What are EZH2 inhibitors and how do you quickly get the latest development progress?
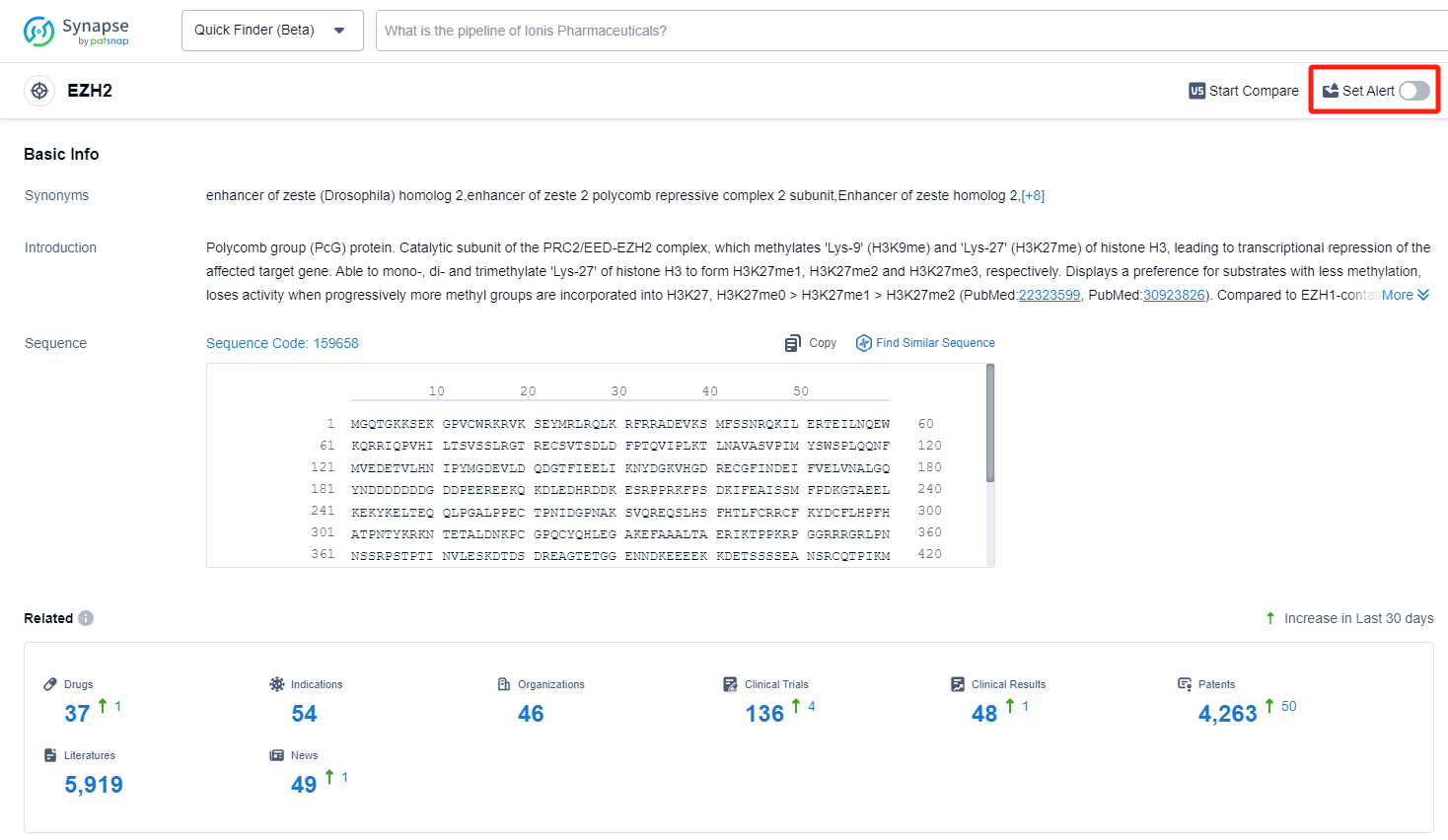
EZH2, also known as enhancer of zeste homolog 2, is an enzyme that plays a crucial role in regulating gene expression and cell differentiation. It belongs to the polycomb group protein family and is involved in the addition of methyl groups to histone proteins, leading to gene silencing. EZH2 is particularly important in embryonic development and tissue regeneration, as it helps maintain stem cell pluripotency and controls cell fate determination. Dysregulation of EZH2 has been implicated in various diseases, including cancer, where it can promote tumor growth and metastasis. Targeting EZH2 has emerged as a potential therapeutic strategy in the pharmaceutical industry for the treatment of certain cancers.
EZH2 inhibitors can enhance the function of CD8+ T effector cells, promote the secretion of chemoattractants by tumor-infiltrating DC cells, and facilitate the migration of effector T cells to the tumor microenvironment (TME). EZH2 inhibitors decrease the lineage stability of Tregs and suppress their function, thereby overcoming drug resistance problems related to immune checkpoint inhibitors to some extent. EZH2 inhibitors promote the maturation, activation, and activation receptor expression of NK cells, boosting the inherent immunity against tumors. Additionally, EZH2 inhibitors can enhance the antigen presentation capability of the tumor microenvironment, triggering the activation of adaptive immune responses against tumors.
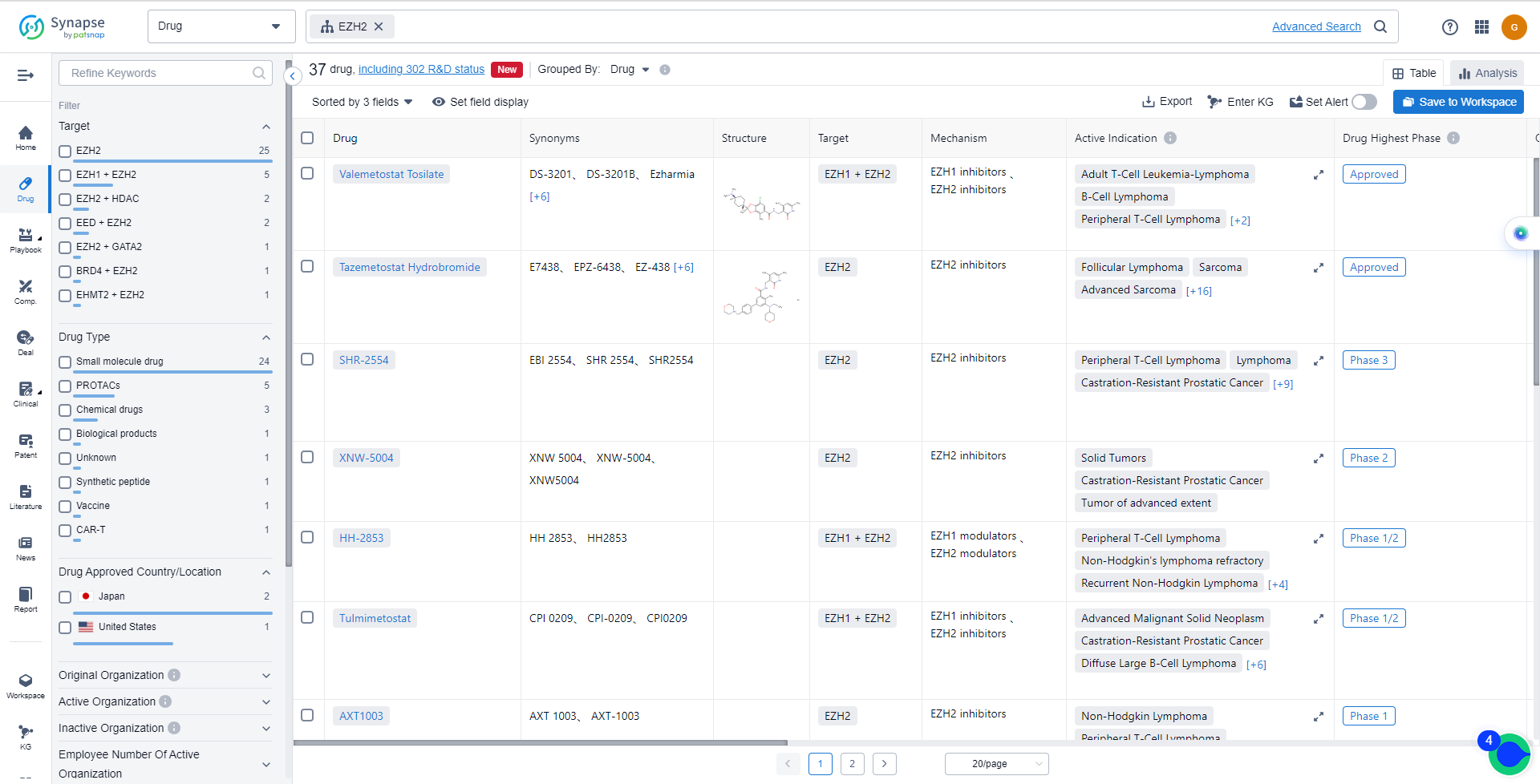
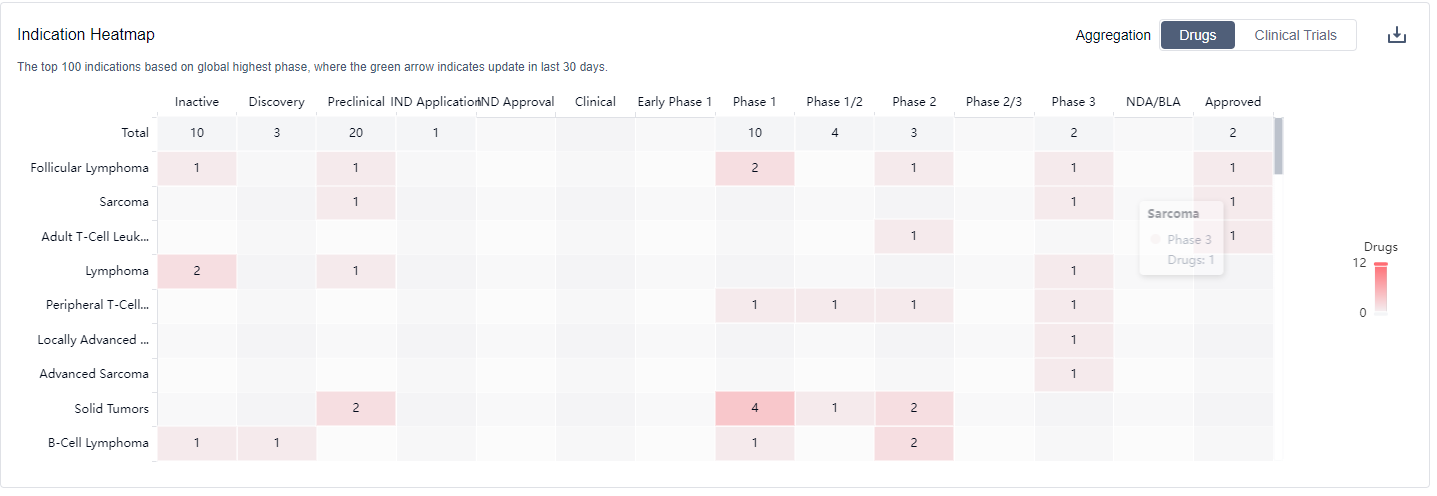
The analysis of the current competitive landscape of target EZH2 reveals that multiple companies are actively involved in the research and development of drugs targeting this target. Ipsen SA, Daiichi Sankyo Co., Ltd., and Jiangsu Hengrui Pharmaceutical Group Co. Ltd. are among the companies with the highest stage of development on this target. Drugs targeting EZH2 have been approved for indications such as Follicular Lymphoma, Sarcoma, Adult T-Cell Leukemia-Lymphoma, and Lymphoma. Small molecule drugs are progressing rapidly, with intense competition from biosimilars. China is showing significant progress in the development of drugs targeting EZH2. The future development of target EZH2 is promising, with ongoing research and development efforts by various companies and countries/locations.
EZH2 Inhibitors: A Promising Novel Approach in Cancer Therapeutics
EZH2 inhibitors are a type of drug that target and inhibit the activity of the EZH2 enzyme. EZH2, or Enhancer of Zeste Homolog 2, is a protein involved in the regulation of gene expression and plays a role in various cellular processes, including cell growth and differentiation.
From a biomedical perspective, EZH2 inhibitors are of particular interest in the field of cancer research. EZH2 is often overexpressed in various types of cancer, including prostate, breast, and lymphomas. Overexpression of EZH2 can lead to abnormal gene silencing and promote tumor growth. By inhibiting the activity of EZH2, these inhibitors aim to restore normal gene expression patterns and potentially slow down or stop the growth of cancer cells.
EZH2 inhibitors are being investigated as potential therapeutic agents in preclinical and clinical studies. Some examples of EZH2 inhibitors include tazemetostat and GSK126. These inhibitors have shown promise in early studies and are being evaluated for their efficacy and safety in treating different types of cancer.
Catalog of EZH2 Inhibitors
The currently marketed EZH2 inhibitors include:
- Valemetostat Tosilate
- Tazemetostat Hydrobromide
- SHR-2554
- XNW-5004
- HH-2853
- Tulmimetostat
- AXT1003
- HM-97662
- PF-06821497
- TR115
For more information, please click on the image below.
What is the purpose of using EZH2 inhibitors?
EZH2 inhibitors have been approved for indications such as Follicular Lymphoma, Sarcoma, Adult T-Cell Leukemia-Lymphoma, and Lymphoma. For more information, please click on the image below to log in and search.
How to acquire the most recent advancement in EZH2 inhibitors?
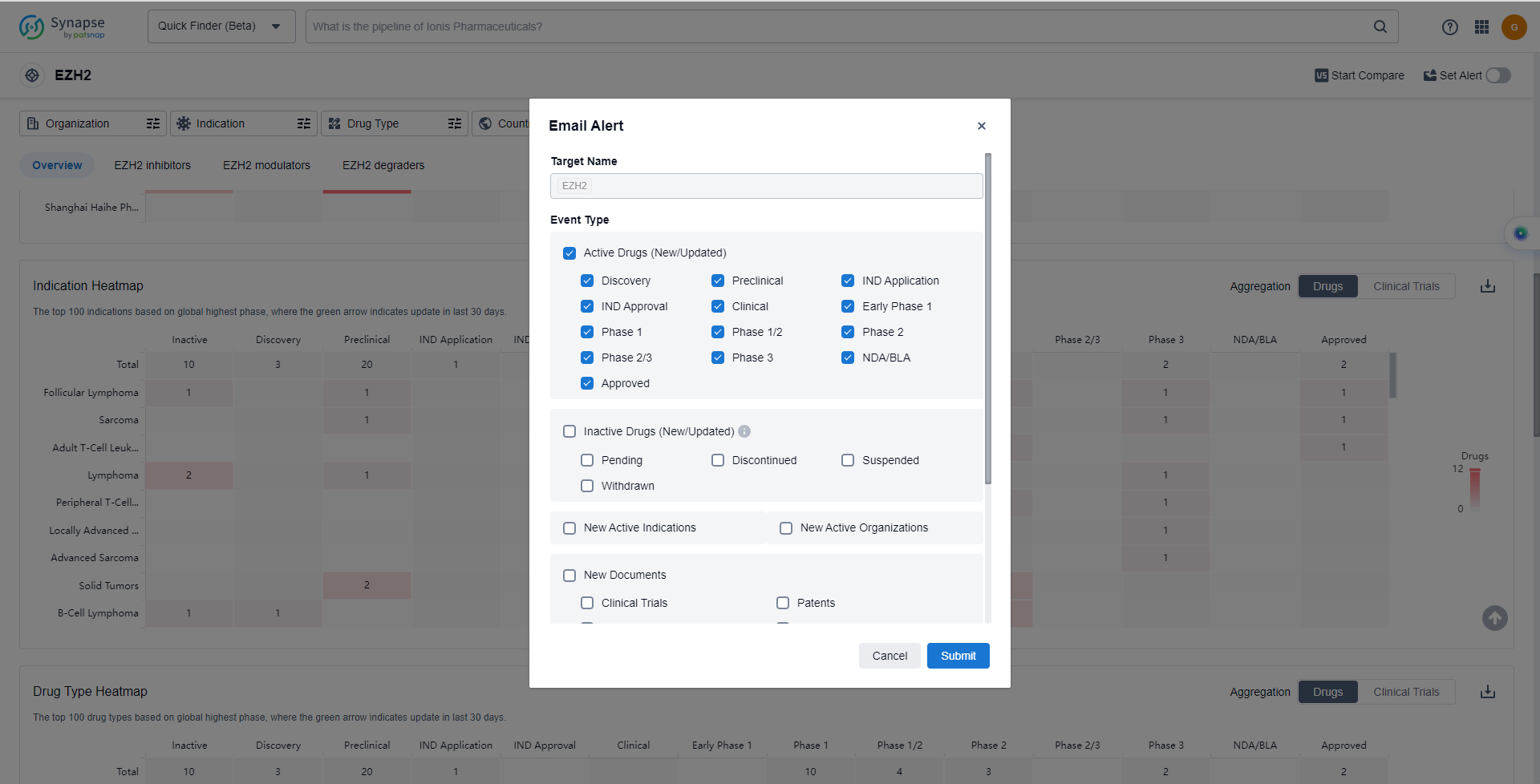
In the Synapse database, you can keep abreast of the latest research and development advances of EZH2 inhibitors anywhere and anytime, daily or weekly, through the "Set Alert" function. Click on the image below to embark on a brand new journey of drug discovery!