How to find the core components of Loncastuximab tesirine?
Loncastuximab tesirine is an antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) developed by ADC Therapeutics, targeting CD19, a protein that is expressed on the surface of B cells, including those found in various hematological malignancies such as diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL). As a novel therapeutic agent, Loncastuximab tesirine is designed to deliver a potent cytotoxic payload specifically to tumor cells expressing CD19, thereby minimizing toxicity to healthy tissues.
Summary of Research Progress of Loncastuximab tesirine
The research progress of Loncastuximab tesirine has been significant. The drug works by binding to CD19 on the surface of cancer cells, internalizing the ADC, and releasing the cytotoxic payload within the cell. This mechanism allows for targeted delivery of the drug, enhancing its efficacy while reducing systemic side effects. Loncastuximab tesirine has received accelerated approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory DLBCL after two or more lines of systemic therapy. Globally, the drug is also under review in other regions, with ongoing efforts to secure approvals in additional markets.
The global competition in the ADC market is intense, with several other ADCs targeting various cancers at different stages of development. Key competitors include Roche's Polivy (polatuzumab vedotin) for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and Seattle Genetics' Adcetris (brentuximab vedotin) for Hodgkin lymphoma and systemic anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Despite this competition, Loncastuximab tesirine stands out due to its specific targeting of CD19 and its potential in treating DLBCL, a disease area with limited treatment options. Clinical trials have shown promising results, particularly in patients with relapsed or refractory DLBCL who have progressed on or after multiple lines of therapy.
Structural Characteristics of Loncastuximab tesirine
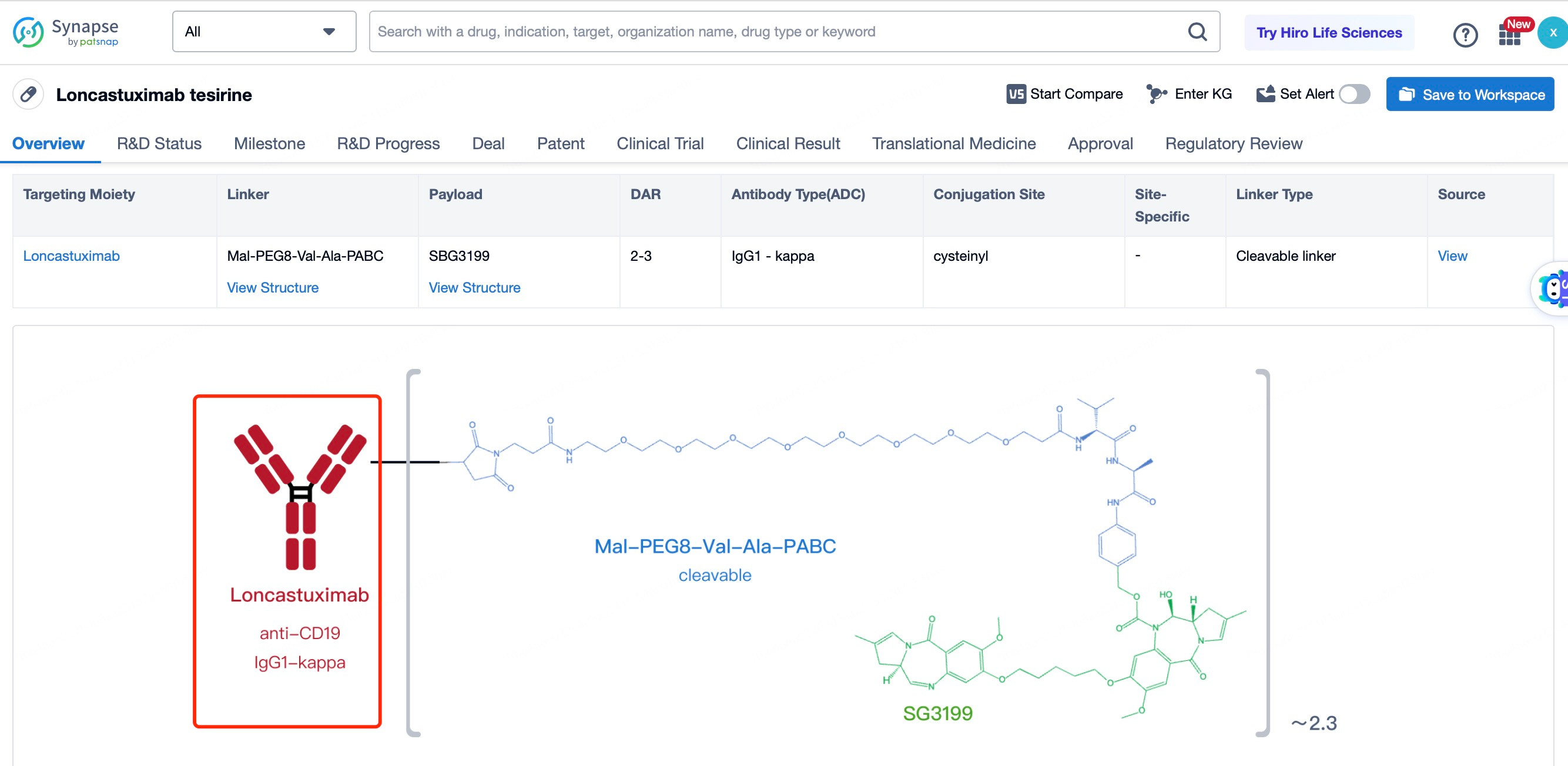
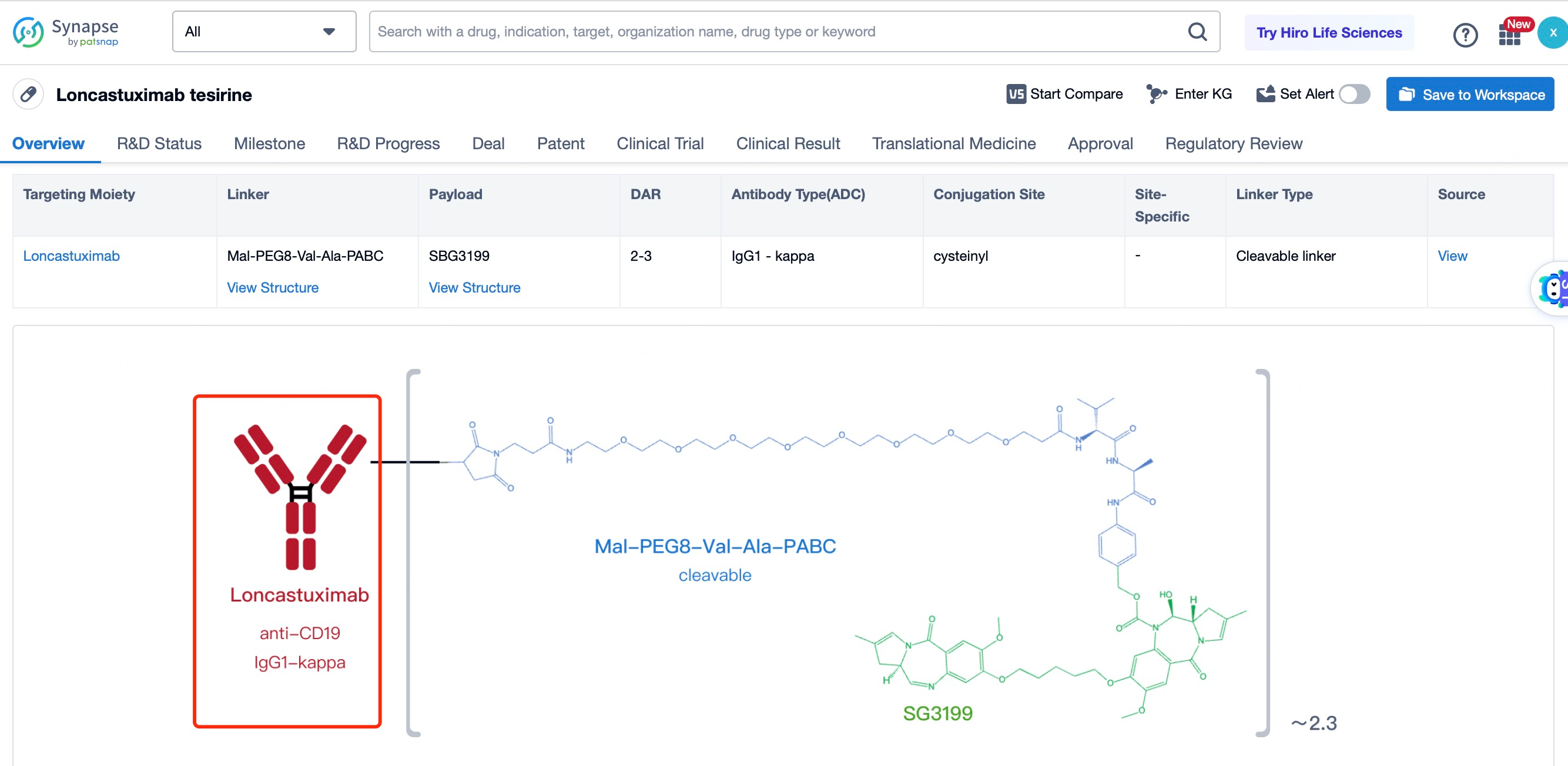
The overall structural characteristics of Loncastuximab tesirine are designed to optimize its therapeutic potential. The ADC consists of three main components: the antibody, the linker, and the cytotoxic payload. The antibody is a humanized IgG1 monoclonal antibody that binds to CD19 with high affinity and specificity. The linker is a cleavable maleimide-based linker that ensures the payload remains attached to the antibody during circulation and is released only upon internalization into the target cell. The cytotoxic payload is a pyrrolobenzodiazepine (PBD) dimer, a potent DNA alkylating agent.
The selection and advantages of the antibody in Loncastuximab tesirine are crucial for its effectiveness. The antibody used, known as ADCT-402, is a humanized IgG1 monoclonal antibody that binds to CD19 with high affinity and specificity. CD19 is a transmembrane protein that is expressed on the surface of B cells and is overexpressed in various hematological malignancies, including DLBCL. The high affinity and specificity of ADCT-402 ensure that the ADC can effectively target and bind to CD19-expressing cancer cells, thereby maximizing the delivery of the cytotoxic payload. Additionally, the antibody has been engineered to enhance its stability and reduce immunogenicity, making it suitable for repeated dosing. The high binding affinity and low immunogenicity of the antibody contribute to the overall safety and efficacy of Loncastuximab tesirine. The antibody also has a favorable pharmacokinetic profile, with a long half-life that allows for less frequent dosing, improving patient convenience and compliance.
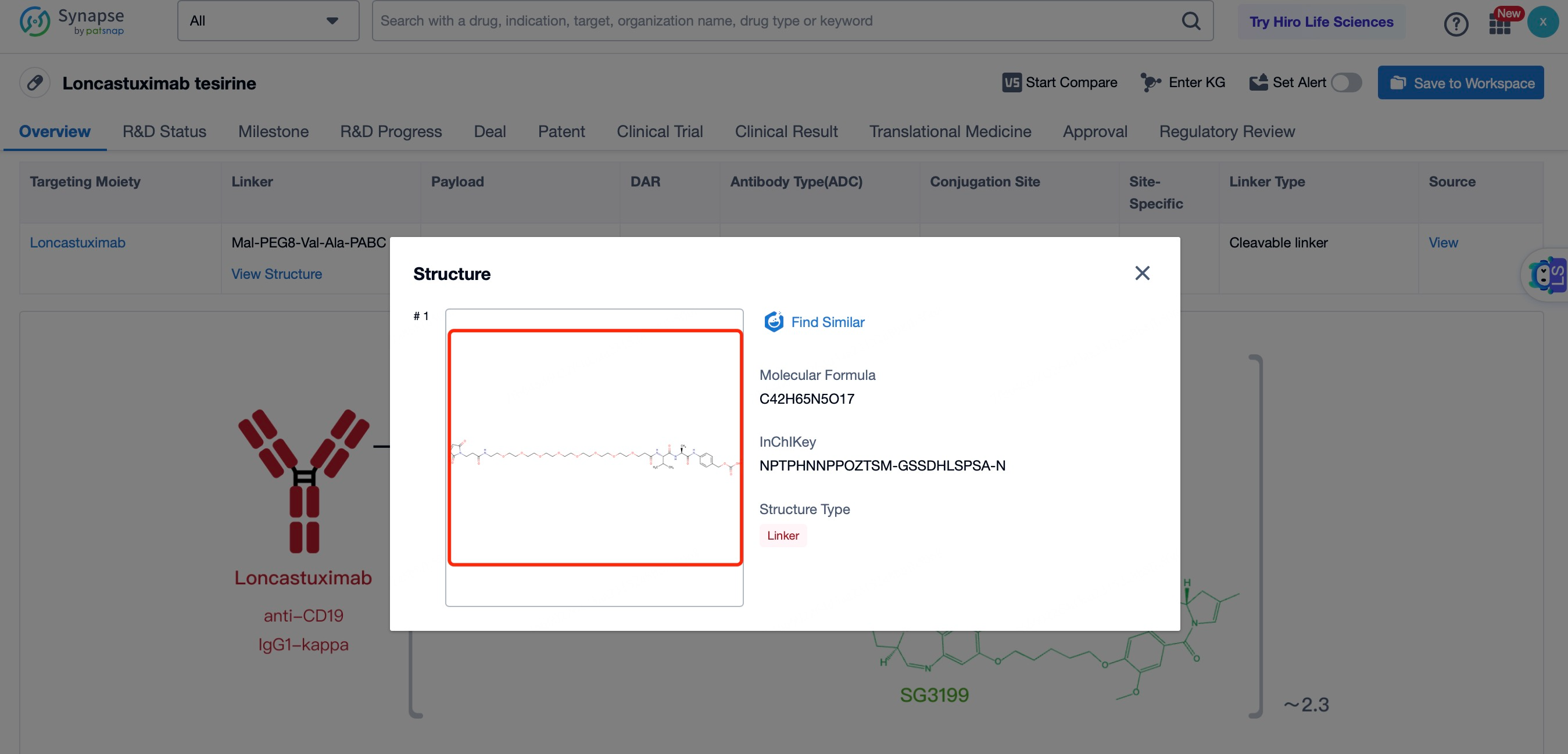
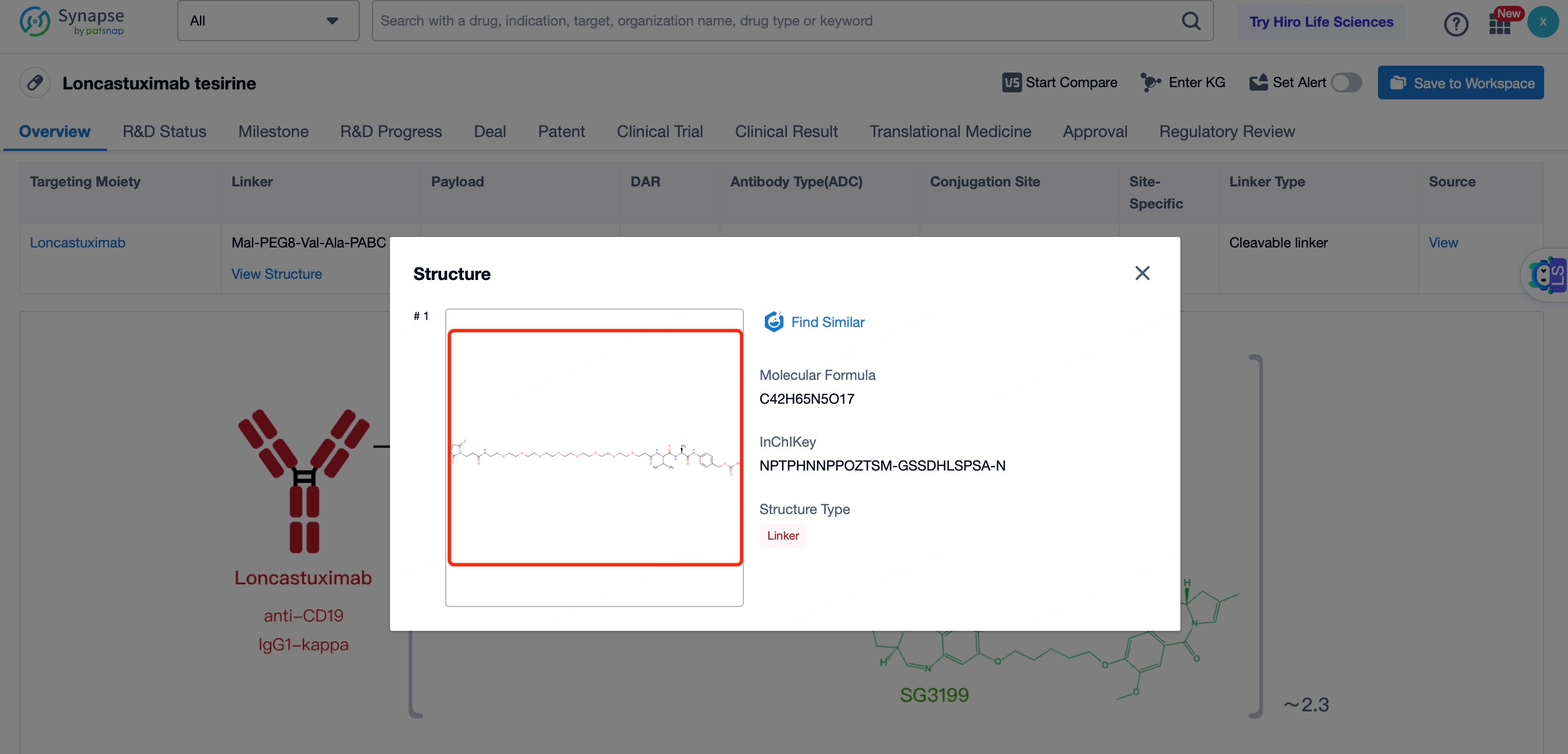
The linker in Loncastuximab tesirine is a key component that ensures the stability of the ADC in circulation and the controlled release of the payload inside the target cell. The linker used is a cleavable maleimide-based linker. This linker is stable in the bloodstream but can be cleaved by lysosomal enzymes once the ADC is internalized into the cell. This design minimizes the risk of premature release of the cytotoxic payload, which could cause off-target toxicity. The cleavable nature of the linker also allows for the efficient release of the payload within the tumor cell, ensuring maximum therapeutic effect. The linker is designed to maintain the integrity of the ADC during systemic circulation, preventing the payload from being released before reaching the target cells. This stability is crucial for minimizing systemic toxicity and ensuring that the drug reaches its intended target. The maleimide-based linker also provides a high drug-to-antibody ratio (DAR), typically around 4, which enhances the therapeutic index of the ADC.
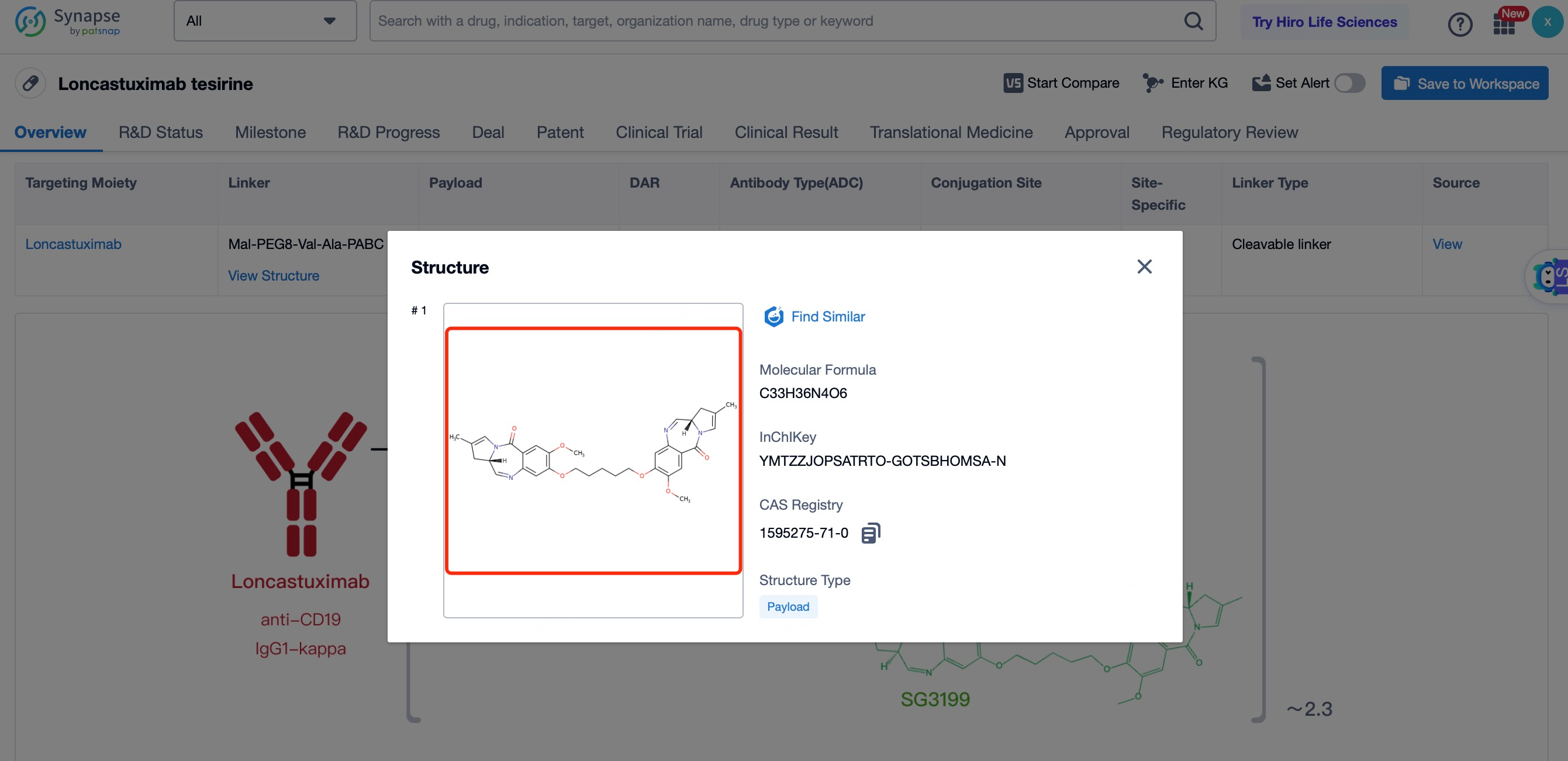
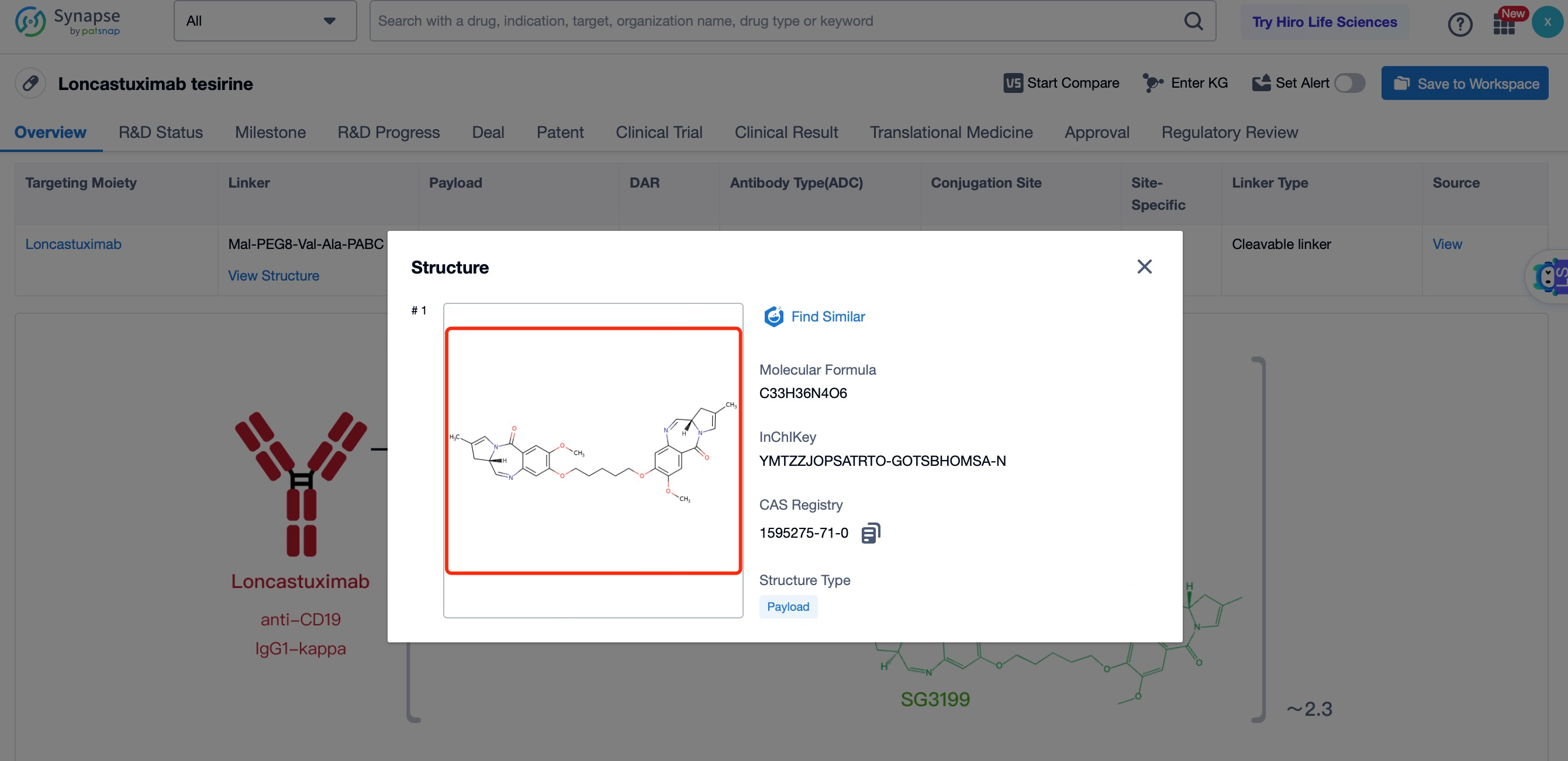
The cytotoxic drug payload in Loncastuximab tesirine is a pyrrolobenzodiazepine (PBD) dimer, a potent DNA alkylating agent. PBD dimers work by forming interstrand cross-links in DNA, leading to replication fork collapse and double-strand breaks, which ultimately result in cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in rapidly dividing cancer cells. PBD dimers are chosen for their high potency and ability to induce cell death at low concentrations. The payload is linked to the antibody through the cleavable linker, ensuring that it remains inactive during circulation and is only activated once inside the target cell. This design enhances the safety and efficacy of the ADC by minimizing systemic toxicity. PBD dimers are particularly effective against cancer cells because they target DNA, which is essential for cell division and survival. By disrupting DNA replication and repair mechanisms, PBD dimers prevent cancer cells from completing the cell cycle, leading to cell death. The high potency of PBD dimers allows for the use of lower doses of the ADC, further reducing the risk of side effects. Additionally, PBD dimers have a broad spectrum of activity against various cancer types, making them a versatile choice for the development of ADCs.
Summary and Prospect
In summary, Loncastuximab tesirine represents a significant advancement in the treatment of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), particularly for patients with relapsed or refractory disease who have progressed on or after multiple lines of therapy. The drug's unique mechanism of action, combined with its optimized antibody, linker, and cytotoxic payload, positions it as a promising therapeutic option. Ongoing clinical trials continue to evaluate its safety and efficacy, and if successful, Loncastuximab tesirine has the potential to become a standard treatment for DLBCL, addressing a critical unmet medical need. Future research will focus on expanding its use to other CD19-expressing cancers and exploring combination therapies to further enhance its therapeutic benefits. The detailed selection and engineering of the antibody, the stability and cleavability of the linker, and the high potency of the cytotoxic payload all contribute to the overall effectiveness and safety of Loncastuximab tesirine, making it a promising candidate in the field of targeted cancer therapy.
How to find the the core components of an ADC drug?
In Patsnap Synapse and Patsnap Bio, you can find the sequence and latest research and development advances of all ADC drugs.
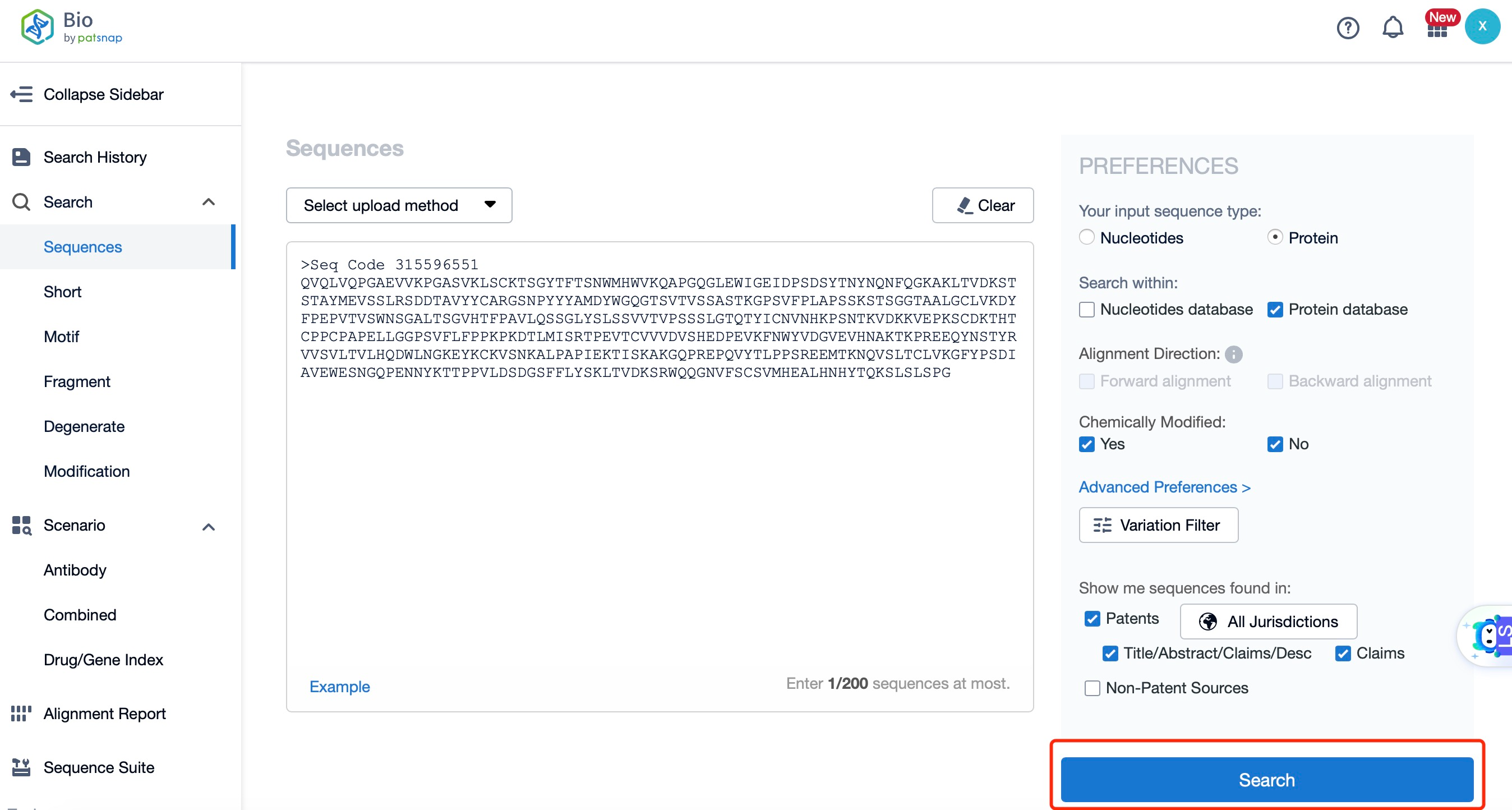
Taking Loncastuximab tesirine as an example, First, you can log in to Patsnap Synapse, enter ' Loncastuximab tesirine ' in the search box and click to view the details. On the details page, you can find the basic information and research progress of Loncastuximab tesirine.
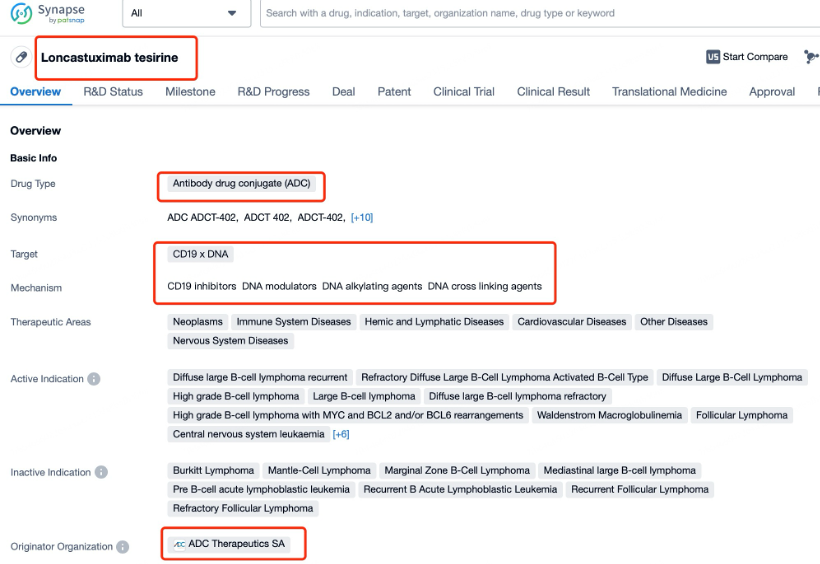
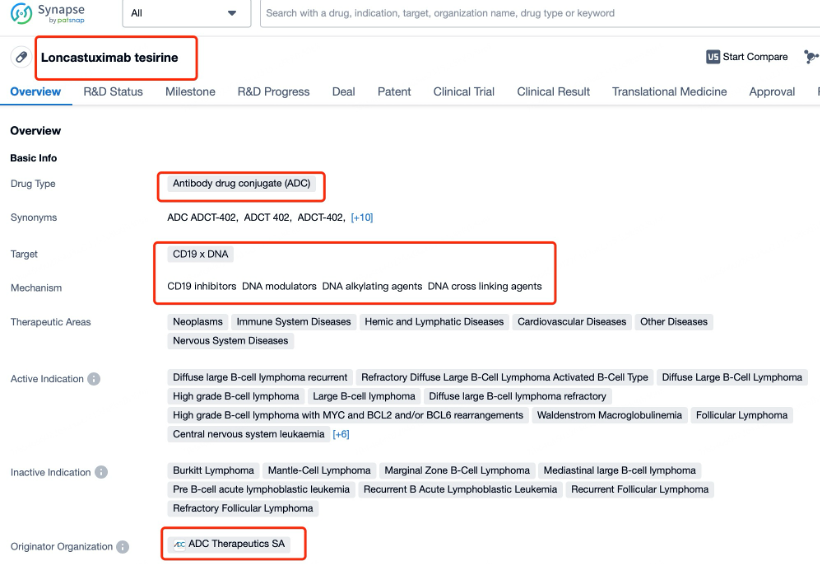
After entering the details page, drop down to find the core Structure information of ADC drug and click view Structure in the Linker section to find the structure and type of ADC drug Linker.
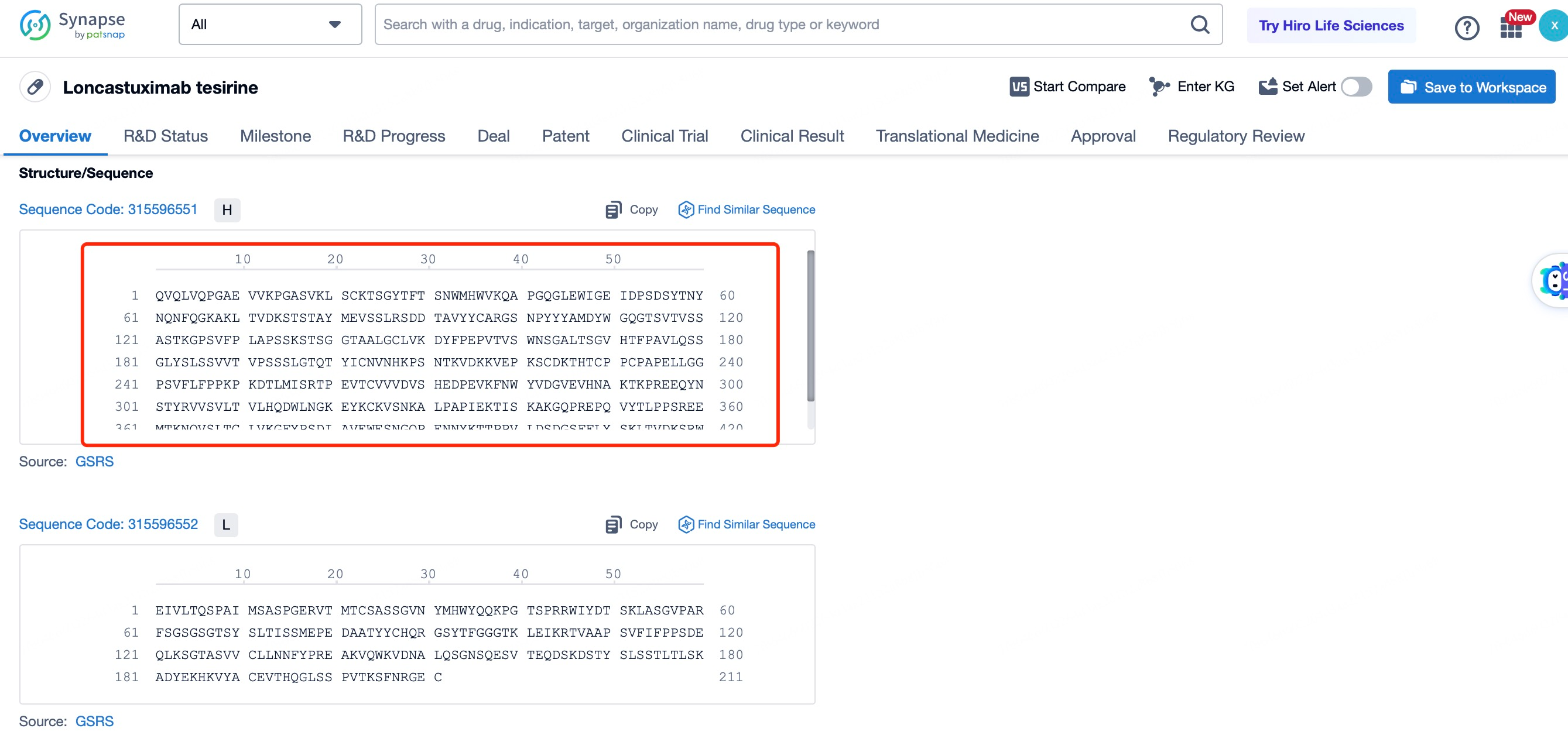
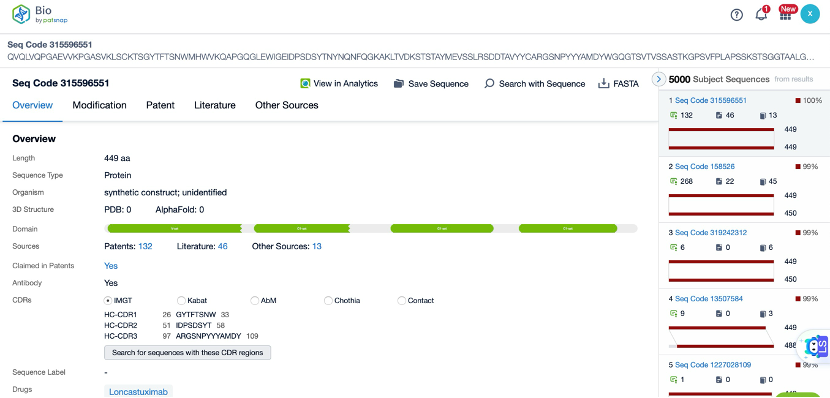
The details page also lists the complete sequence information of the antibody part. By clicking on "Find Similar Sequence", you can be redirected to Patsnap Bio to search for similar sequences of the antibody.
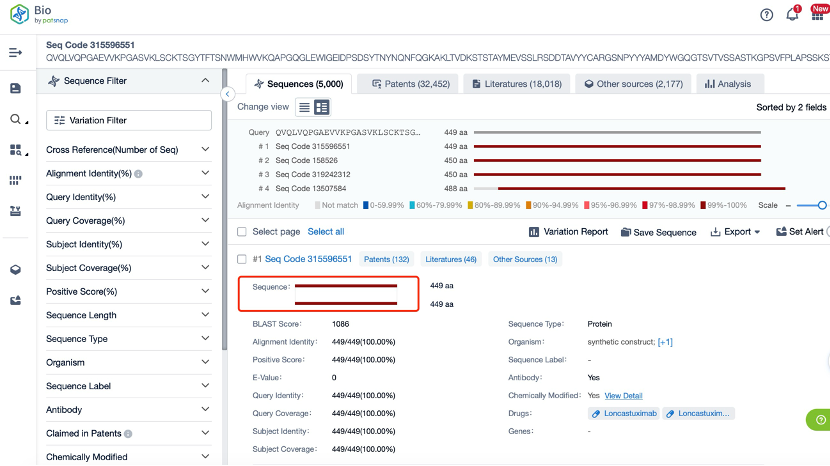
Clicking on the sequence name will provide you with all the basic information of that sequence.
Patsnap Bio helps you turn weeks into minutes with cutting-edge AI-enabled tools built to master the complexities of sequence retrieval and automate IP analysis with precision and ease.