AChE inhibitors are an important choice in the comprehensive management of Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder that commences subtly. Clinically, it is characterized by comprehensive dementia symptoms including memory impairment, aphasia, apraxia, agnosia, impairment of visuospatial skills, executive function disorder, as well as alterations in personality and behavior. The exact etiology of the disease remains unknown to this day.
Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) is an essential enzyme found in the human body that plays a crucial role in the nervous system. It is responsible for breaking down the neurotransmitter acetylcholine (ACh), which is involved in various physiological processes such as muscle contraction, cognition, and memory. AChE ensures the proper functioning of the cholinergic system by rapidly hydrolyzing AChE, preventing its accumulation and maintaining a delicate balance.
Dysfunction or inhibition of AChE can lead to an excess of AChE, resulting in various neurological disorders like Alzheimer's disease and myasthenia gravis. Understanding the role of AChE is vital for developing therapeutic strategies to regulate cholinergic activity and treat associated conditions.
AChE inhibitors function by reversibly inhibiting AChE, leading to the accumulation of ACh at synaptic locations, thus extending and enhancing the role of AChE, which in turn improves cognitive functions in Alzheimer's disease (AD) patients. Cholinesterase inhibitors are commonly used to treat patients with mild-to-moderate AD, offering moderate improvements to cognitive function, emotion, behavioral symptoms, and daytime life functions.
AChE Competitive Landscape
According to the data provided by Patsnap Synapse-Global Drug Intelligence Database: the following figure shows that as of 7 Sep 2023, there are a total of 128 AChE drugs worldwide, from 166 organizations, covering 82 indications, and conducting 1117 clinical trials.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or login directly if you have freemium accounts, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs , indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target.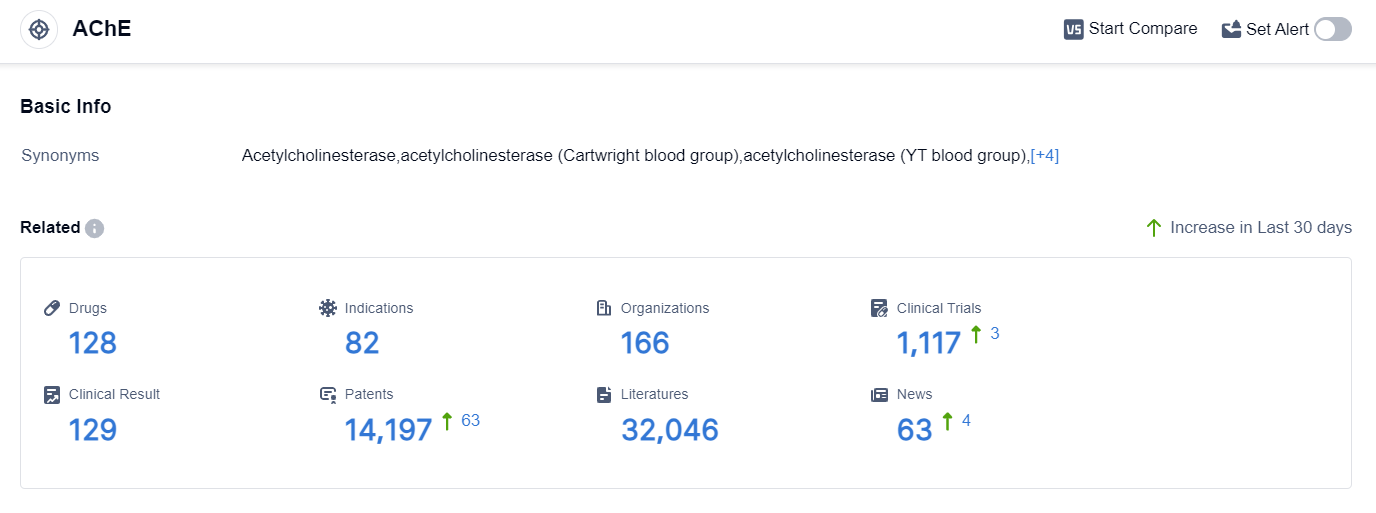
The analysis of the target AChE reveals a competitive landscape with multiple companies actively involved in R&D. AbbVie, Inc., Shanghai Pharmaceuticals Holding Co., Ltd., Pfizer Inc., Zeria Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., and Eisai Co., Ltd. are among the companies growing fastest in this area.
The approved drugs for the target AChE cover indications such as Myasthenia Gravis, Alzheimer Disease, Poisoning, Glaucoma, and more. Small molecule drugs dominate the drug types progressing rapidly under the target AChE, indicating intense competition.
China, the United States, Japan, and the European Union are the countries/locations developing fastest under the target AChE, with China showing significant progress. Overall, the target AChE presents a promising area for pharmaceutical development, with potential applications in various neurological and gastrointestinal disorders.
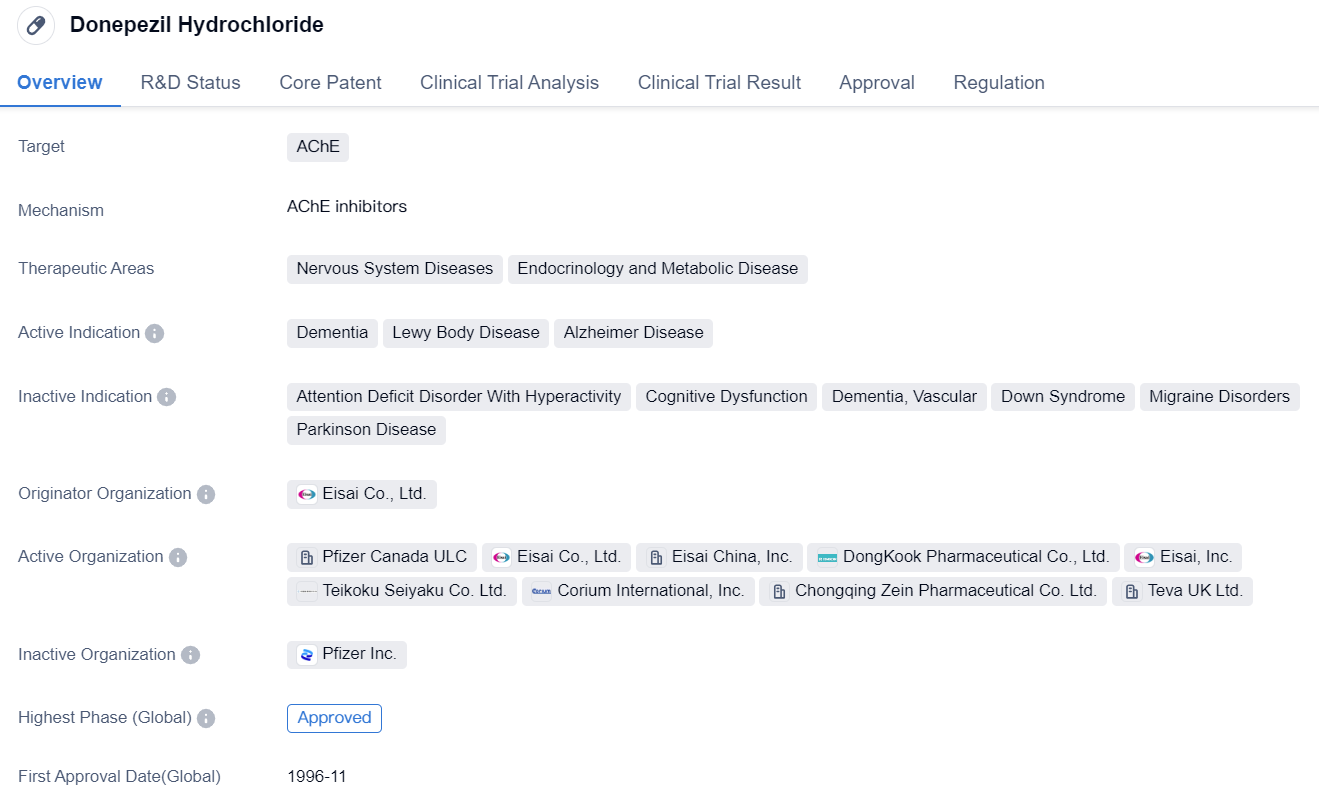
Key Drug: Donepezil Hydrochloride
Donepezil Hydrochloride is a small molecule drug that targets the AChE. It is primarily used in the treatment of nervous system diseases and endocrinology and metabolic diseases. The drug has been approved for the treatment of dementia, Lewy Body Disease, and Alzheimer's Disease.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
The essence of Donepezil Hydrochloride is a highly selective, non-competitive, reversible inhibitor of AChE. Pharmacological studies show that Donepezil Hydrochloride can long-term and effectively inhibit the AChE activity in the central nervous system, increase the ACh levels in the cortical and basal ganglia synapses, activate the central cholinergic system, and significantly improve cognition and memory.
Secondly, Donepezil Hydrochloride can protect the stability of neuronal structures, alleviate the toxic side effects of β-amyloid, maintain the normal energy metabolism of central neurons, and play a significant role in maintaining normal brain activity. Finally, Donepezil Hydrochloride has a protective effect on the neuronal bodies in the hippocampus region, has an antioxidant effect, can protect neuronal tissue by reducing the oxidative stress response to neuronal damage, and can regulate the energy metabolism of neuronal bodies to prevent neuronal injury.
As Alzheimer's Disease itself is irreversible, it is necessary to regularly evaluate the patient's condition during the intake of Donepezil Hydrochloride. If there are significant declines in memory and cognition, it indicates that the therapeutic effect of Donepezil Hydrochloride is no longer significant. At this point, it may be considered to adjust the dosage or switch to other drugs.
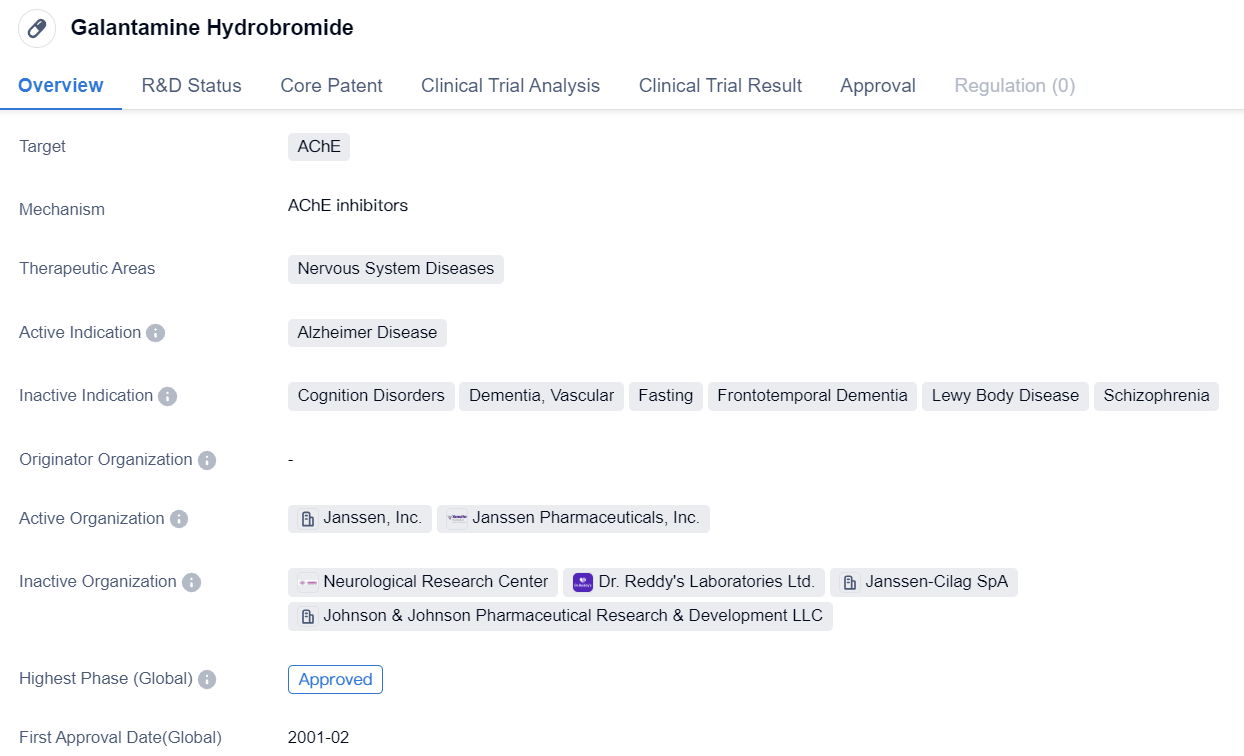
Galantamine Hydrobromide
Galantamine Hydrobromide is a small molecule drug that is primarily used in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. It targets the AChE, which is responsible for breaking down the neurotransmitter ACh in the brain. By inhibiting AChE, Galantamine Hydrobromide helps to increase the levels of ACh, which is important for memory and cognitive function. The therapeutic area for Galantamine Hydrobromide is nervous system diseases, specifically Alzheimer's disease.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Galantamine Hydrobromide is a selective, competitive, reversible AChE inhibitor. High in selectivity and competitiveness, it competes with ACh in the synaptic gap for binding with AChE, thus blocking this enzyme from breaking down ACh. This implies that Galantamine Hydrobromide can generate maximum activity in areas with post-synaptic cholinergic deficiency. As the therapeutic effects mainly occur post-synaptically, this characteristic allows Galantamine Hydrobromide to achieve maximal clinical effectiveness.
Galantamine Hydrobromide has received approval for use in both the global market and China. The drug was first approved in the United States in February 2001, making it one of the early treatments available for Alzheimer's disease. Since then, it has been approved in several other countries as well.
The approval of Galantamine Hydrobromide in multiple countries highlights its efficacy and safety profile in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. It has undergone rigorous clinical trials to demonstrate its benefits and potential side effects.
As a small molecule drug, Galantamine Hydrobromide is likely to be available in oral dosage forms, such as tablets or capsules. This allows for convenient administration and patient compliance.
In summary, Galantamine Hydrobromide is a small molecule drug that targets AChE and is used in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. It has received approval in both the global market and China, with its first approval in the United States in 2001. The drug's approval highlights its efficacy and safety in treating Alzheimer's disease, a significant therapeutic area in the field of biomedicine.