A Comprehensive Review of Clofarabine's R&D Innovations and Drug Target Mechanism
Clofarabine's R&D Progress
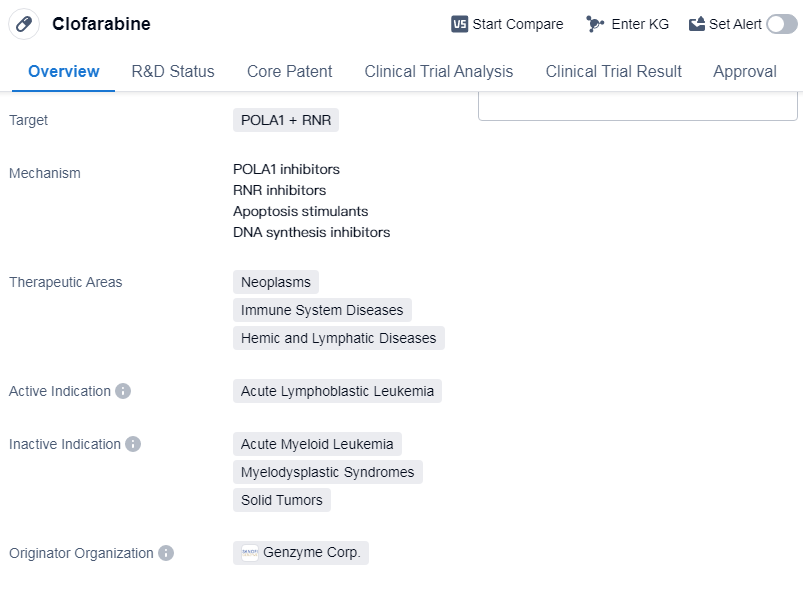
Clofarabine is a small molecule drug that targets POLA1 and RNR. It is primarily used in the treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), a type of cancer that affects the white blood cells. Clofarabine is classified as a small molecule drug, which means it is composed of relatively low molecular weight compounds.
The therapeutic areas in which clofarabine is used include neoplasms (abnormal growth of cells), immune system diseases, and hemic and lymphatic diseases. These areas encompass a wide range of conditions related to the blood, immune system, and various types of cancers.
Clofarabine was first approved for use in the United States in December 2004. It received accelerated approval, which means it was granted based on promising early results and further studies were required to confirm its effectiveness. Additionally, clofarabine was designated as an orphan drug, indicating that it is intended to treat a rare disease or condition.
The originator organization of clofarabine is Genzyme Corp., a biotechnology company that specializes in the development of innovative therapies for rare diseases. As the highest phase of development, clofarabine has been approved for use globally. This indicates that it has successfully completed all necessary clinical trials and regulatory requirements to be deemed safe and effective for its intended use.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for Clofarabine: POLA1 inhibitors, RNR inhibitors, Apoptosis stimulants and DNA synthesis inhibitors
POLA1 inhibitors are substances or drugs that inhibit the activity of the enzyme POLA1. POLA1 is a DNA polymerase alpha enzyme that plays a crucial role in DNA replication. By inhibiting POLA1, these inhibitors can prevent the replication of DNA, which can be useful in certain medical conditions such as cancer, where uncontrolled DNA replication is a hallmark feature.
RNR stands for ribonucleotide reductase, which is an enzyme involved in the synthesis of DNA precursors. RNR inhibitors are drugs or compounds that inhibit the activity of this enzyme. By blocking the function of RNR, these inhibitors can disrupt DNA synthesis and cell proliferation. They are commonly used in cancer treatment to inhibit the growth of tumor cells.
Apoptosis is a programmed cell death mechanism that plays a crucial role in maintaining tissue homeostasis and eliminating damaged or abnormal cells. Apoptosis stimulants are substances that promote or enhance the process of apoptosis. They can trigger a cascade of cellular events leading to cell death. These stimulants can be used in cancer therapy to induce apoptosis in cancer cells, helping to eliminate the tumor.
DNA synthesis inhibitors are drugs or compounds that interfere with the process of DNA replication or synthesis. They can target various steps in the DNA synthesis pathway, such as inhibiting enzymes involved in DNA replication or blocking the incorporation of nucleotides into the growing DNA strand. By inhibiting DNA synthesis, these inhibitors can prevent cell division and proliferation, which is particularly important in diseases like cancer where uncontrolled cell growth is a problem.
Drug Target R&D Trends for Clofarabine
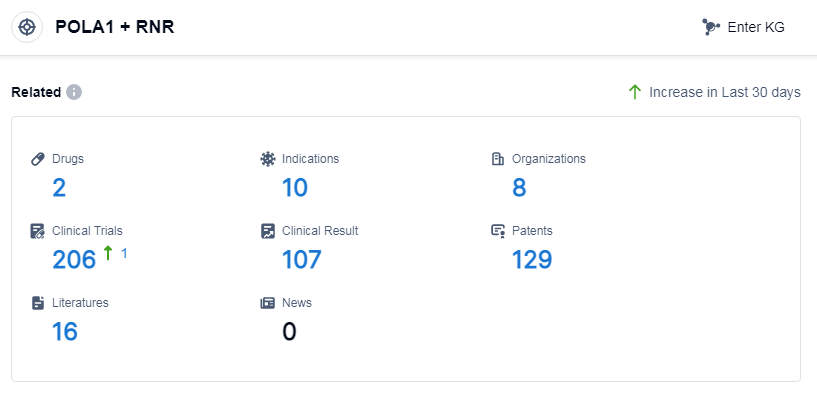
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 14 Sep 2023, there are a total of 2 POLA1 and RNR drugs worldwide, from 8 organizations, covering 10 indications, and conducting 206 clinical trials.
The analysis of the target POLA1 andRNR reveals that Sanofi, ORPHELIA Pharma SAS, Matrix Pharmaceutical, Inc., Kirin Holdings Co., Ltd., and Novartis AG are the companies growing fastest under this target. The highest stage of development is seen in Sanofi, with one drug approved and one drug in an inactive phase. Drugs targeting POLA1 and RNR have been approved for the indication of acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Small molecule drugs are progressing rapidly, with one approved and two in an inactive phase. Japan, the United States, and the European Union are the countries/locations developing fastest under this target. The competitive landscape for POLA1 and RNR indicates a focus on specific indications and drug types, with potential for intense competition in the small molecule drug category.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
In summary, Clofarabine is a small molecule drug that targets POLA1 and RNR. It is primarily used in the treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia and is approved for use globally. Its therapeutic areas include neoplasms, immune system diseases, and hemic and lymphatic diseases. The drug was developed by Genzyme Corp., a biotechnology company specializing in rare disease therapies. It was first approved in the United States in 2004 and received accelerated approval as an orphan drug.