A Comprehensive Review of Belantamab mafodotin's R&D Innovations and Drug Target Mechanism
Belantamab mafodotin's R&D Progress
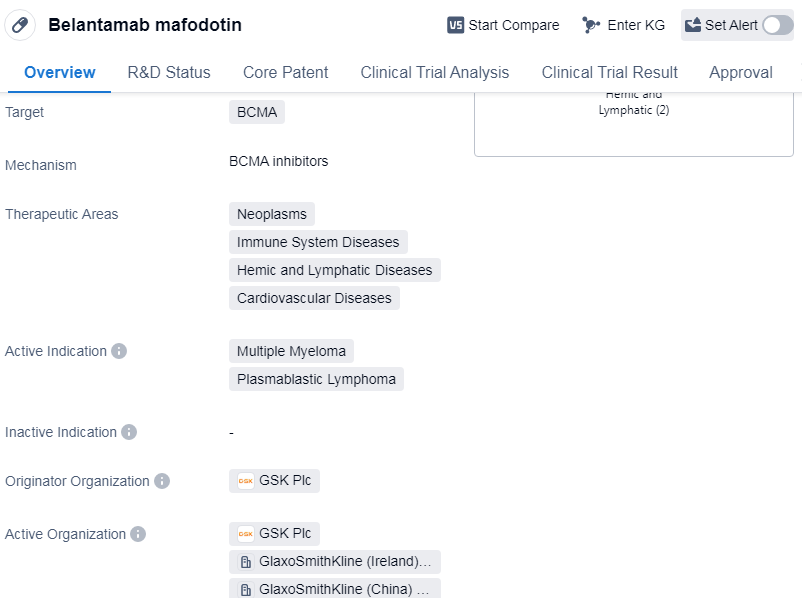
Belantamab mafodotin is a drug in the field of biomedicine that falls under the category of Monoclonal antibody and Antibody drug conjugate (ADC). It specifically targets BCMA, which stands for B-cell maturation antigen. The drug is primarily used for the treatment of neoplasms, immune system diseases, hemic and lymphatic diseases, and cardiovascular diseases.
Belantamab mafodotin has been approved for the treatment of multiple myeloma and plasmablastic lymphoma. The drug was first approved in the United States in August 2020. It is important to note that the drug has received accelerated approval and has been designated as an orphan drug.
The originator organization of Belantamab mafodotin is GSK Plc, a well-known pharmaceutical company. The drug has reached the highest phase of development, which is approved, on a global scale. In China, it has reached phase 3 of development.
The approval of Belantamab mafodotin marks a significant milestone in the treatment of multiple myeloma and plasmablastic lymphoma. As a monoclonal antibody and antibody drug conjugate, it offers a targeted approach to treating these diseases by specifically targeting BCMA.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for Belantamab mafodotin: BCMA inhibitors
BCMA inhibitors are a type of medication that specifically target and inhibit B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA). BCMA is a protein that is primarily expressed on the surface of plasma cells, which are a type of white blood cell involved in the immune response. BCMA plays a crucial role in the survival and growth of plasma cells.
In the context of biomedicine, BCMA inhibitors are being investigated and developed as a potential treatment for multiple myeloma, a type of cancer that affects plasma cells. By inhibiting BCMA, these medications aim to disrupt the survival signals that promote the growth of cancerous plasma cells.
BCMA inhibitors can be designed as small molecules or as biologic drugs, such as monoclonal antibodies. Monoclonal antibodies are laboratory-produced molecules that can bind specifically to BCMA, blocking its activity and preventing the growth of cancerous plasma cells. Bispecific antibodies, on the other hand, are a type of BCMA inhibitor that can simultaneously bind to BCMA and another target, such as CD3 on T cells. This dual binding mechanism helps to recruit immune cells to attack and eliminate cancer cells expressing BCMA.
Overall, BCMA inhibitors represent a promising therapeutic approach in the field of oncology, particularly for the treatment of multiple myeloma. Ongoing research and clinical trials are further exploring the efficacy and safety of these inhibitors in order to provide better treatment options for patients.
Drug Target R&D Trends for Belantamab mafodotin
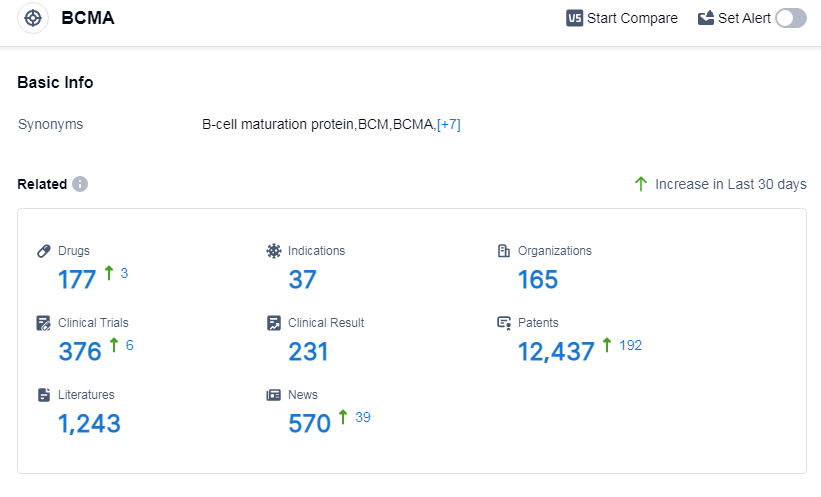
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 12 Sep 2023, there are a total of 177 BCMA drugs worldwide, from 165 organizations, covering 37 indications, and conducting 376 clinical trials.
The analysis of the target BCMA reveals a competitive landscape with multiple companies actively developing BCMA-targeted therapies. Johnson & Johnson and Bristol Myers Squibb Co. are leading in terms of the highest stage of development. Multiple myeloma is the primary indication for approved drugs, but there is ongoing research for other indications as well. CAR-T therapies, bispecific antibodies, and monoclonal antibodies are progressing rapidly, indicating intense competition and innovation in drug types. The United States, European Union, and China are the key locations for BCMA development, with China showing significant progress. Overall, the target BCMA presents a promising area for the pharmaceutical industry, with potential for further advancements and therapeutic options.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
Overall, Belantamab mafodotin represents a significant advancement in the field of biomedicine, particularly in the treatment of Multiple myeloma and plasmablastic lymphoma. Further research and clinical trials will provide more insights into the potential benefits and limitations of this drug.