An In-depth Analysis of Calcifediol's R&D Progress and Mechanism of Action on Drug Target
Calcifediol's R&D Progress
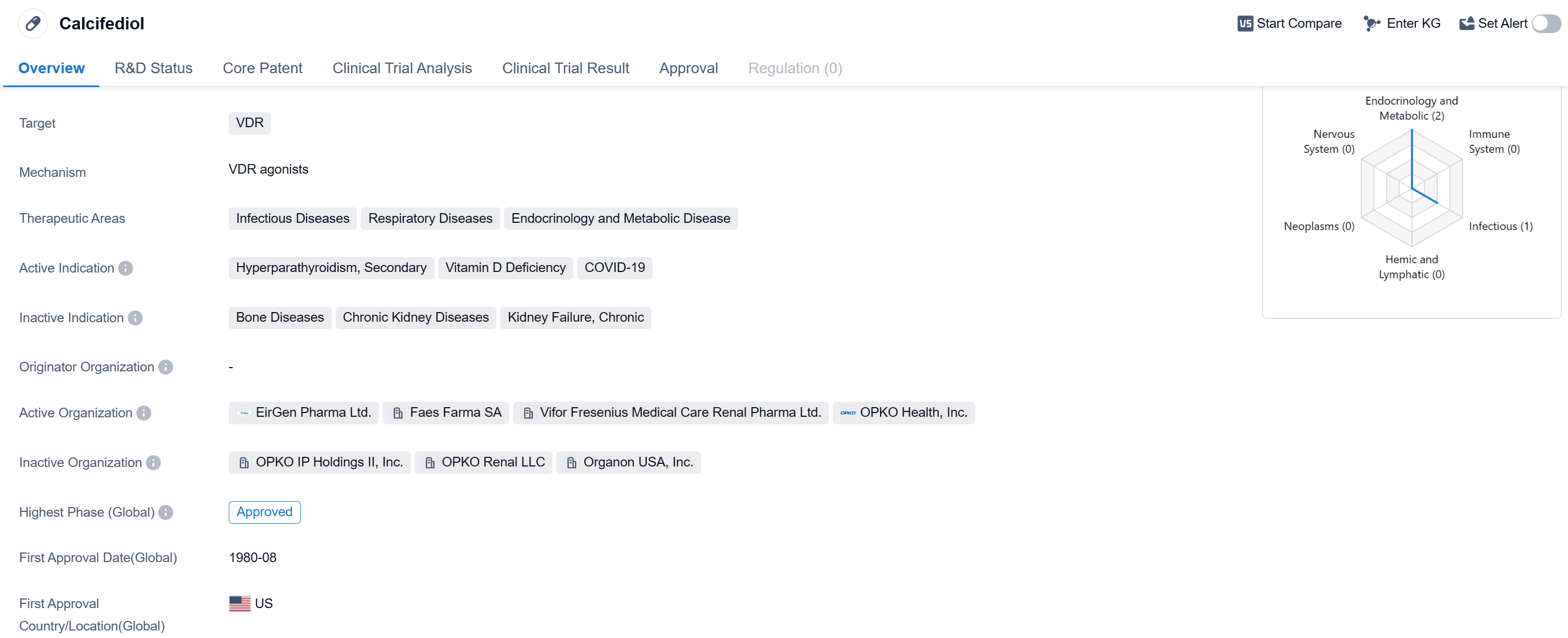
Calcifediol is a small molecule drug that primarily targets the vitamin D receptor (VDR). It is used in the treatment of various therapeutic areas including infectious diseases, respiratory diseases, endocrinology, and metabolic diseases. The drug has been approved for the treatment of hyperparathyroidism, secondary, vitamin D deficiency, and most recently, COVID-19.
Calcifediol received its first approval in the United States in August 1980, making it a well-established drug in the pharmaceutical market. It has since gained global recognition and has been approved in several countries worldwide. In China, it has obtained IND (Investigational New Drug) approval, indicating its potential for further development and potential market entry in the country.
The drug's approval for the treatment of hyperparathyroidism, secondary, highlights its effectiveness in managing this condition. Hyperparathyroidism is a disorder characterized by excessive production of parathyroid hormone, leading to abnormal calcium levels in the blood. Calcifediol helps regulate calcium levels and restore balance in patients with this condition.
Additionally, calcifediol is indicated for the treatment of vitamin D deficiency. Vitamin D plays a crucial role in maintaining bone health and immune function. Deficiency in this vitamin can lead to various health issues, including weakened bones and increased susceptibility to infections. Calcifediol supplementation helps address this deficiency and promotes overall well-being.
In light of the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, calcifediol has emerged as a potential treatment option. Studies have suggested that vitamin D supplementation, including calcifediol, may have a positive impact on COVID-19 outcomes. It is believed that adequate vitamin D levels can enhance the immune response and reduce the severity of respiratory infections, including COVID-19.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for Calcifediol: VDR agonists
VDR agonists are a type of drug that activate the Vitamin D receptor (VDR) in the body. The VDR is a nuclear receptor that plays a crucial role in regulating various biological processes, including calcium and phosphorus metabolism, immune function, and cell growth and differentiation. When VDR agonists bind to the VDR, they initiate a cascade of molecular events that lead to changes in gene expression and cellular responses.
From a biomedical perspective, VDR agonists are of particular interest in the field of biomedicine due to their potential therapeutic applications. By activating the VDR, these agonists can modulate the expression of genes involved in immune regulation, bone health, and other physiological processes. This makes them promising candidates for the treatment of various diseases, including autoimmune disorders, osteoporosis, and certain types of cancer.
It is important to note that the specific mechanism of action and clinical applications of VDR agonists may vary depending on the specific compound. Different VDR agonists may have varying affinities for the receptor and may exhibit distinct pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties. Therefore, further research and clinical trials are needed to fully understand the potential benefits and risks associated with the use of VDR agonists in different disease contexts.
Drug Target R&D Trends for Calcifediol
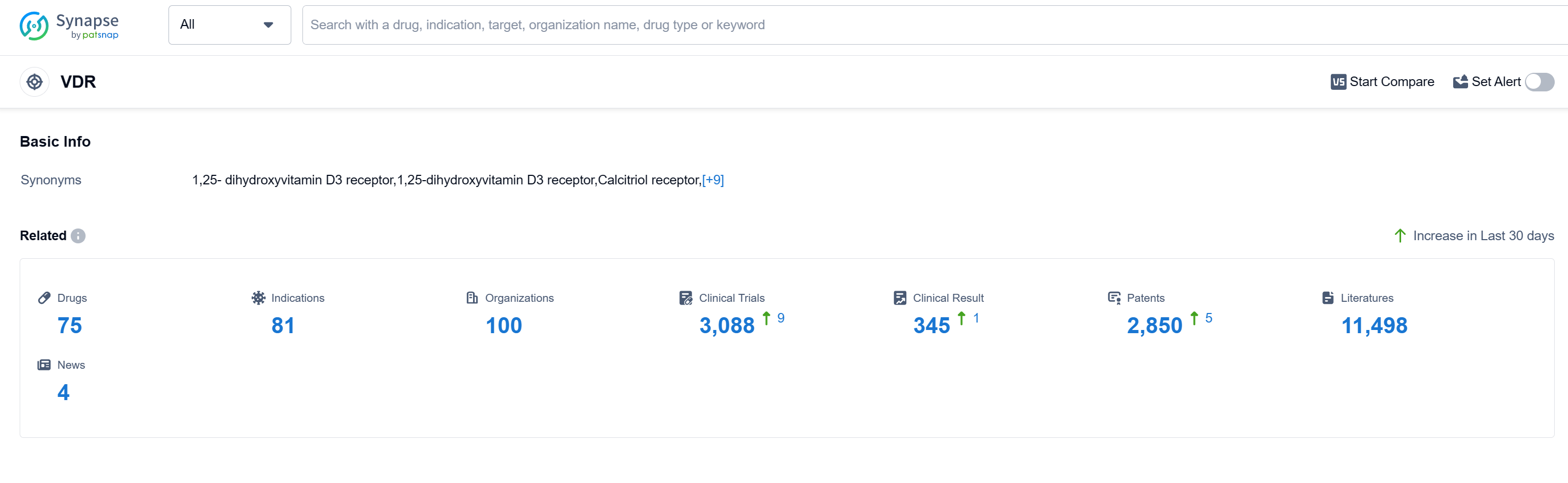
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 15 Sep 2023, there are a total of 75 VDR drugs worldwide, from 100 organizations, covering 81 indications, and conducting 3088 clinical trials.
The analysis of the target VDR reveals a competitive landscape with multiple companies actively developing drugs for various indications. Roche Holding AG, LEO Fondet, LEO Pharma A/S, OPKO Health, Inc., and Maruho Co., Ltd. are the companies growing fastest under the target VDR. The indications with the highest number of approved drugs include Hyperparathyroidism, Secondary, Osteoporosis, Psoriasis, and Vitamin D Deficiency. Small molecule drugs are progressing rapidly, indicating intense competition around innovative drugs. China, the United States, Japan, and the European Union are the countries/locations developing fastest under the target VDR, with China showing significant progress. Overall, the target VDR presents a competitive landscape with diverse R&D activities and promising future developments.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
Overall, calcifediol is a small molecule drug that targets the VDR and is approved for the treatment of hyperparathyroidism, secondary, vitamin D deficiency, and COVID-19. Its long-standing presence in the market, coupled with its potential in addressing various therapeutic areas, makes it a valuable asset in the pharmaceutical industry. Further research and development efforts, including its potential entry into the Chinese market, may pave the way for expanded usage and improved patient outcomes.