Deep Scientific Insights on Vildagliptin's R&D Progress, Mechanism of Action, and Drug Target
Vildagliptin's R&D Progress
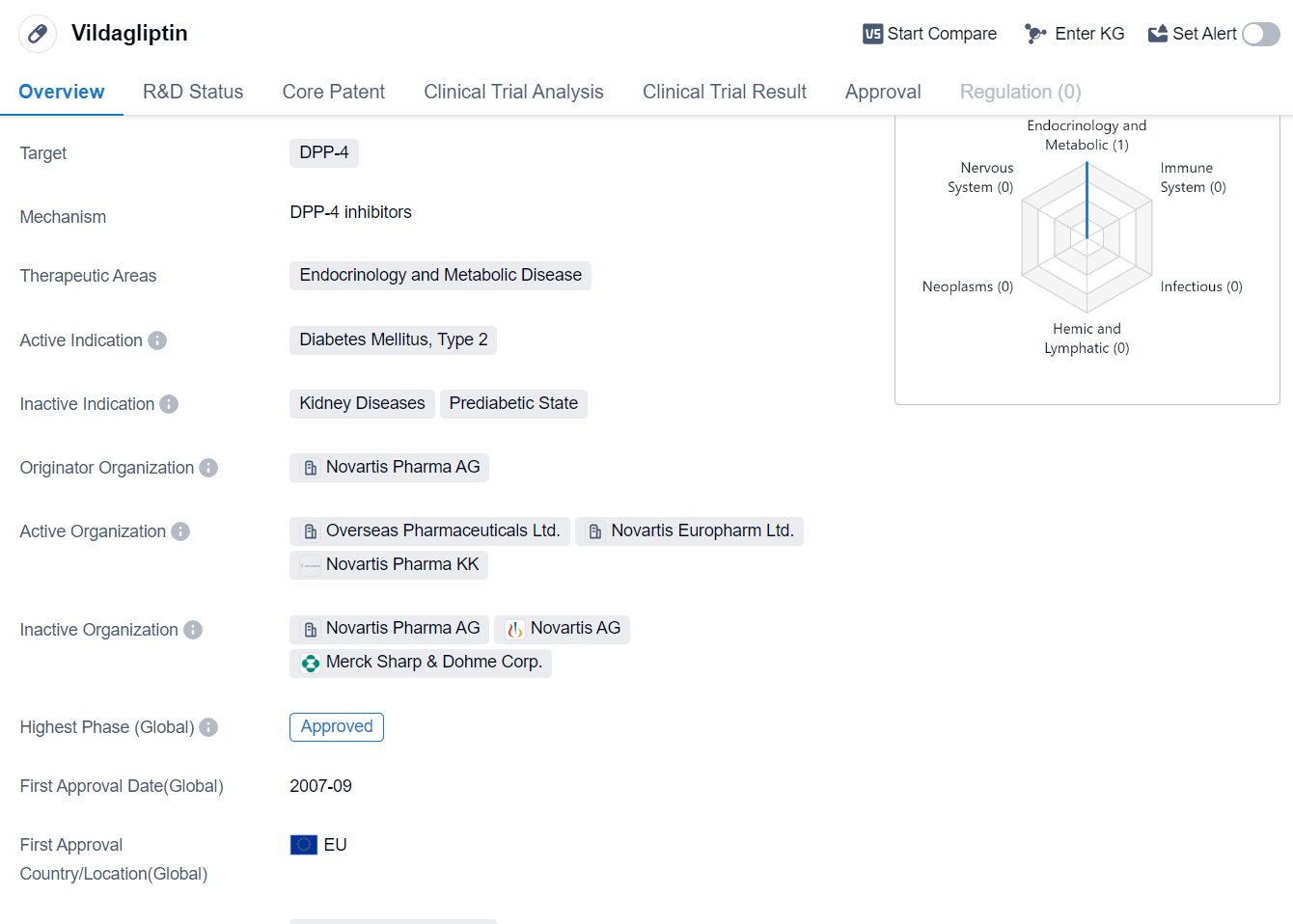
Vildagliptin is a small molecule drug that falls under the therapeutic area of endocrinology and metabolic disease. It specifically targets DPP-4, which stands for dipeptidyl peptidase-4. This drug is primarily used for the treatment of Diabetes Mellitus, Type 2.
Vildagliptin was developed by Novartis Pharma AG, a renowned pharmaceutical organization.It has reached the highest phase of clinical trials which is approved globally. The drug was first approved in the European Union in September 2007.
As a small molecule drug, Vildagliptin is designed to interact with the DPP-4 enzyme, which plays a crucial role in the regulation of blood sugar levels. By inhibiting this enzyme, Vildagliptin helps to increase the levels of incretin hormones, such as GLP-1 and GIP, which stimulate insulin secretion and reduce glucagon release. This mechanism of action ultimately leads to improved glycemic control in patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.
The approval of Vildagliptin in multiple regions, including the European Union and China, highlights its efficacy and safety profile. It has undergone rigorous testing and evaluation to ensure its suitability for patients suffering from Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.
The introduction of Vildagliptin has provided healthcare professionals with an additional treatment option for managing this chronic metabolic disorder. Its approval signifies the potential benefits it offers in terms of glycemic control and overall disease management.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for Vildagliptin: DPP-4 inhibitor
DPP-4 inhibitors are a type of medication used in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. DPP-4 stands for dipeptidyl peptidase-4, which is an enzyme that breaks down incretin hormones in the body. Incretin hormones help regulate blood sugar levels by stimulating the release of insulin and reducing the production of glucose. By inhibiting the action of DPP-4, these medications increase the levels of incretin hormones, leading to improved blood sugar control. DPP-4 inhibitors are typically taken orally and are often prescribed in combination with other diabetes medications. They have been shown to be effective in lowering blood sugar levels and have a relatively low risk of causing hypoglycemia (low blood sugar). Some common examples of DPP-4 inhibitors include sitagliptin, saxagliptin, and linagliptin.
Drug Target R&D Trends for Vildagliptin
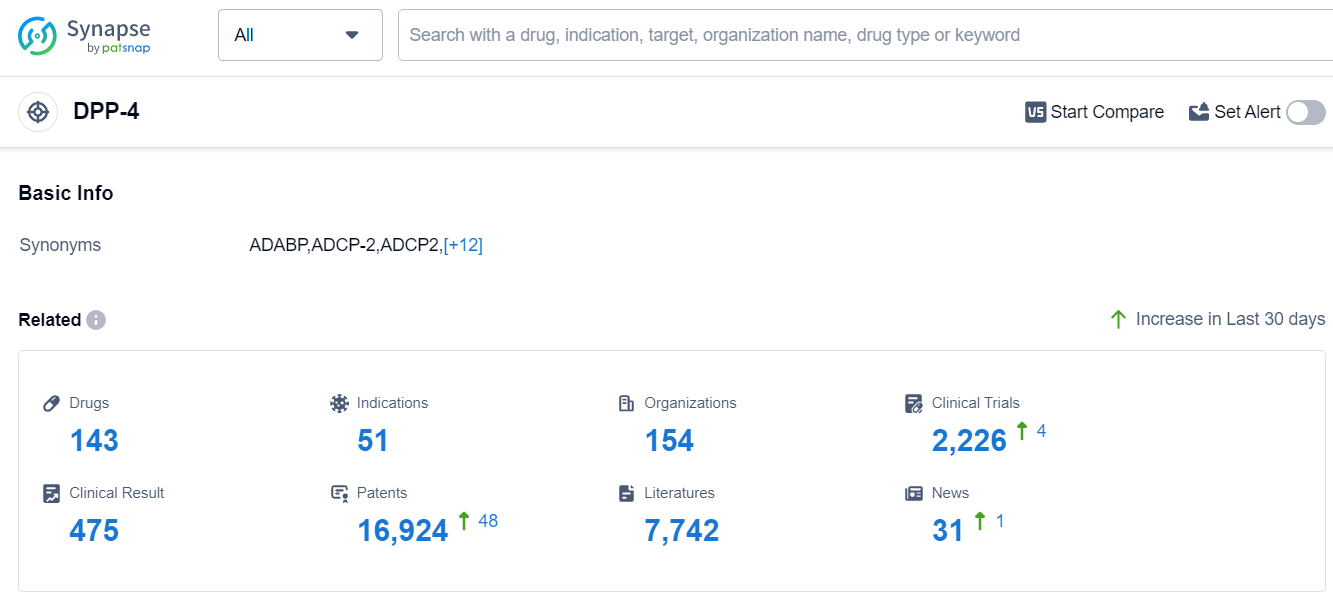
The analysis of the target DPP-4 reveals a competitive landscape with multiple companies actively involved in research and development. Merck & Co., Inc., Takeda Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., C.H. Boehringer Sohn AG & Co. KG, AstraZeneca PLC, and LG Chem Ltd. are the companies growing fastest under this target. The indication analysis shows a strong focus on treating Diabetes Mellitus, Type 2. Small molecule drugs are progressing rapidly, with a significant number of approved drugs. The presence of biosimilars, such as monoclonal antibodies, indicates intense competition. The countries/locations developing fastest include the European Union, Japan, the United States, South Korea, and China. China has shown notable progress in drug development. Overall, the target DPP-4 presents a competitive landscape with a focus on addressing Diabetes Mellitus, Type 2, and a strong emphasis on small molecule drug development.
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 11 Sep 2023, there are a total of 143 DPP-4 drugs worldwide, from 154 organizations, covering 51 indications, and conducting 2226 clinical trials.
Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
In conclusion, Vildagliptin is a small molecule drug developed by Novartis Pharma AG. It targets the DPP-4 enzyme and is primarily used for the treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. With its approval in various regions, including the European Union and China, Vildagliptin has demonstrated its efficacy and safety in improving glycemic control. Its introduction has expanded the treatment options available for healthcare professionals in managing this chronic metabolic disease.