Decoding gemcitabine hydrochloride: A Comprehensive Study of its R&D Trends and Mechanism on Drug Target
Gemcitabine hydrochloride's R&D Progress
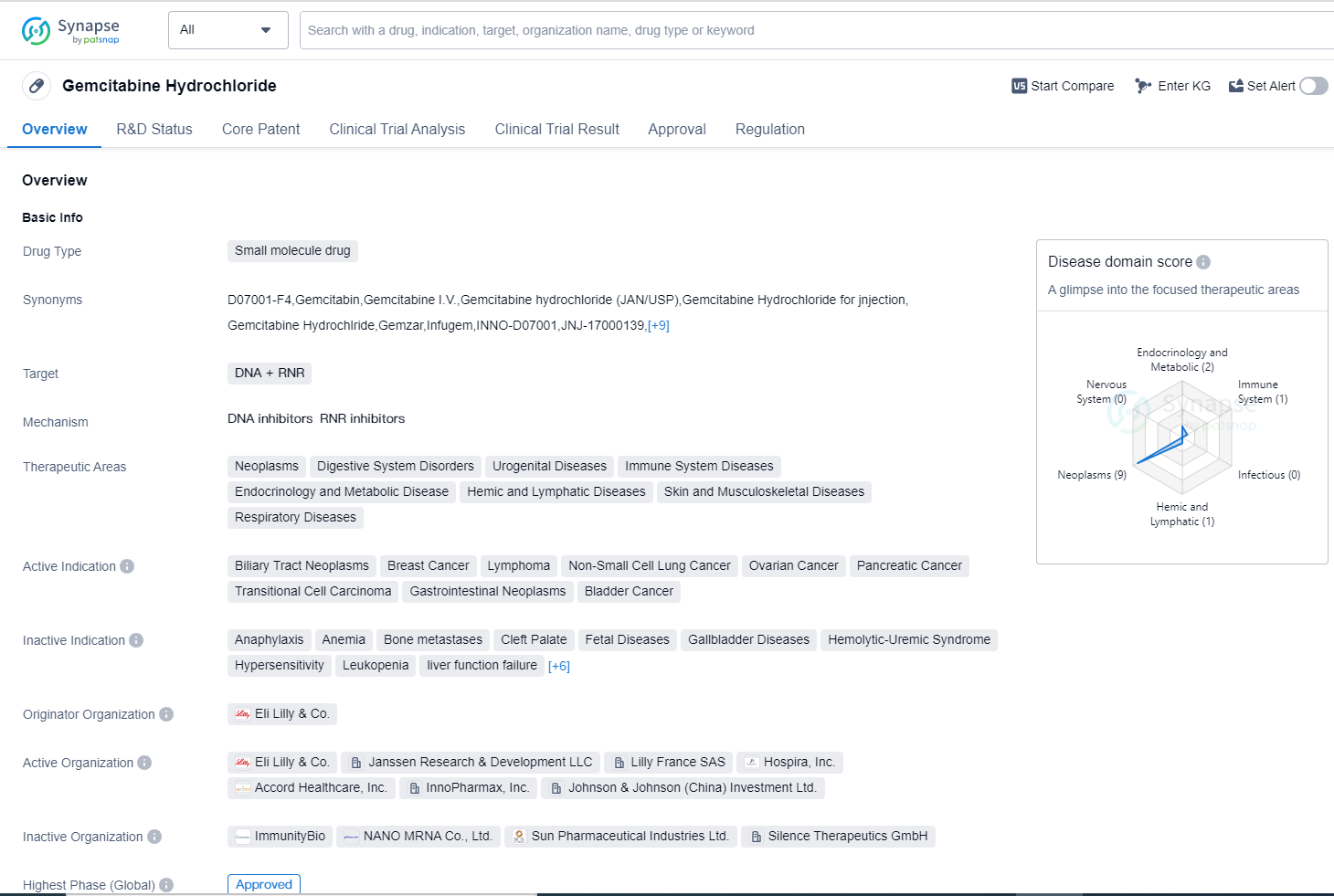
Gemcitabine Hydrochloride is a small molecule drug that targets DNA and RNR (ribonucleotide reductase). It has been approved for use in various therapeutic areas including neoplasms, digestive system disorders, urogenital diseases, immune system diseases, endocrinology and metabolic disease, hemic and lymphatic diseases, skin and musculoskeletal diseases, and respiratory diseases.
The drug has shown efficacy in treating several types of cancers, including biliary tract neoplasms, breast cancer, lymphoma, non-small cell lung cancer, ovarian cancer, pancreatic cancer, transitional cell carcinoma, gastrointestinal neoplasms, and bladder cancer. This wide range of active indications highlights the potential of Gemcitabine Hydrochloride in combating various forms of cancer.
Gemcitabine Hydrochloride was first approved in South Africa in January 1995, making it a well-established drug in the market. Its originator organization is Eli Lilly & Co., a renowned pharmaceutical company known for its contributions to the field of biomedicine.
The highest R&D phase of this drug is approved. It has also received approval in China, further expanding its market reach.
Gemcitabine Hydrochloride is regulated as an orphan drug. Orphan drugs are medications developed to treat rare diseases or conditions that affect a small number of patients. This regulatory status highlights the drug's potential to address unmet medical needs and provide therapeutic options for patients with limited treatment options.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for gemcitabine hydrochloride: DNA inhibitors RNR inhibitors
DNA inhibitors and RNR inhibitors are both types of drugs that target specific biological processes in the body.
From a biomedical perspective, DNA inhibitors are drugs that interfere with the replication or transcription of DNA molecules. They work by binding to DNA and preventing enzymes or proteins from carrying out their normal functions. DNA inhibitors can be used to treat various medical conditions, including cancer, viral infections, and autoimmune diseases.
RNR inhibitors, on the other hand, target an enzyme called ribonucleotide reductase (RNR). This enzyme plays a crucial role in DNA synthesis by converting ribonucleotides into deoxyribonucleotides, which are the building blocks of DNA. By inhibiting RNR, these drugs can disrupt DNA replication and cell division. RNR inhibitors are commonly used in cancer treatment to prevent the growth and spread of cancer cells.
Both DNA inhibitors and RNR inhibitors are important tools in biomedical research and clinical practice. They offer targeted approaches to interfere with DNA-related processes and can have significant therapeutic effects in various diseases.
Drug Target R&D Trends for gemcitabine hydrochloride
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNR (ribonucleotide reductase) play crucial roles in the human body. DNA carries the genetic information that determines our traits and characteristics. It serves as a blueprint for the synthesis of proteins, which are essential for various biological processes. RNR, on the other hand, is an enzyme that plays a vital role in DNA synthesis by converting ribonucleotides into deoxyribonucleotides, the building blocks of DNA. This process is crucial for cell division, growth, and repair. Together, DNA and RNR ensure the proper functioning and maintenance of our genetic material, enabling the normal functioning of our cells and overall health.
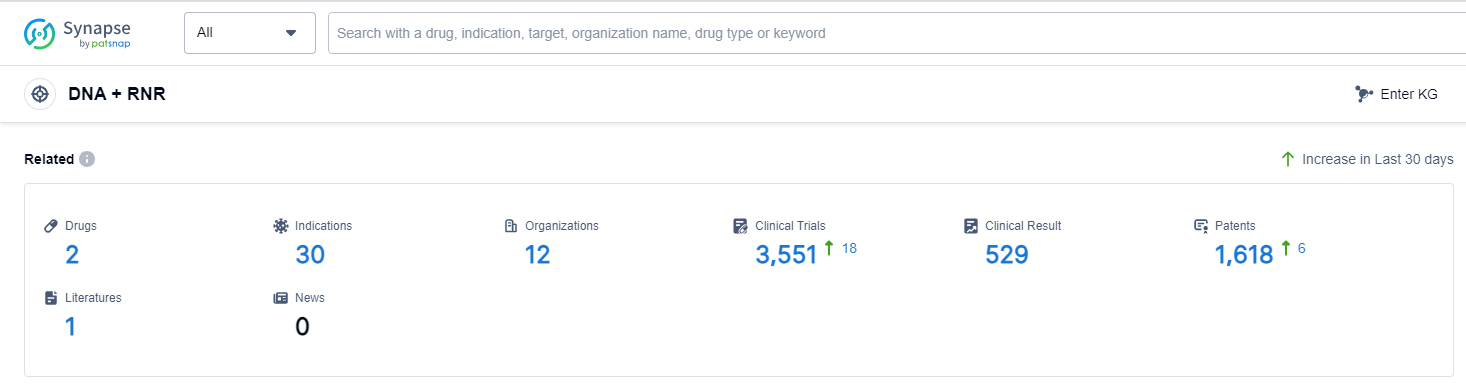
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 13 Sep 2023, there are a total of 2 DNA + RNR drugs worldwide, from 12 organizations, covering 30 indications, and conducting 3551 clinical trials.
The analysis of the current competitive landscape and future development of target DNA + RNR reveals promising growth opportunities in the pharmaceutical industry. Companies such as Eli Lilly & Co., Pfizer Inc., and Intas Pharmaceuticals Ltd. are leading the way with drugs in the approved phase. These drugs target indications such as breast cancer, pancreatic cancer, and non-small cell lung cancer, among others. The presence of small molecule drugs indicates intense competition, highlighting the potential for innovation in this area. Additionally, countries like China, the United States, Japan, and South Africa are actively developing drugs under the target DNA + RNR, showcasing global efforts in advancing this field. Overall, the analysis suggests a positive outlook for the future development and commercialization of target DNA + RNR in the pharmaceutical industry.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
In summary, Gemcitabine Hydrochloride is a small molecule drug that targets DNA and RNR. It has been approved for use in various therapeutic areas and has shown efficacy in treating multiple types of cancers. With its first approval in South Africa in 1995 and subsequent global approvals, Gemcitabine Hydrochloride has established itself as a well-established and regulated drug. Its orphan drug status further emphasizes its potential to address unmet medical needs in the field of biomedicine.