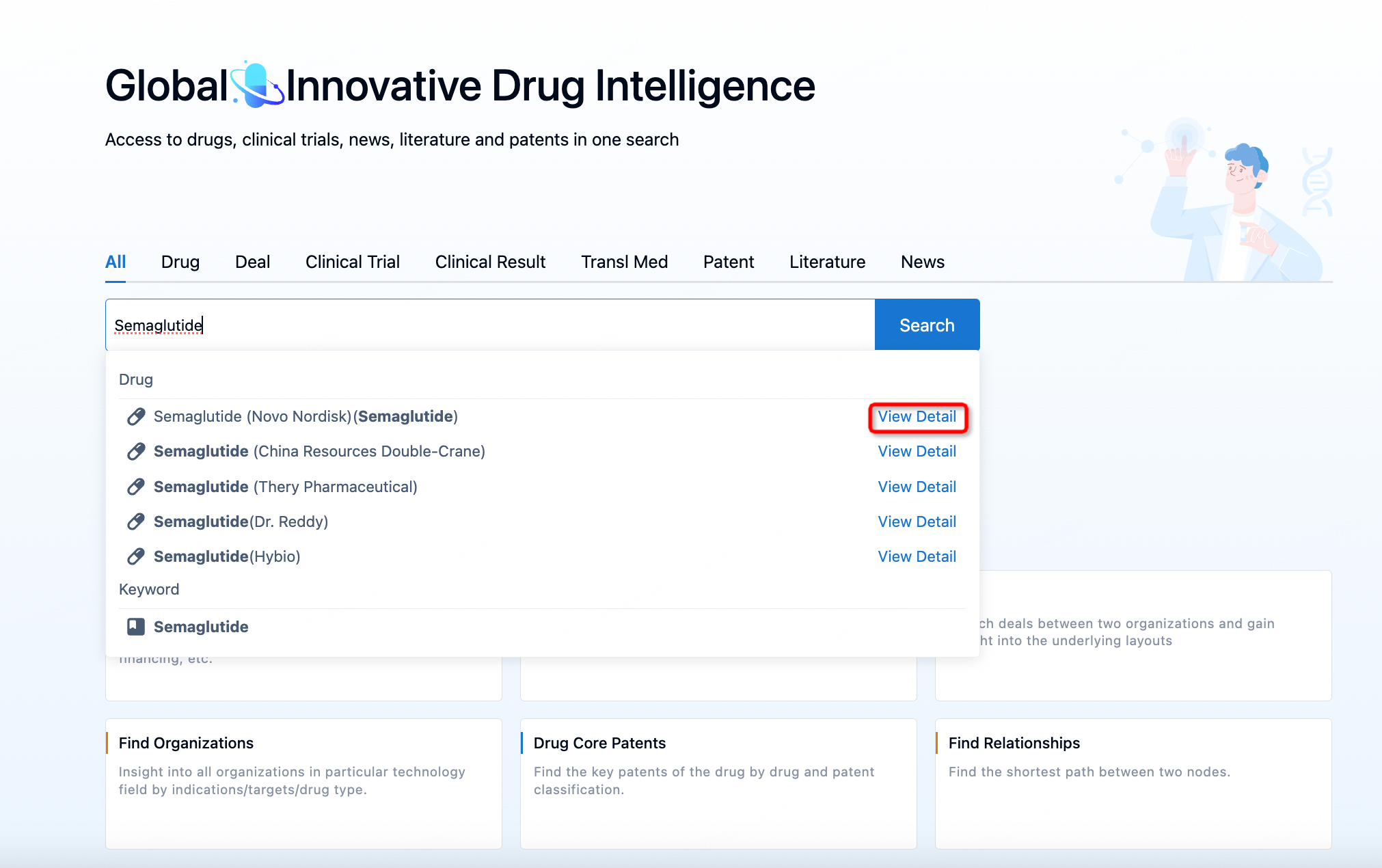
How to obtain the latest development progress of all drugs?
In the Synapse database, you can keep abreast of the latest research and development advances of all drugs anywhere and anytime, daily or weekly, through the "Set Alert" function. Click on the image below to embark on a brand new journey of drug discovery!